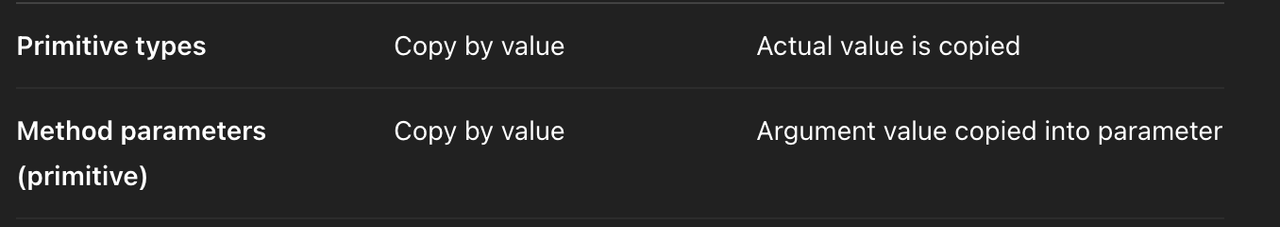
Primitive type, Reference type
✅ Primitive type
int,long,double,boolean- save value itself
int A = 10;
✅ Reference type
classis reference typeString- save memory value
1
2
Student student = new Student();
student.age = 10;
- reference type can be initialized as
null nullmeans address has not been set yet
📌 대원칙: 자바는 항상 변수의 값을 복사해서 대입한다
1
2
자바는 항상 변수의 값을 복사해서 대입한다
Java is always pass-by-value, even for wrapper classes or objects
✅ copy value
- ✔️ primitive type
- a, b have different memory address
- 기본형은 변수의 실제 값을 복사해서 대입
- copies the actual value
- 나도 종이를 가지고 있고, 상대방도 종이를 가지고 있는데 내 종이에 있는 값을 그대로 상대방 종이에 복사해 줌
- 내 종이 내용을 바꾼다고 해서 상대방 종이 내용은 바뀌지 않음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = a;
System.out.println("a: " + a);
System.out.println("b: " + b);
a = 20;
System.out.println("a is changed to 20");
System.out.println("a: " + a); // a = 20
System.out.println("b: " + b); // b = 10
b = 30;
System.out.println("b is changed to 30");
System.out.println("a: " + a); // a = 20
System.out.println("b: " + b); // b = 30
}
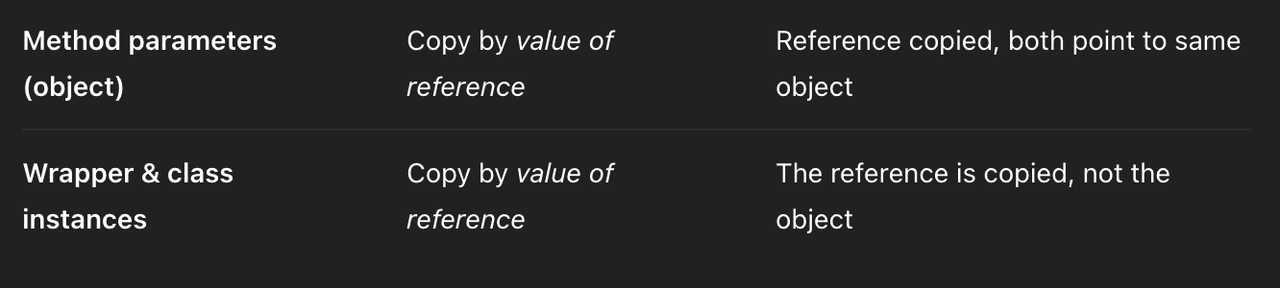
✅ copy reference
- ✔️ reference type
- 참조형은 변수에 들어있는 참조값을 복사해서 대입
- value being copied is a reference to the object, not the object itself.
- 나와 상대방은 구글 클라우드에서 같은 문서를 공유함
- 내 문서를 바꾸면 상대방 문서 내용도 바뀜
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data dataA = new Data();
dataA.value = 10;
Data dataB = dataA; //dataB copy address of dataA
System.out.println("dataA 참조값=" + dataA); //Data@7344699f
System.out.println("dataB 참조값=" + dataB); //Data@7344699f
System.out.println("dataA.value = " + dataA.value); //10
System.out.println("dataB.value = " + dataB.value); //10
//dataA 변경
dataA.value = 20;
System.out.println("a is changed to 20");
System.out.println("dataA.value = " + dataA.value); //20
System.out.println("dataB.value = " + dataB.value); //20
//dataB 변경
dataB.value = 30;
System.out.println("b is changed to 30");
System.out.println("dataA.value = " + dataA.value); //30
System.out.println("dataB.value = " + dataB.value); //30
}
💡 심화 pritive type: copy value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int a = 10;
int b = changeNum(a);
System.out.println(a); //10
System.out.println(b); //20
public static int changeNum(int i){
return i+10;
}
a는 바뀌지 않음int는
pritive type, 따라서copy value- 바뀐
a의 값을 프린트하기 위해서는 다른 변수b에 저장해서 프린트해야 함 b는 바뀐a의 값을 대입했으니 바뀜- method parameter도 pritive type일때는 copy value
- 내가 아무리
changeNum안에서i를 지지고 볶아봤자a는 변하지 않아요
💡 심화 reference type:
- instance의 attribute은 primitive type인데, 이걸 바꾸면 어떻게 될까?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Student studentA = new Student(10);
Student studentB = studentA; //point to ssme reference
Student studentC = new Student(studentA); //copy constructor
studentA.setAge(20);
System.out.println(studentA.getAge()); //20
System.out.println(studentB.getAge()); //20
System.out.println(studentC.getAge()); //10
studentB.setAge(30);
System.out.println(studentA.getAge()); //30
System.out.println(studentB.getAge()); //30
System.out.println(studentC.getAge()); //10
StudentA: 나이 10살로 정함StudentB:studentA를 대입, copy by value of Reference- same reference as studentA
- studentA and B are same objects
StudentC:copy constuctor, studentA를 사용해 새로운 student instance 생성- new Student object, with copied age value
- 새로운 memory address, creates a new object by copying data from another object of the same class
- DOES NOT share reference(deep copy) ❌
- 따라서 age 변하지 않음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// method에 class instance(copy reference)를 parameter로 넘기면
// instance의 attribute는 바뀔까?
changeAge(studentC);
System.out.println(studentC.getAge()); //11
changeAgeReturn(studentC);
System.out.println(studentC.getAge()); //12
int age = changeAgeReturn(studentC);
System.out.println(age); //13
System.out.println(studentA.getAge()); //30
public static void changeAge(Student student){
student.setAge(student.age + 1);
}
public static int changeAgeReturn(Student student){
student.setAge(student.age + 1);
return student.age;
}
- instance는 copy by reference value이므로 age가 바뀜
✅ Null
- reference type can be initialized as
null nullmeans no address has been allocated
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Data data1 = null;
System.out.println(data1); //no address, null
Data data2 = new Data();
System.out.println(data2); //has address
System.out.println(data2.value); //0
data2 = null; //free address space
System.out.println(data2); //now no address, null
GCwill free unusedaddress space- after
data2 = null, theaddress spacethatdata2was using will be freed bygarbage collector - ⭐️
GCis big advantage of Java, keeps freeing unused address space, making memory use efficient
✅ NullPointerException
- cannot point null
- because
nullmeans no address space
1
2
3
4
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data1 = null;
data1.value = 100; //cannot point null! NullPointerException
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.