1.12 Hardware specifications_1
- ⭐️ how do you call the mother board that the RAM is perpendicular…
- ⭐️ how do you call the name of RAM that is….
📌 A. Motherboard, Printed Circuit Board
main board of the computer
also called Printed Circuit BoardPCB
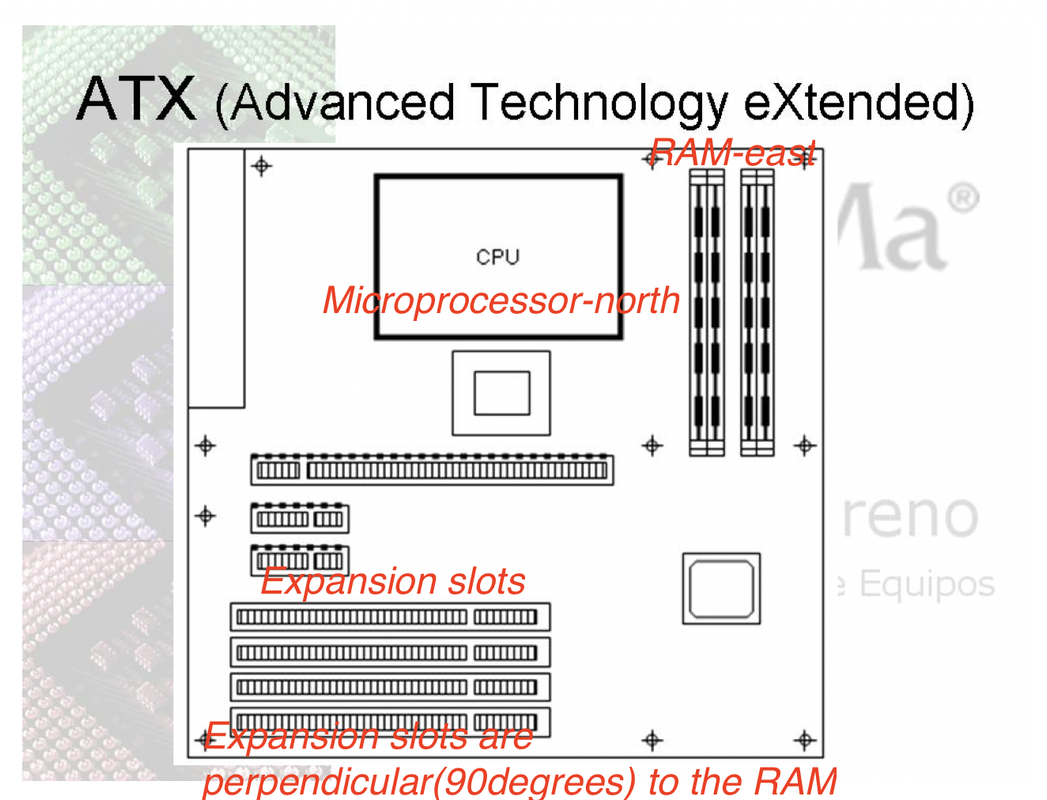
- normally mother boards contain
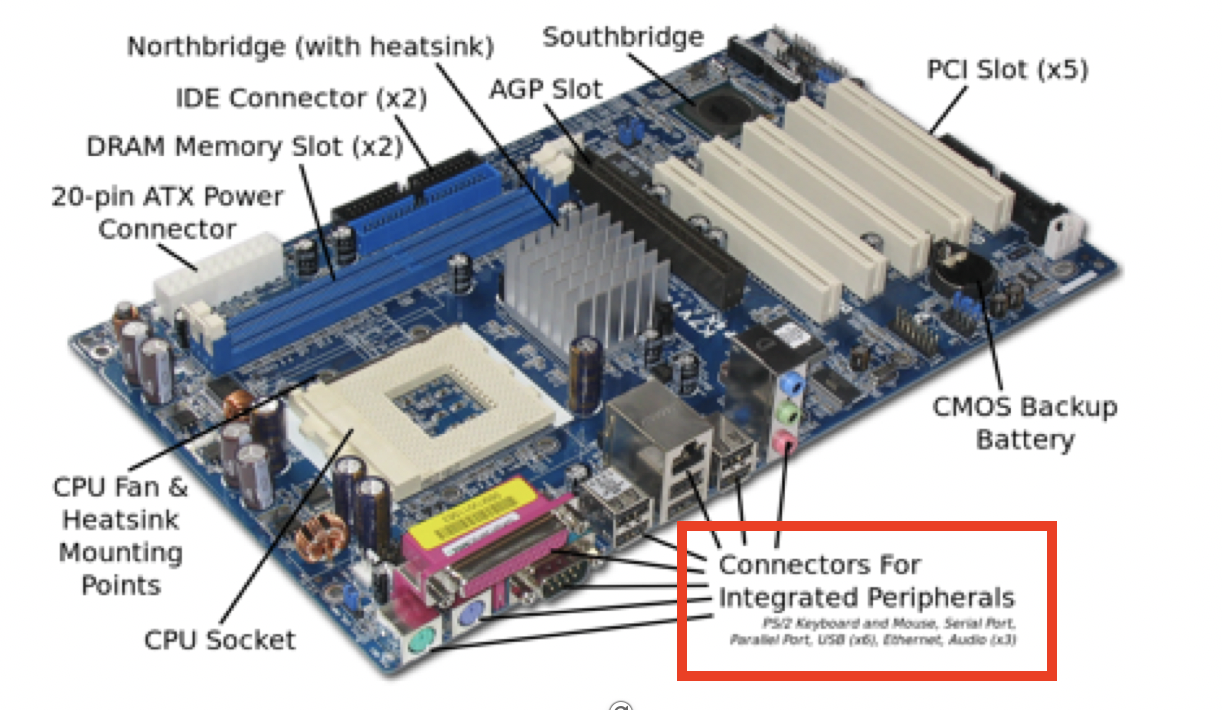
microprocessor: northRAM: at the eastExpansion slots: some slots for extending the capabilities according to your needs(TV card,ecography cardfor hospitals,vibration measurement cardfor measuring earthquakes…)
☑️ Two different form factors(structures) of motherboard
Which PCB form factor do you want to buy to make a computer?
