Interview_literal/StringBuilder/Exception/Generic/lambda, stream/Functional programming/Functional Interface/Annotation
✅ String literal과 new String(““)의 차이
String literal: saved in constant poolnew String(""): saved in memory heapconstant pool에 저장되면 동일한 문자열에 대해서는 하나의 참조를 재사용constant pool에서는 같은 값이 존재한다면, 새로 정의한 변수여도 같은 주소값을 가진다
✅ What is literal?
- fixed, constant value
int PI = 3.14;String greeting = "Hello, world!";
String 🆚 StringBuilder 🆚 StringBuffer
- String: immutable
- StringBuilder: mutable(same memory), single thread
- StringBuffer: mutable(same memory), multithread safe
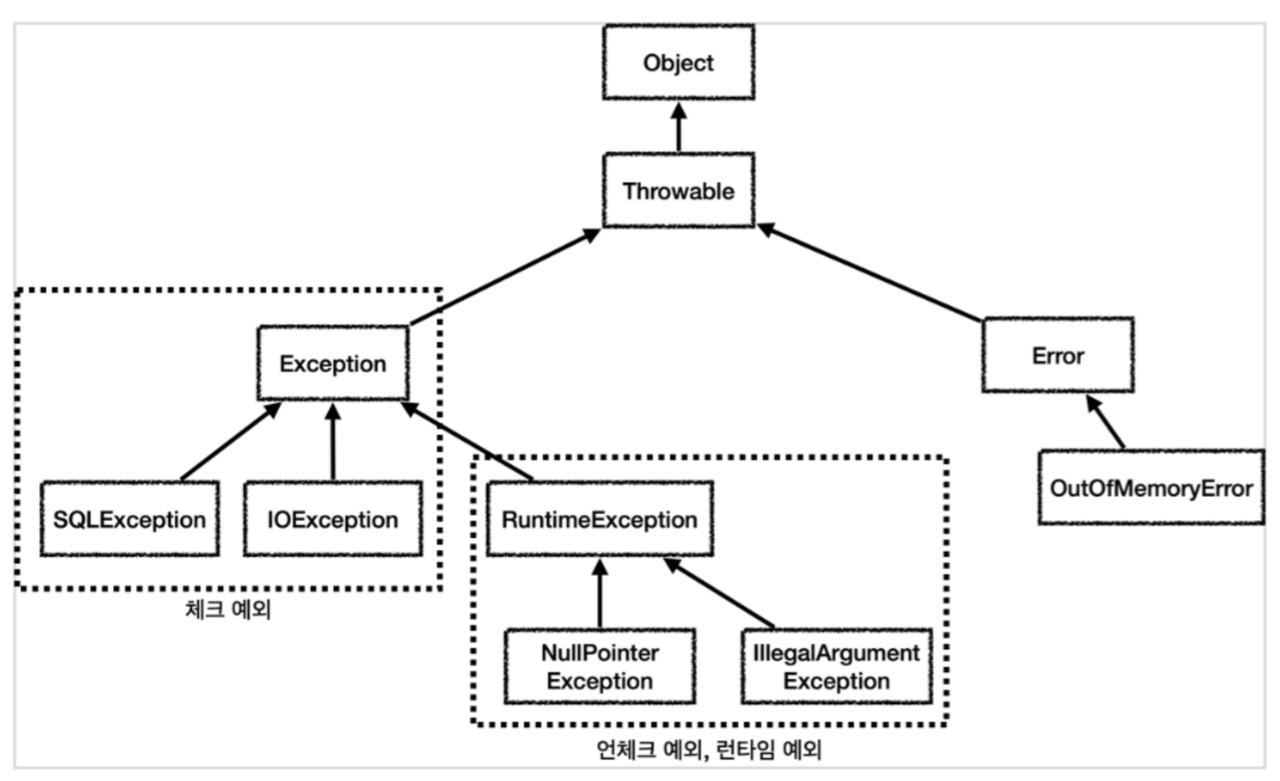
Exception 🆚 Error
- Exception: event that disrupts flow, usually recoverable
- checked exception: exception in compile time, handled with
try-catchorthrows,IO exception,SQL exception - unchecked exception: exception in runtime,
NPE,IAE
- checked exception: exception in compile time, handled with
- Error: system level failure, usually not recoverable
Out of Memory,JVM crash
✅ Exception 클래스의 예시
IO exception: checked exceptionSQL exception: checked exceptionNull Pointer Exception: unchecked runtime exceptionIllegal Argument Exception: unchecked runtime exception, divide by 0
Checked Exception 🆚 Unchecked Exception
- Checked Exception: exception in compile time,
"You must deal with me, or your code won’t compile.", thus,try-catch or throws - Unchecked Exception: exception in runtime, ` “You can deal with me, but I won’t force you — until I crash your app.”`
throw 🆚 throws
throw: throw exception
1
2
3
4
5
public void checkAge(int age) {
if (age < 18) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Age must be 18 or older.");
}
}
throws: declare exception in method declaration
1
2
3
public void myMethod() throws IOException, SQLException {
// method code
}
✅ try-catch-finally 구문에서 finally의 역할
try: code that might throw exceptioncatch: what to do when exception occursfinally: code that must be run regardless of exceptionfinally: afterIO, return DB connectoin pool regardless of exception
Throwable 🆚 Exception의 차이
Throwable: super class of bothExceptionandErrorException: child class ofThrowable, a problem developer can fix
✅ 제네릭(Generic)이란 무엇이고, 왜 사용할까요?
