Singleton
🛠️ When to use singleton
- when only one instance should exist
- 👀 settings of an application
✅ How to create singleton
- should not use
new❌ create method
getInstance()- ✔️ Setting instance class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Settings {
private Settings() {}
//private constructor
private static Settings instance;
public static Settings getInstance(){
if(instance == null){
return new Settings();
}else{
return instance;
}
}
}
- ✔️ Main class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//In singleton, cannot create instance with constructor ❌
//Settings settings = new Settings();
//how to create instance in singleton ➡️ use getInstance()
Settings settings = Settings.getInstance();
}
}
✅ How to create singleton in multithreading environment
- how to create singleton thread-safe
1️⃣ Use synchronized
- 👍🏻 threadsafe
- 👎🏻 lots of resources in using
synchronized - 👎🏻 aquiring, releasing lock is heavy work
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class Settings {
private Settings() {}
//private constructor
private static Settings instance;
// use synchronized
public static synchronized Settings getInstance(){
if(instance == null){
return new Settings();
}else{
return instance;
}
}
}
2️⃣ Eager initialization
create instance when the class is loaded, not when it’s first requested
- 👍🏻 threadsafe, instance is created once
- 👍🏻 create instance before, if creating the instance is not so heavy
- 👎🏻 instance is created even if never used
- 👎🏻 no lazy loading
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Settings {
//initiate setting instance
//use static final
private static final Settings INSTANCE = new Settings();
//private constructor
private Settings() {}
public static Settings getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
3️⃣ Double checked locking
- check if instance is
nulltwo times - 👍🏻 do not use
synchronizedevery timegetInstance()is called - 👍🏻 the instance is created when it is needed, lazy loading
- (no lazy loading was disadvantage of eager initialization)
- 👎🏻 keyword
volatile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Settings {
private static volatile Settings instance;
private Settings() {}
public static Settings getInstance(){
if(instance == null ){ //check 1
synchronized (Settings.class){
if(instance == null){ //check2
instance = new Settings();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
4️⃣ Double checked locking without volatile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Settings {
private Settings() {}
//create an inner class
private static class SettingsHolder{
private static final Settings INSTANCE = new Settings();
}
public static Settings getInstance(){
return SettingsHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
💔 How can we break singleton?
- 아무리 내가 이쁘게 singleton을 구현해두더라도
- singleton 클래스 밖에서 reflection을 쓰거나 Serialization을 해버리면
내가 열심히 만든 singleton이 깨지게된다
- Serialization은 대응 방법이라도 있지, reflection은 대응 방법도 없음
1️⃣ By using reflection
- create the constructor from outside
Settings class - inside
main method() - no way to solve reflection problem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Settings settings = Settings.getInstance();
Constructor<Settings> constructor = Settings.class.getDeclaredConstructor();
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Settings settings1 = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(settings == settings1);
}
}
- This code accesses the private constructor via Reflection
- gets the private constructor of
Settings😱 - and breaks access control!!!!!
- and creates a second instance
2️⃣ Serialization
- serialization: save java into a file
- deserialization: start with byte stream and recreate the saved file into java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Settings settings = Settings.getInstance();
Settings settings1 = null;
try(ObjectOutput out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("settings.obj"))){
out.writeObject(settings);
}
try(ObjectInput in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("settings.obj"))){
settings1 = (Settings) in.readObject();
}
}
}
//now settings and settings1 will be different
💊 How to save singleton in serialization issue
- in deserialization, it uses the
readResolve()method - so,
OverridethereadResolve()method - and make it return
getInstance()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Settings implements Serializable {
private Settings() {}
private static class SettingsHolder{
private static final Settings INSTANCE = new Settings();
}
public static Settings getInstance(){
return SettingsHolder.INSTANCE;
}
//add readResolve()
public Object readResolve(){
return getInstance();
}
}
✅ How to implement singleton in safe, simple manner
make singleton class
ENUMENUMsettings
1
2
3
public enum Setting {
INSTANCE
}
- As
ENUMdoes not allow creating constructor from outside, reflection problem solved - Now in main class, serialization problem solved
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Setting setting = Setting.INSTANCE;
Setting setting1 = null;
try(ObjectOutput out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("settings.obj"))){
out.writeObject(setting);
}
try(ObjectInput in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("settings.obj"))){
setting1 = (Setting) in.readObject();
}
System.out.println(setting == setting1); //true
}
}
- 👎🏻 class has to be created before being used
- 👎🏻 no inheritence can be used in ENUM
🛠️ When is singleton used?
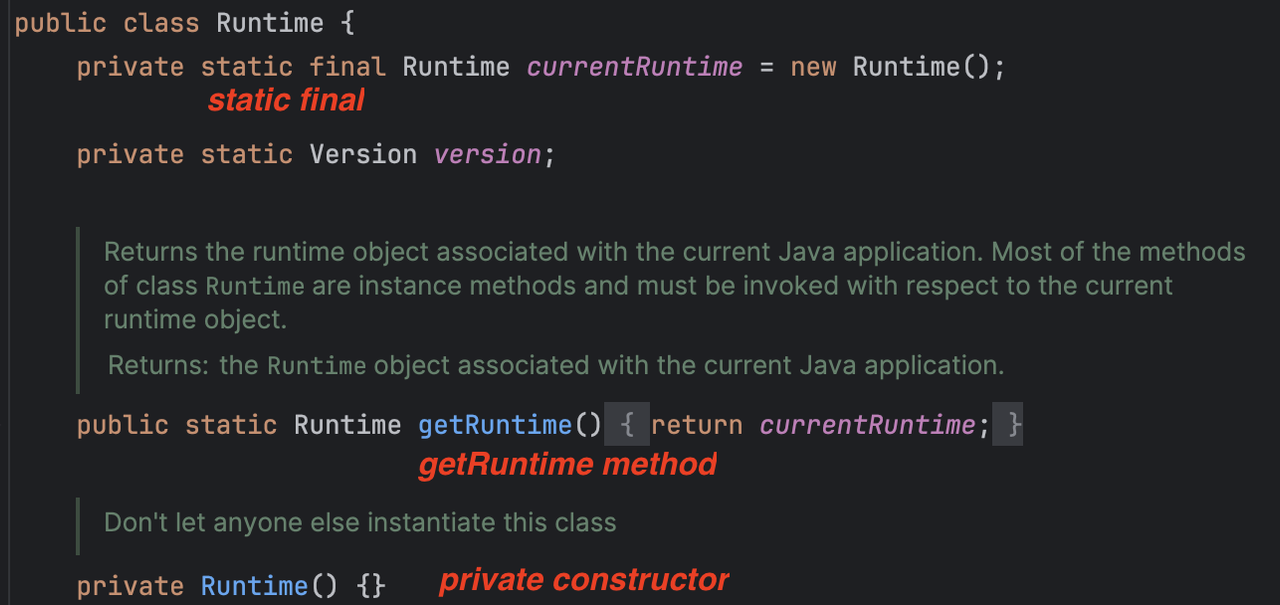
1️⃣ java.lang.Runtime
- can only create one instance of
Runtime - need to create instance with
getRuntime() - 🛠️ used to measure java resources in runtime
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class RuntimeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println(runtime.maxMemory());
}
}
2️⃣ Singleton scope
- strictly speaking not singleton,
- but to create bean scope
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class SpringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
String hello = applicationContext.getBean("hello", String.class);
String hello2 = applicationContext.getBean("hello", String.class);
System.out.println(hello == hello2); //true
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.