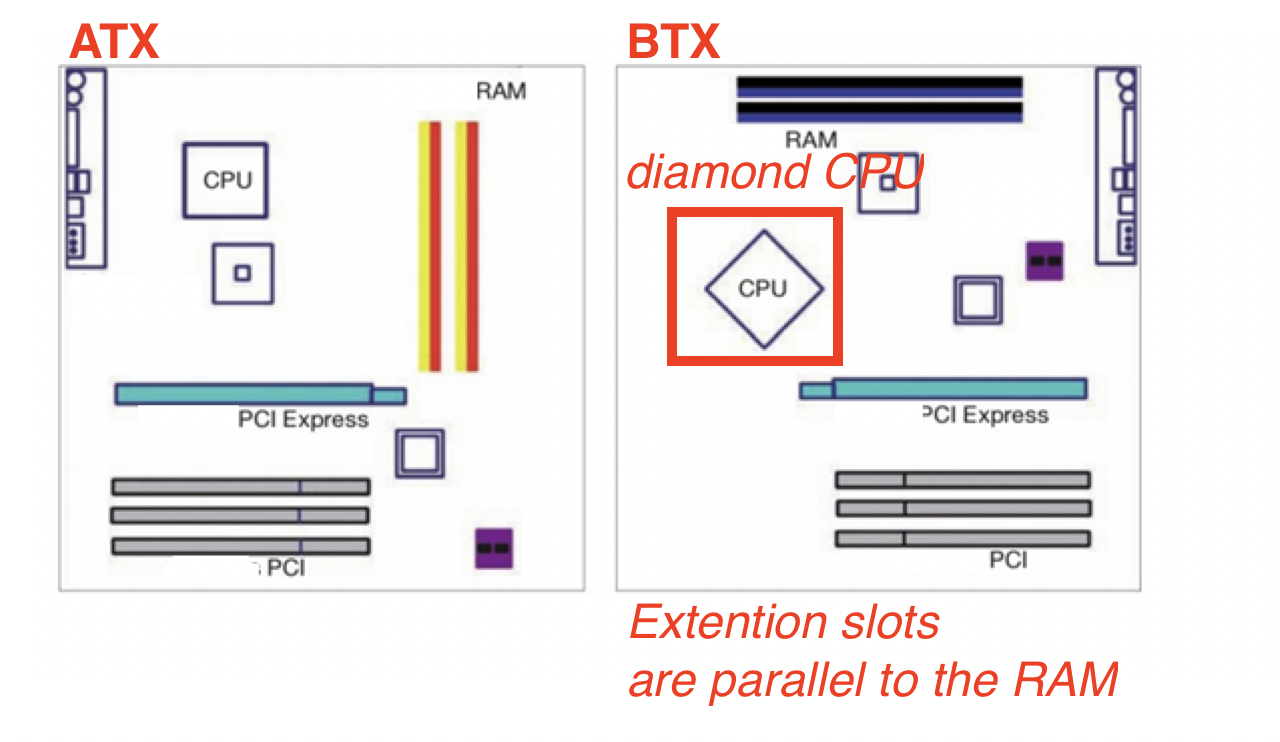
1️⃣ ATX
- Advanced Technology Extended
- the
Extention slotsare perpendicular to theRAM - 🛠️ Used more these days
2️⃣ BTX
microprocessor: the micro chip is shown as a diamond- the
Extention slotsare parallel to theRAM - not many computers select
BTXthese days - 👎🏻
BTXhas a worse air flow thanATX - 👎🏻 more heat, has worse ventilation
- 🛠️
BTXis still used in servers - so server rooms are very cold
- but
ATXis more preferred for personal computer - ↔️ the distribution of heat
✔️ There were more form factors, like DTX, but failed to become commercial
3️⃣ IXT
- Model based on ATX, without so many expansion slots
- No expansion slot ❌
- example: we cannot add
ecography cardto the phone
1
2
3
4
5
❓ What is a form factor that the RAM and the exention slot are perpendicular?
- ATX
❓ What is a form factor that the RAM and the exention slot are parallel?
- BTX
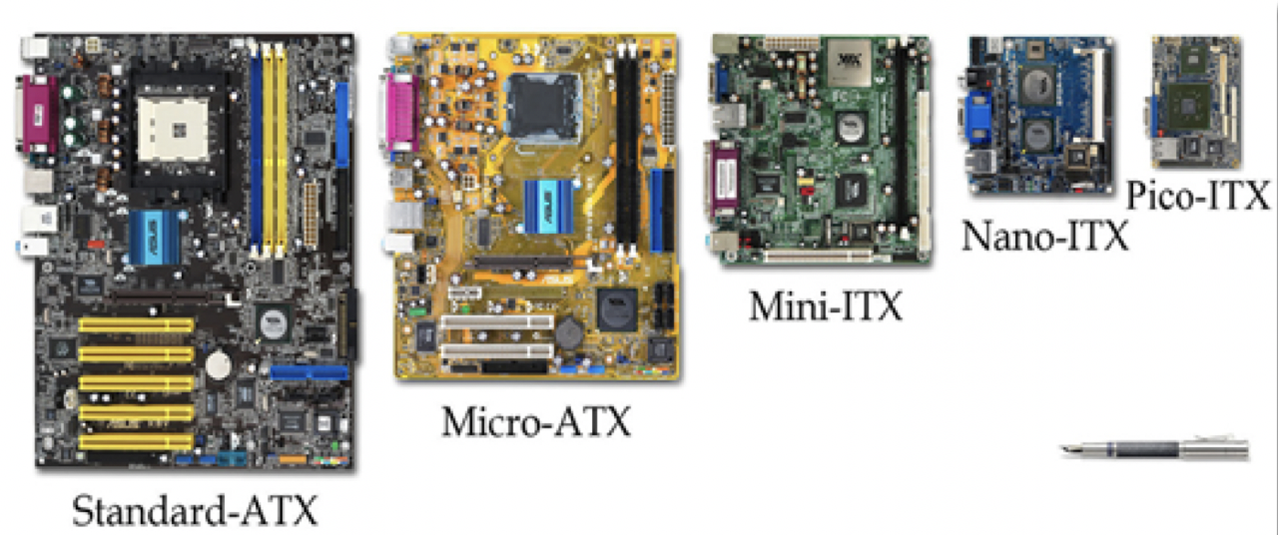
☑️ Size of motherboard
- put a size of motherboard before
ATX/BTX example:
Standard ATXStandard ATX: normal size computerMicro ATX: tabletMini ATX: smaller tabletNano ATX: phonePico ATX: smart watch- There were more sizes, but they did not become commercial
1
2
3
❓ What is the smallest motherboard?
