Factory
- Loose coupling
- OC principle
defaultin interface
🛠️ When to use factory
- When you want to create several types of smth with different values
- give the creation role to a factory
- 👀 You have class
CircleandSquareextendingInterface Shape - you want to create
CircleorSquareusing one constructor - 👀 You have class
WhiteShipandBlackShipextendingShip - you want to create
WhiteShipandBlackShipjust with one method, without usingelse-iffor checking the names and settings colors…
✅ Factory Pattern
- factory안에서 구체적인 클래스를 만들어낸다
- ⭐️ Loosely coupled: make coupling between class and constructor loose
<<Interface>>will be responsible for constructing a class- delegate object creation to a factory
- ⭐️ Open/Closed principle: open to extension, closed to modification
👎🏻 If there was no factory pattern
- ✔️ Class
Ship
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Ship {
private String name;
private String color;
private String logo;
//getters
//setters
}
- ✔️ Class
ShipFactory - 👎🏻 need to check name and set logo and color accordingly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// Customizing for specific name
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("whiteship")) {
ship.setLogo("\uD83D\uDEE5️");
} else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("blackship")) {
ship.setLogo("⚓");
}
// coloring
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("whiteship")) {
ship.setColor("whiteship");
} else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("blackship")) {
ship.setColor("black");
}
✅ After factory pattern
- ✔️ Class
Ship
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Ship {
private String name;
private String color;
private String logo;
//getters
//setters
}
- ✔️ Class
WhiteShipandBlackShip - ⭐️ How to set attributes of parent without using constructor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class WhiteShip extends Ship {
public WhiteShip() {
setName("White Ship");
setLogo("aaa");
setColor("white");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class BlackShip extends Ship{
public BlackShip() {
setName("BlackShip");
setLogo("bbbb");
setColor("black");
}
}
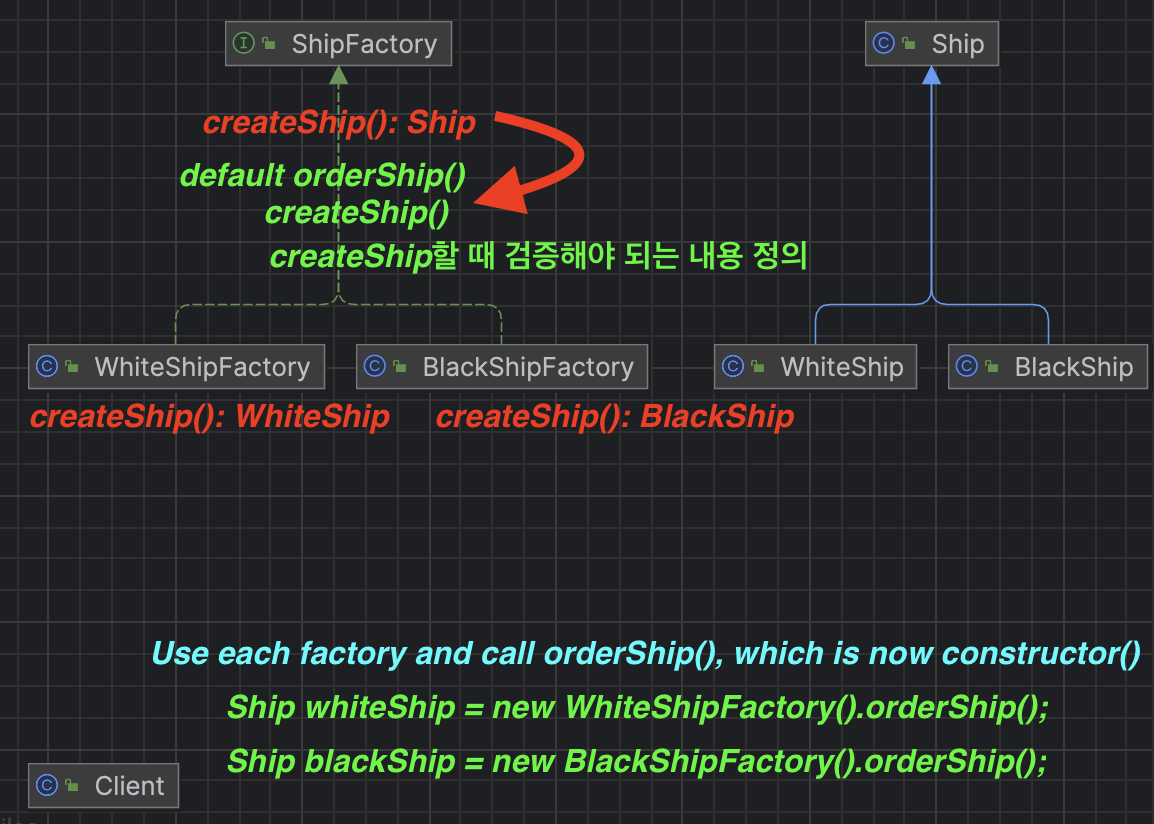
- ✔️ Interface ShipFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public interface ShipFactory {
//default, could/could not be overrided
default Ship orderShip(String name, String email){
validate(name, email);
Ship ship = createShip(); //use createShip();
sendEmailTo(email, ship);
return ship;
}
Ship createShip(); //not defined, must be overrided
}
validate(),sendEmailTo()are methods I want to run as soon as I create Ship✔️ Class WhiteShipFactory and BlackShipFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class WhiteShipFactory implements ShipFactory{
@Override
public Ship createShip() {
return new WhiteShip();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class BlackShipFactory implements ShipFactory{
@Override
public Ship createShip() {
return new BlackShip();
}
}
- ✔️ CLient code
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ship whiteShip = new WhiteShipFactory().orderShip("WhiteShip", "aaa@gmail.com");
Ship blackShip = new BlackShipFactory().orderShip("BlackShip", "bbb@gmail.com");
}
}
👍🏻 Advantages 👎🏻 Disadvantages
- 👍🏻 do not need to use else-if
- 👍🏻 open/closed principle: open for extension, closed for modification
- can create another function/interface without modifying the old code
- this is bc of coupling between class and constructor is loose
👍🏻 can use
defaultto write a default method ininterface- 👎🏻 need to create more classes
default and private in interface
- can use
defaultto define a method ininterface - and the helper methods for the
default methodshould beprivate - as it would be used only inside the interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public interface ShipFactory {
default Ship orderShip(String name, String email){
validate(name, email);
prepareFor(name);
Ship ship = createShip();
sendEmailTo(email, ship);
return ship;
}
//helper methods inside default method
//access modifier: private
private void validate(String name, String email){
}
private void prepareFor(String name) {
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.