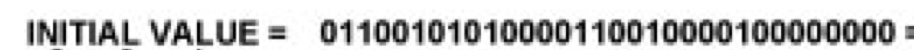1.4 Protection of bits, 1.5 Hashing
- ⭐️ one exercise of ECC on paper
- ⭐️ one exercise on CRC, how to use polynomial, and how to get checksum
- ⭐️ how CRC works
- ⭐️ what is hashing
- ⭐️ what is salt, pepper
- ⭐️ what is firewall
- ⭐️ what is DMZ
- ⭐️ what is mirroring
- ⭐️ three types of clouding, what is the idea of contracting a compnay for…
- ⭐️ 5’ 9s availability: How do you give to company that has…
- ⭐️ UPS: what is the name of energy not stopped…
- ⭐️ DPC: how do you call these centers that…
☑️ ECC and CRC
- 🛠️ protection for transport/download
- network
- protection for files
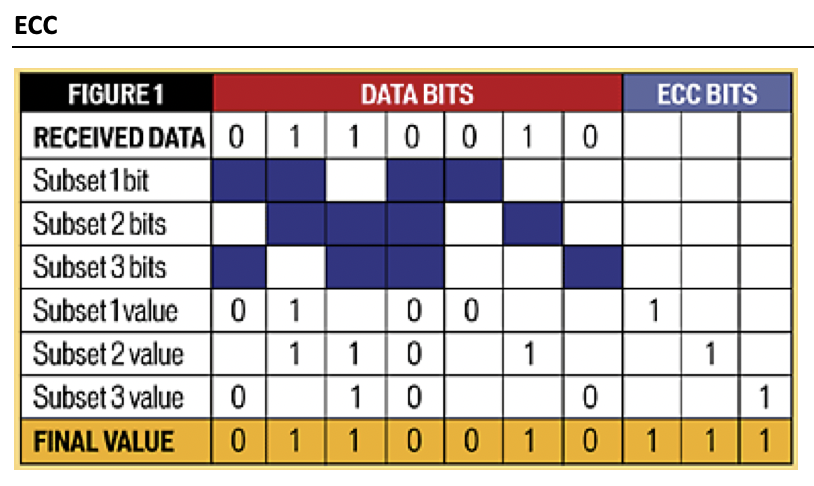
✅ ECC
Error Checking and Correction
added by groups
- add extra bits(
Redundance) in order to correct possible failures - send extra information to check if the information is correct
- need to transmit both
data + extra bits - several ECC techniques exists, each technique has its own subset creating method
✔️ How to apply ECC
- 1️⃣ Initial sequence
- 2️⃣ Create subsets of bits of the initial sequence
- each ECC technique has its own subset creating method
- 3️⃣ On each subset, apply an
even parity - 4️⃣ All extra
1sare added at the end of the sequence - 5️⃣ Using the extra
1swe can use reverse engineering to find the original initial sequence - 👉🏻 We can check if the initial sequence has been changed using the
extra 1 bits
📌 Even parity
👉🏻 even parity: number of
1shas to be even- if number of
1is even, add0 - if number of
1is odd, add an extra1
✔️ Example of subsets
- subset 1:
0100 - ➡️ odd number of
1s - ➡️ according to
even parity, need to add extra1to make it even - subset 2:
1101 - ➡️ odd number of
1s - ➡️ according to
even parity, need to add extra1to make it even - subset 3:
0100 - ➡️ odd number of
1s - ➡️ according to
even parity, need to add extra1to make it even - In total, we have to add extra
1, 1, 1in the end
✔️ Example of getting extra bits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
001101011010
( 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, count from right to left, but write from left to write)
subset1 = 1, 2, 3, 4 = 1010 ➡️ do not add ➡️ 0
subset2 = 4, 5, 6, 7 = 1011 ➡️ add extra ➡️ 1
subset3 = 4, 6, 7, 8 = 0101 ➡️ do not add ➡️ 0
subset4 = 9, 10, 11, 12 = 0011 ➡️ do not add ➡️ 0
extra bits: 0100
result: 001101011010 + 0100
❓ What do we need to create a computer with ECC?
- 1️⃣ need a counter to count the
extra bits - 2️⃣ comparison chip to compare if the
count of 1sare even or not - 3️⃣ flag to give you an
extra bitif the count of 1 is odd - normally called ECC flag
📌 Logic Gates
- pre-built chips that perform mathametical operations
✔️ 3 main logic gates
- 1️⃣ chip
ANDgate - two for input, one output
output
1, only if input is both1and1- 2️⃣ chip
ORgate - two for input, one output
output
1, whenever there is any1- 3️⃣ chip
XORorExclusive OR - very picky!
- symbol: OR triangle with a border to the left
- two for input, one output
- output
1, when there is only one1 - output
1, when there is one1, but when there is 21s, it outputs0 - 두꺼비집, when electicity is too high, everything goes down
- so when there is too many
1, outputs0. very picky!