- Pico ITX
- ⭐️ The sizes orders will be in the exam
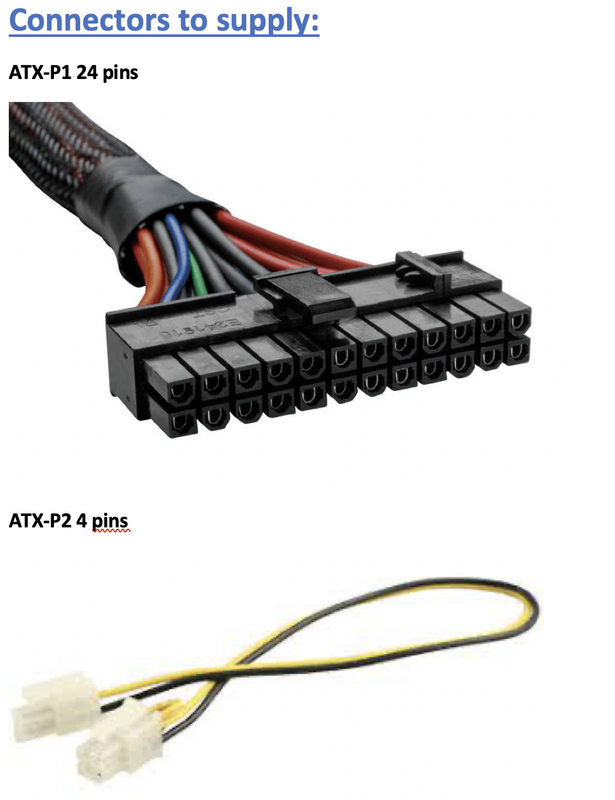
✅ Two different connectors to supply
- All mother boards need both
ATX-P1andATX-P2, mandatory ATX-P3is optional, is an extra distributor to energy- 🗺️ connectors are always close to the component they feed
1️⃣ ATX-P1
- If you are using
ATXmotherboard - has 24 pins
- 🛠️ to supply electricity to the mother board
- there is a place to connect normally on the East
- 🗺️ close to the motherboard
2️⃣ ATX-P2
- has 4 pins, but sometimes has 6 pins
- 🛠️ to give extra electricity to the micro processor
- give extra electricity for the micro processor
- 🗺️ close to CPU(micro processors)
3️⃣ ATX-P3
- optional
- an extra distributor to energy
- extra wire distribute extra energy to extra components
- example: to
extra HDDs,extra DVDs
✅ Sockets
- where to put the CPU
- structure to insert the micro-processor
☑️ Two different types of sockets
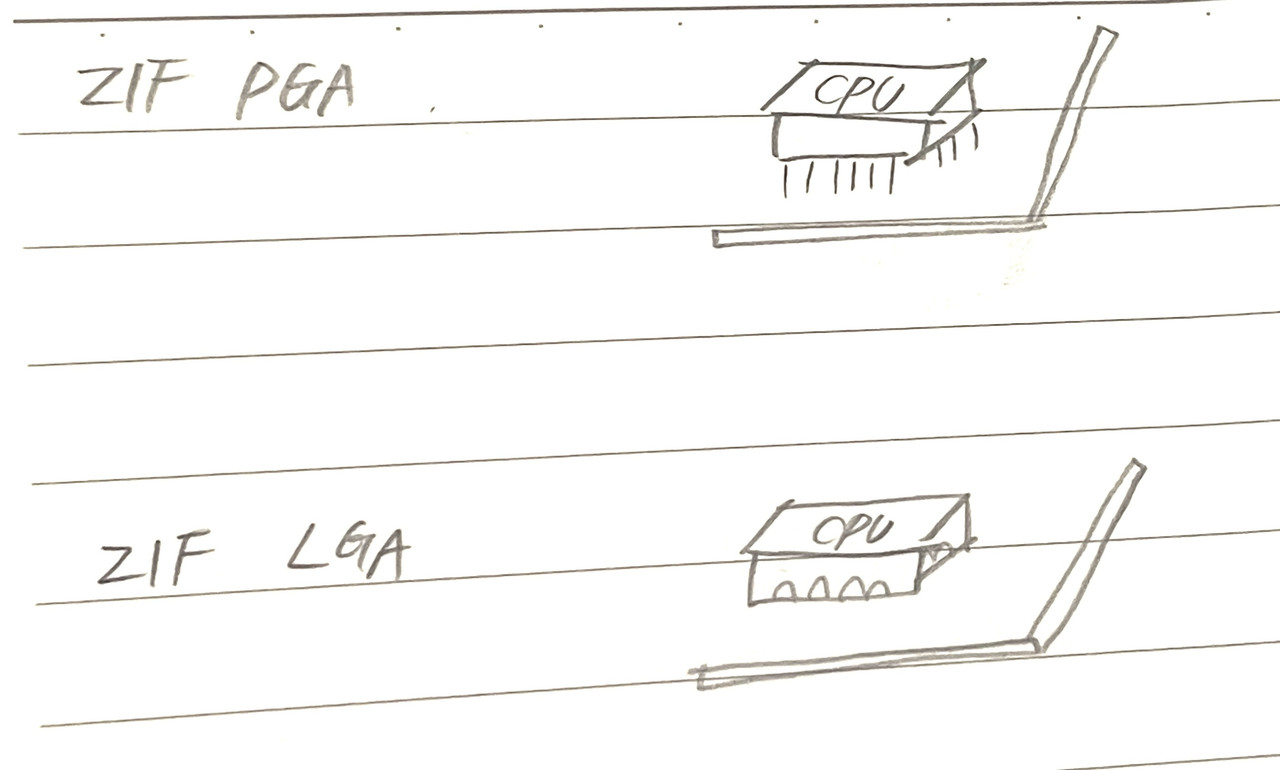
1️⃣ PGA
Pin Grid Array
- If the socket is PGA
- the micro-processor has the pins(male)
- and the socket has the holes(female)
- pins are in the micro processor
2️⃣ LGA
Land Grid Array
- micro-processor is female
- socket is male(pins on the land)
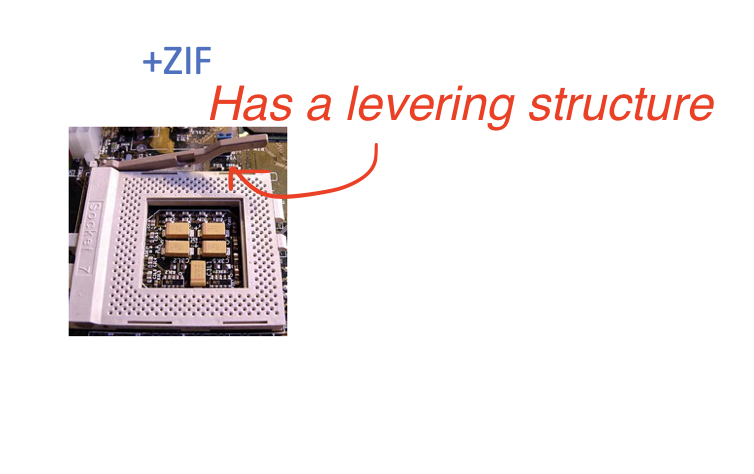
3️⃣ ZIF
Zero Insertion Force
- most of the sockets these days have a levering structure
- and the levering structure helps the insertion of the micro-processor to the motherboard