- create class, interface, methods that operate on
typed parameter - postpone the decision of instance type until we use the type
- decide type from outside class
- 👍🏻 type safe at compile time
- 👍🏻 write one class/method that works with many types
1
2
3
4
5
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
👍🏻 only need to create one List, ArrayList class
- can create ArrayList with both String and Integer
✅ What is Lambda?
- an anonymous method(method without name) written in one line
- omit return, method name
(parameters) -> expression
1
2
User user = userRepository.getByUserId(userId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new UserNotFoundException());
✅ What is functional programming(함수형)?
- focus on function, data flow
- focus on immutable
in Java,
lambda,Stream API(map(),filter())- 🆚 OOP
- focus more on Object and how they interact
- focus on mutable
- inheritence, polymorphism, abstract, encapsulation
✅ What is functional interface?
- interface that has exactly one abstract method
functional interfaceis designed to be used with lambda expressions- 자바가 자주 사용할 것 같은 lambda 함수 형태를 함수형 인터페이스로 만들어 제공해준 것
1
2
3
4
@FunctionalInterface //add annotation, limit to one abstract method
public interface Consumer<T> {
void accept(T t); //only one abstract method
}
1
2
Consumer<String> printer = s -> System.out.println("Hello " + s); //use functional interface
printer.accept("Java"); // Output: Hello Java
- also can use
functional interfacewithList,Map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
//replace all: method provided by functional interface
// 각 요소에 10을 곱함
list.replaceAll( (x) -> x * 10 );
//forEach: method provided by functional interface
list.forEach( (x) -> System.out.println(x) );
}
✅ What is Stream?
- API to efficiently process data in
Collections, likeArrayorList - operate on data, and produce results in pipeline
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
List<String> names = userRepository.findByName();
List<String> result = names
.stream() //create stream
.filter(name -> name.startsWith("A")) //intermediate operations
.map(String::toUpperCase) //intermediate operations
.collect(Collectors.toList()); //terminal operations
✅ 람다와 스트림은 왜 생겨났을까요?
- to support
functional programmingin Java - example of
functional programmingin Java islambdaandStream API
✅ 어노테이션이란?
- metadata to add to class, method, variable, parameters…
@Override@Autowired: inject dependency into class automatically@Controller: tell Spring MVC controller to handle web requests@RestController:@Controller+@ResponseBody, so returnJSONorXML@GetMapping,@RequestMapping,@PostMapping: map HTTP methods@Service: this class is business logic service class@Repository: this class isDAO(Data Access Object)and interacts with interface@Component@Value: inject value fromapplication.yaml@RequestParam: extract query parameter from request URL@PathVariable: extract variable from URL
✅ 어노테이션 사용 이유
- compiler uses
annotationfor checks, like missing@Override - metadata for tools,
@Autowiredfor dependency injection - clean code, other developers can know
@Repository,@Controller
✅ 리플렉션이란
- inspect and manipulate classes/members at runtime
- 구체적인 클래스 타입을 몰라도 그 클래스의 method, variable에 접근할 수 있게 해준다
- can access private field, methods
- can create objects dynamically
- ⚠️ can break encapsulation
✅ System.out.println 클래스는 성능이 좋지 않다고 하는데 이유?
- lock can occur in
blocking I/Oandmultithreading printlnissynchronized lock
✅
✅
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.