✅ CRC
Cyclic Redundance Code
- send
extra bitsprotected with anotherextra bit - however, need to send more data
- more cyles(more redundance) ⬆️ more secure ⬆️ efficiency ⬇️
- uses
XOR
✔️ How does CRC work
- CRC = Initial sequence +
Polynomial each CRC uses has own
Polynomial sequencemethod- 1️⃣ Convert
Polynomialinto a sequence of bits - exponents of the
xindicate which bits are1 - if exponent of
Polynomialis8, 2, 1, 0then bit position8, 2, 1, 0will be1 - other bits will be
0 - ⭐️ In CRC, has different changes the numbering of the bit
- most right bit is
0 - result:
100000111 - Thus the size of the sequence will depend on the exponent of the
Polynomial - 2️⃣ Write the
Polynomial sequencebelow the original sequence - starting by the left
- ⭐️ but, discard all the
0son the left - 3️⃣
XORbit by bit - 4️⃣ the rest of the original sequence, just retype again, copy
- 5️⃣ Now repeat the step 2️⃣~4️⃣, cyclic
- ⭐️ remember, first
0swill be discarded - 6️⃣ repeat until the final result is shorter or same length as the original polynomial, stops
- 7️⃣ Final result
checksumget we get will be added at the end of the original message - Then, will be transmitted
- 8️⃣ Reciever will perform the reverse engineering, then will check if the message has any errors
✔️ Checksum
- final result of the CRC process
- used to check if the message has arrived correctly
✅ Hashing
- 🛠️ used for protecting passwords
- needs to be more secure than file protection
example of hashing:
yescrypt- there is always a mathematical function in Hashing ➡️
Hash function - apply the
hash functionto the password that you type - Hashing applies
hash functionto each of the the original bits - if my password is
ZORRO, as eachCHAR is 8 bits, will be 40 bits apply
hash functionto each of the 40 bits- method for
Hashing
✔️ Goal of hashing
- goal is to get something very different from the original password
even if two passwords are very simmilar, the result will be totally different
- If the system has hashing, you can use simmilar passwords, as they will be converted into totally different results(GMAIL)
- However, if the system does not have hashing, you can not use simmilar passwords(HOTMAIL)
1
2
Q: If the teacher can use `hola` and when it expires uses `hola1`, what kind of technology is the systems using?
A: Hashing
✅ Salt
use hashing, use math
store in hard drive
- add salt to a password
- salt: random
0s and 1s, transforming the password before hashing the password - add salt: get random sequence of
0s and 1sto the original password - then
XORthe salt and the original password - then hash the result of
original password + salt XOR
✔️ Where do we use salt? Where is it stored?
saltneeds to be recorded/stored in order to log in the system- ⭐️ thus,
saltshould be stored in the hard-disk of the computer, so it is kept involatile - which means you can use only that computer for logging in
- we use salt for computers that should be protected themselves
✅ Pepper
use hashing, use math
store in cloud
- store
salt(pepper)in a cloud/server - 1️⃣ Now
salt(pepper)can be accessed from all, several computers - We can log-in from any computer
- not me, but a compnay server would be protecting my
salt(pepper) - 2️⃣ As
salt(pepper)is protected by a company,pepperis considered more protected thansalt
✔️ Clouds
- clouds are comuters protected physically and logically with protocols
✅ Security
☑️ Logic Security
- Security using software
- example:
- ✔️ Hashing:
salt,pepper - ✔️ Anitivirus
✔️ Firewall: machine with specific software that opens or closes ports
- if I close HTTP, you cannot browse internet
- if I close SMTP, you cannot send emails
✔️ DMZ: Demilitarized Zone, in a company a set of computers that are free of public access with no much protection, normally contain non-essential information
- having DMZ protects MZ from being extra abused
- for example,
DMZ: public webpage for FP,MZ: my private aula virtual, need to log-in
✔️ Mirroring: having my computer mirror/copy another computer
- mirroring is NOT a backup
- 👎🏻 backups are not totally updated
- 👍🏻 mirroring is duplicated in real-time
- with mirroring, you can sync both computers only when an important and correct
- can sync just incase you have to go back to the past
✔️ Backups: every x months make a backup of your data
- backups should be taken into isolated environments
- ✔️ Security Patch: software that solves an error found without needing to reinstall the operating system
☑️ Physic Security
Security using hardware
✔️ Clouding: Taking my company data to the cloud
- Three types of clouding
- 1️⃣ IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
- I do not have computers in my company, I use the computer of another company
- use the computer of another company, I do not have the infrastructure
- not very commonly used
- 2️⃣ Paas: Platform as a Service
- contract another company’s computers and their software
- you log-in to their applications
- a lot of loss of control of your company
- the platform will not be tailored to your needs
- 3️⃣ SaaS: Software as a Service
- Everything belongs to the other company
- including the products that are created by you
- very expensive
- streaming platform, you do not have any rights to keep the movie, paying for the service
- When a traditional company contracts a company to take the company into the Internet
✔️ Security and High Availability(5 9’s)
3 9's: The company is available for99.9%4 9's: The company is available for99.99%- Linux OS, AMAZON has a
4 9'scertificate
- Linux OS, AMAZON has a
5 9's: The company is available for99.999%- out of 100,000 only 1 will fail
- systems company always aim for the
5 9's
✔️ Load Balancing
- workload is evenly distributed among the computers
- apply RAID
✔️ UPS
- Uninterrupted Power System
- system for solving electicity failures
- generators
✔️ DPC
- Data Process Centers
- building specialized in databases
- need very strict architectural security
✔️ Access Controls
- finger prints