- So we have
ZIF PGAandZIF LGA
1
2
3
4
5
❓ How do we position the micro processor on the motherboard?
- The micro processor has a small golden triangle
- There is a triangle in the micro processor
- that has to match/fit the triangle on the socket
📌 B. RAM Memory(Main Memory)
- ✔️ Two ways of distinguishing RAM
- depending on physical structure
- depending on internal technology
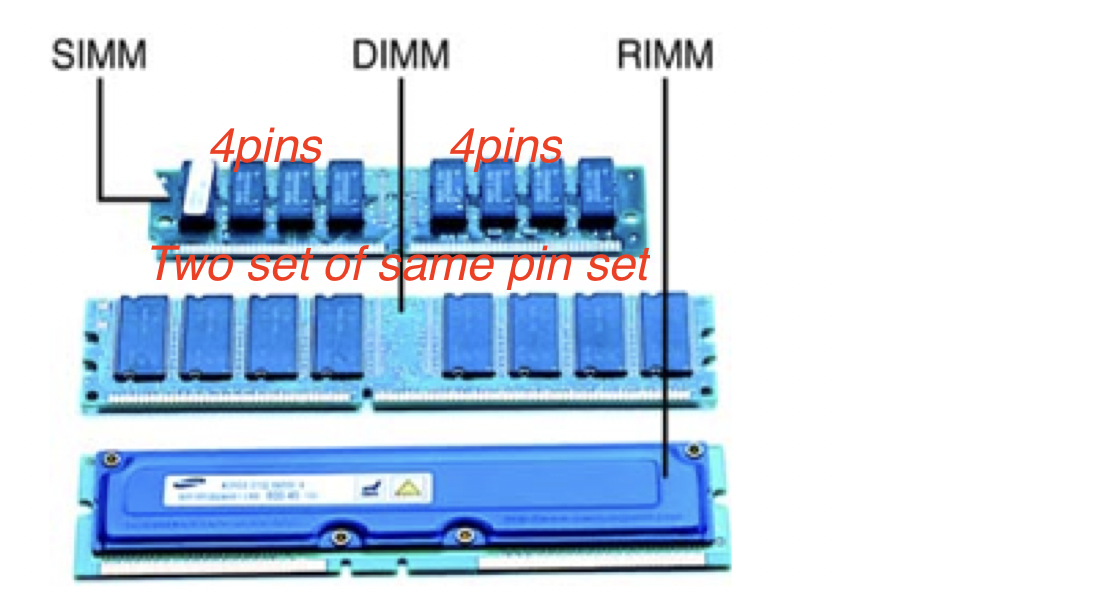
☑️ Three types of RAM depending on the physical structure
RAMcomes in cards- 🛍️ When we buy a RAM, we have to look at the slots of the mother board
- if same two sets ➡️ SIMM
- different size of sets, more than two sets ➡️ DIMM
- need to be encapsulated ➡️ RIMM
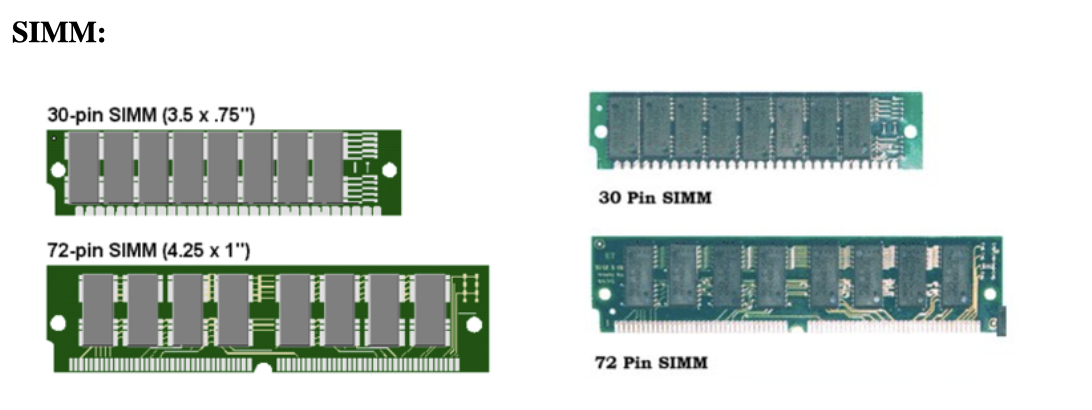
1️⃣ SIMM
Single Inlay Memory Module
- always 2 sets of pins
- two sets of pins of the same size
- very old version of SIMM can have only one set of pins
2️⃣ DIMM
Double Inlay Memory Module
- the size of the pins are different
- and there can be more than two sets/portions
- can have three portions
3️⃣ RIMM
Rambus Inlay Memory Module
- everything is hidden
- encapsulated
- 👍🏻 RIMM’s capsule helps with the airflow
- 🛠️ RIMMs are used for RAMs that need better ventilation
- 🛠️ Computers dedicated to graphic design, architecture(more heat) use RIMM for better ventilation
☑️ How to measure a RAM
✔️ Frequency: The final speed of the RAM
- How many times per second we can access the RAM(
Hertz) - example: I can access the RAM 1 time per second
- How often I have an appointment with the RAM
✔️ Latency:
- How much I have to wait before getting data from the RAM
- waiting time, once you are inside the RAM, once you have access to the RAM, before getting the information
- measured in
nano seconds - nano second:
0.000 000 001 second=1 * 10^(-9) seconds
✔️ Word width:
- number of bits per address/in each address of the RAM
- how much data we can save per address in a RAM
- length of the data we can save on one address of the RAM
✔️ Bandwidth:
- combination of all the
frequency,latency,word width Giga bits/second=Gbps- how much data, real amount of data you can read/write per second
1
2
3
4
5
6
👉🏻 Thus, an ideal RAM is
high frequency ⬆️
low latency ⬇️
word width ⬆️
high bandwidth ⬆️
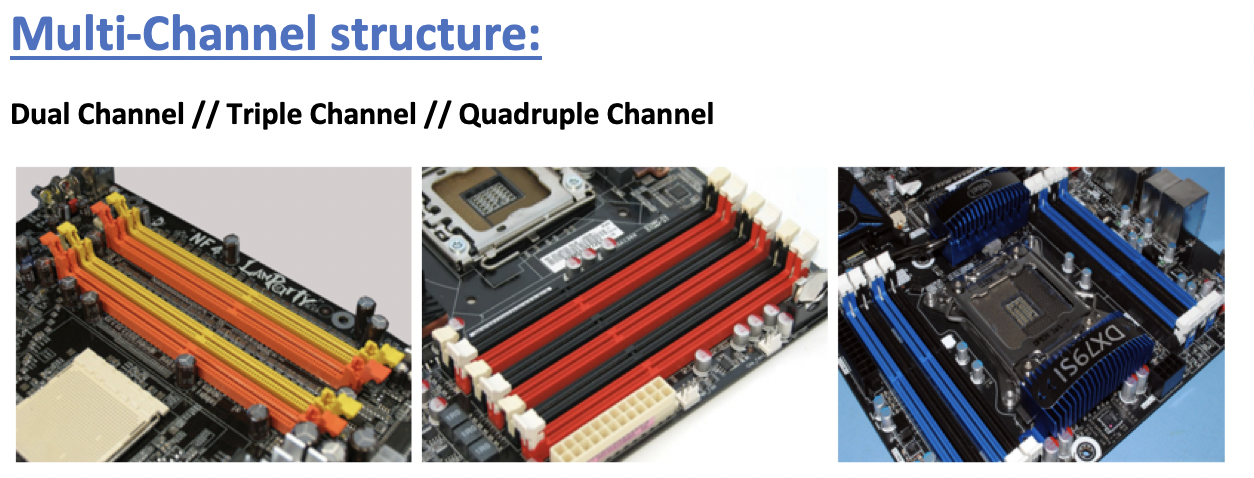
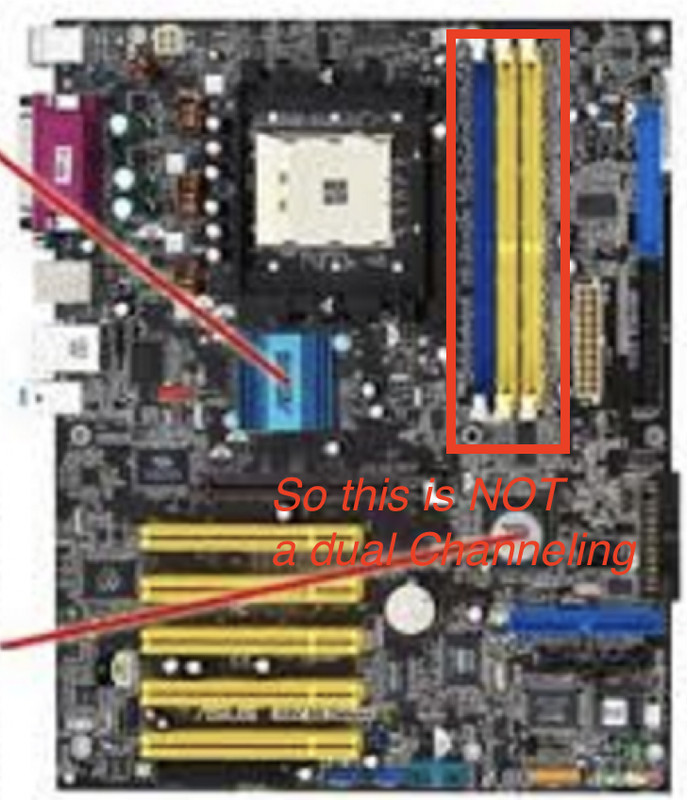
✔️ Channeling
- combination of RAM cards
- in order to increase
- combine several RAM cards to increase capacity of memory
- Multi Channeling
- ✔️ Dual Channel: two sets of two cards, so we have 4 RAMs
- ✔️ Triple Channel: three sets of two cards, so we have 6 RAMs
- ✔️ Quadruple Channel: four sets of two cards, so we have 8 RAMs
- All the RAM cards that are combined, so in the same color should be equal
- equal means: same frequency, same latency, same wordwidth, same capacity, same age(time used)
Recommended, so if you are going to change one RAM, change the others too!
- memory controller, system agent block would help channeling
✔️ Capacity
- RAM of
32bitsis4GB - so capacity is measured in
GB
☑️ Three types of RAM depending internal technology
Depending on HOW a RAM works(internal technology)
1️⃣ SDRAM
Synchronized Dynamic Random Access Memory
Random: address is not decided in order, can access address/directions randomly, not in orderSynchronized: the RAM is synchronized with the ⏰ clock- Synchronized does not mean it has 2GHz like the clock ❌
- Synchronized means that RAM only works when the clock changes from
0to1⭕️ - Thus, the speed of this SDRAM is slow 🐢
- ⭐️EXAM⭐️ only
133MHz=133 million times per second - I can only access
133Mega times per secondto the RAM Frequency: This is called the Frequency of the RAM
- 👎🏻 Nowadays, SDRAM exists, but considered very slow
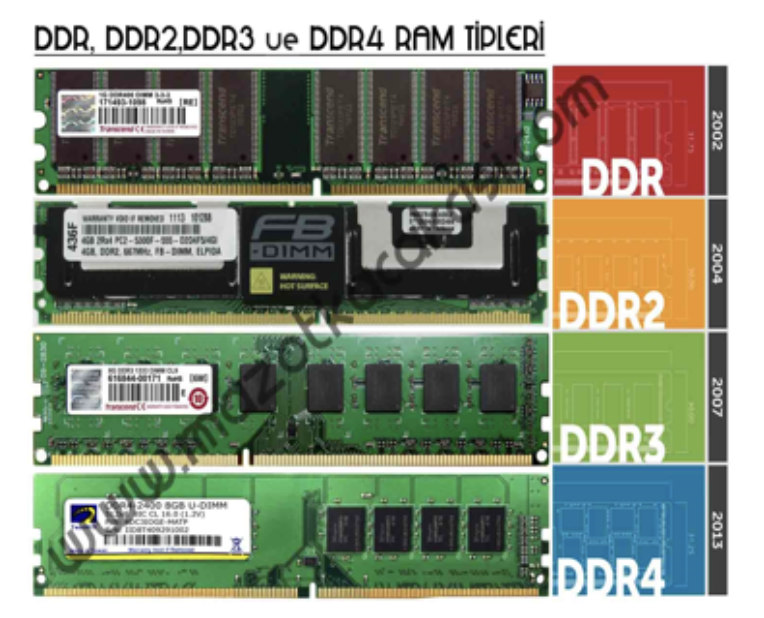
2️⃣ DDR
Double Data Rate RAM
Double: you can have two reads or writes at the same time- the speed would be same
133MHz, but you can read/write 2 times 🐇 more faster than SDRAM
- these days we have
DDR-2,DDR-3,DDR-4,DDR-5… DDR-nmeansn to the power of 2DDR-2: you can read/write2^2times at the same timeDDR-3: you can read/write2^3times at the same timeDDR-4: you can read/write2^4times at the same timeDDR-5: you can do2^5read/writes at the same timethe frequency would be highest in
DDR-5- Nowaways, faster RAMs would come in modern format, which is
DIMM
1
2
3
❓ Which is the fastest speed we can get in a RAM?
A: RAM would be DDR-5
A: speed would be 133MHz * 32
1
2
❓ What do you say when you go to buy a RAM?
- I want a DIMM, DDR-5
3️⃣ RDRAM
Rambus Dynamic RAM
- RAM that is encapsulated
- interal technology of the
RIMM - Frequency: around 1GHz
- this RAM would read/write
1000million times per second - 🛠️ Design, Architecture
- 👍🏻 Encapsulated, fast, good ventilation
💡 SO-DIMMS
- DIMM for laptops
- smaller DIMM for laptops
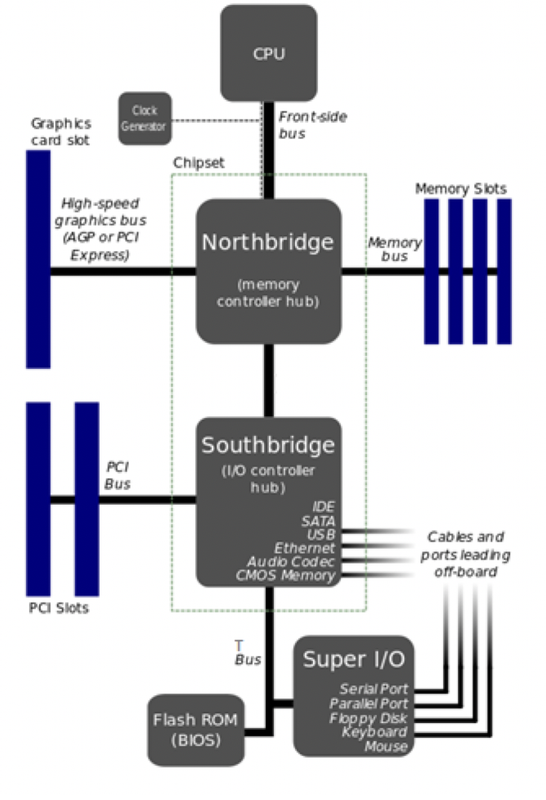
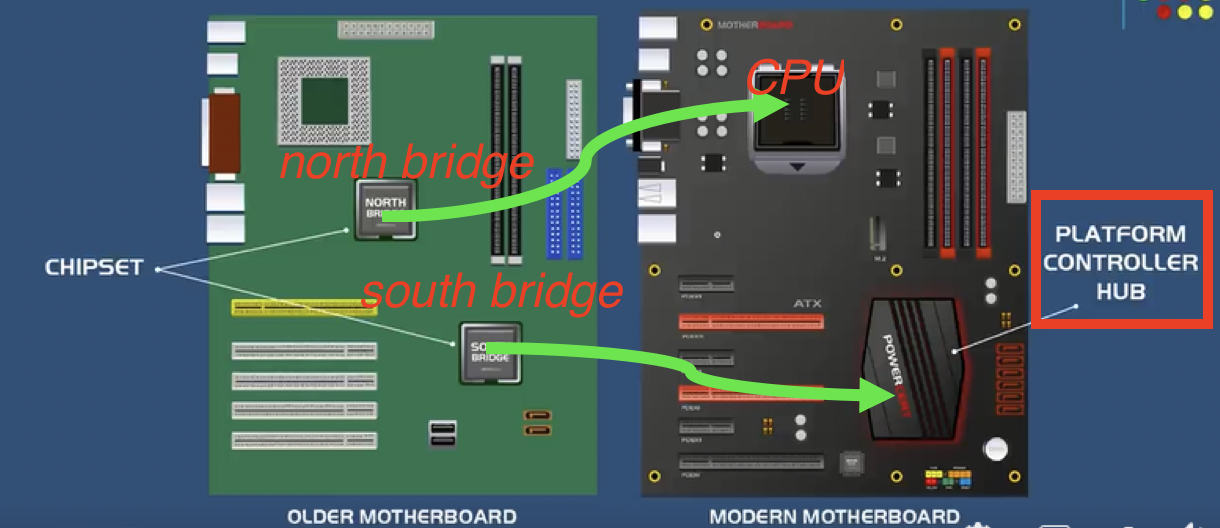
📌 C. Chipset
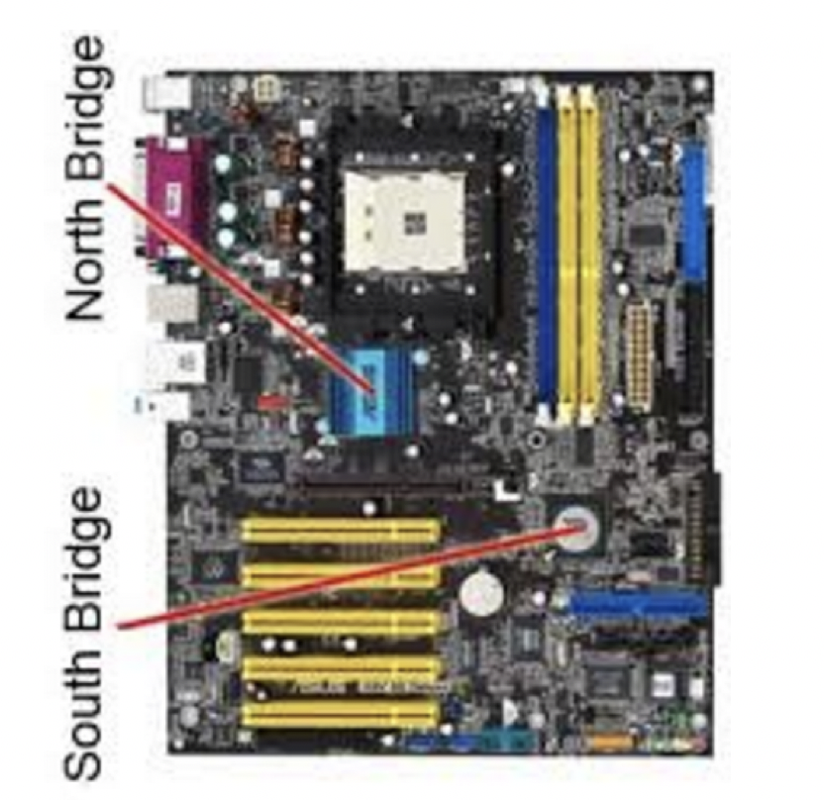
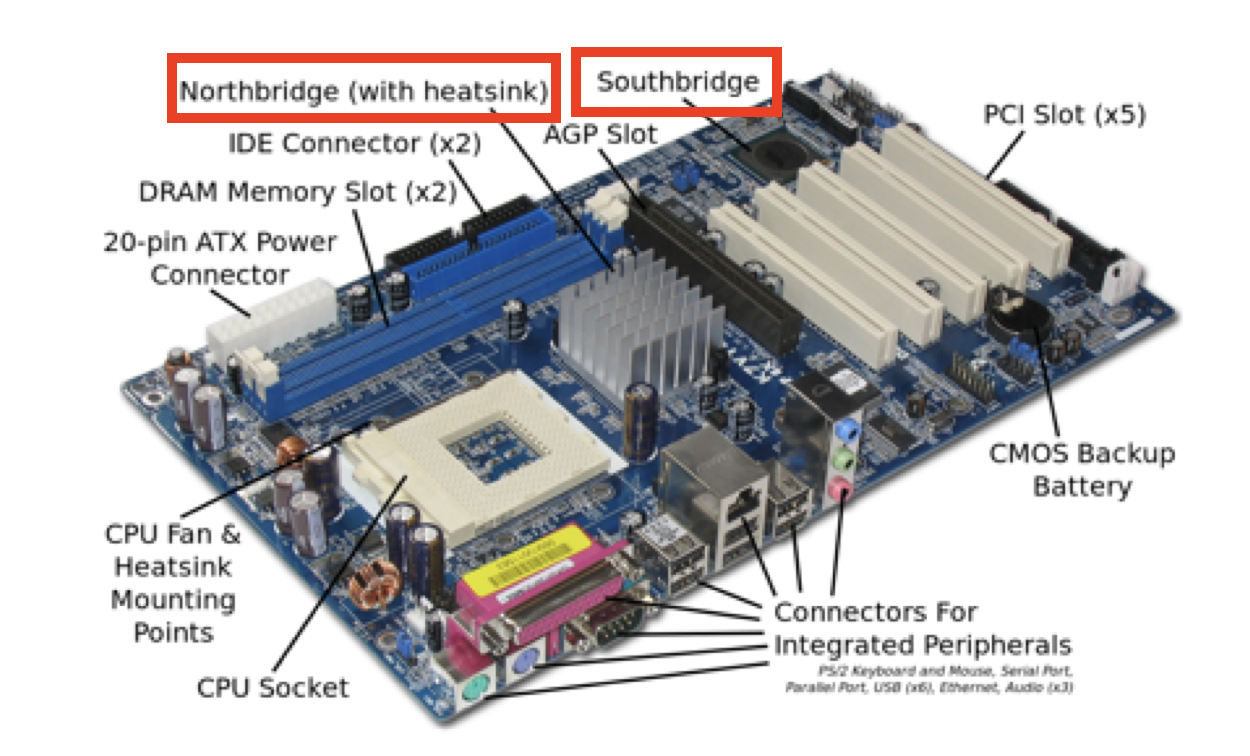
Only traditional motherboards have north bridge and south bridge
Set of chips you can find on the motherboard
purpose: helpers of the CPU, help the micro processor, CPU
- In the traditional motherboard
PCBs, chipset is a set of two bridges
- In chipsets, there are two parts
- north bridge and the south bridge
- north: in charge of elements that need more efficiency
- south: in charge of elements that can be a bit slower
1️⃣ North Bridge
has two jobs, 1️⃣ help fast work for CPU, and 2️⃣ responsible for south bridge
- 1️⃣ help with high speed elements
- help important elements of the motherboard
processor is in the north, so north bridge is also in the north, close to the processor
- 🥵 gets more warmer
- we need to ventilate, refrigirate
- so it has a structure of a corridor
- need airflow
- ✔️ Heat sink: to provide airflow, ventilation for the north bridge
purpose of heatsink: create airflow, for refreshing
- 2️⃣ north bridge is also in charge of controlling the south
- north is in charge of supplying the south
❓ What is controlled by the north bridge?
Memory controller: for controlling several RAMsGraphic cards and expansion cardsare normally inserted in the expasion slotsFront side bus: for communication among coresPeripherals in Transport bus: for peripherals in multicore
❓ If south bridge and north bridge is helping CPU, then what does the CPU do?
- CPU: backside bus + ALU + CU
- and rest of the work would be helped by south bridge and north bridge
2️⃣ South Bridge
Sometimes South bridge is called
Input Output Controller(I/O controller)- relatively not so fast, not so important parts of the processor
situated in the south of the motherboard
- does not need as much as ventilation
- does not get so hot
- does not have heatsink
❓ What is controlled by the south bridge?
Peripherals in mono-core, can be slower, normal keyboardExternal connectorsin the motherboardBIOS: booting system of the computer
📌 External connectors
connect to audio, internet, USBs, mouse, keyboard…
- at the west side of the motherboard(left)
- there are lots of connectors for the peripherals
- in the motherboard, there are connectors for the external connectors
green for earphones
all the external connectors connect to the south bridge of the chipset
- In a computer
all-in-one(computer with no tower, like the one in Clara Del Rey) - the motherboard is placed differently
- so for connecting USBs, peripherals, they are behind the screen
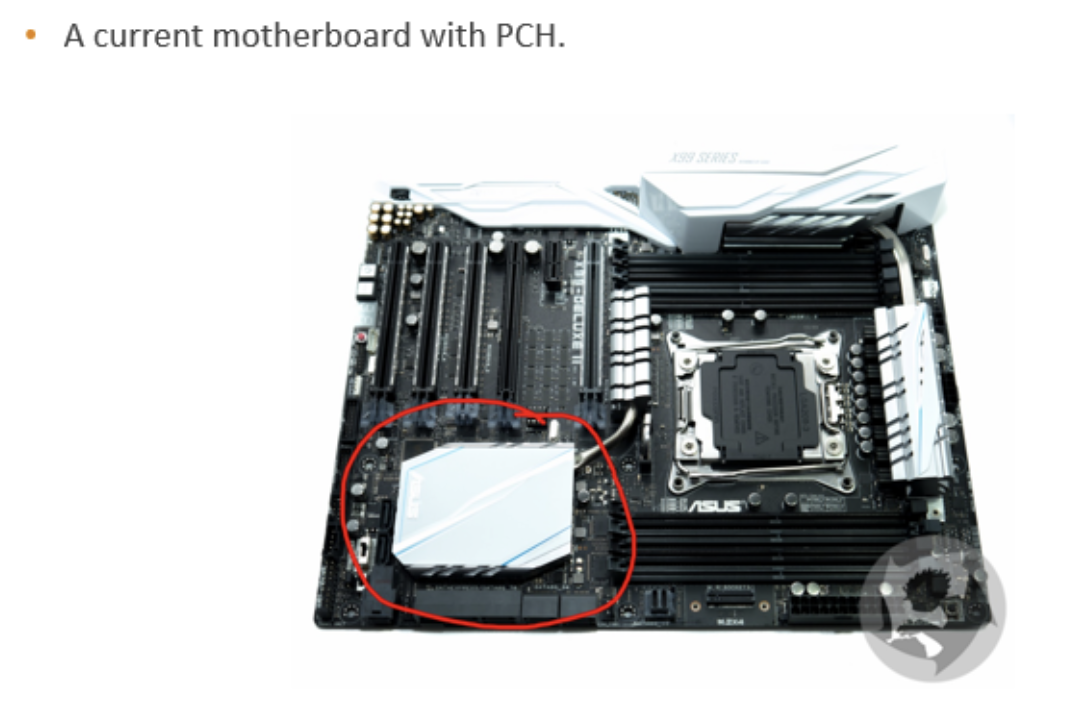
📌 Modern PCBs
- in modern PCBs, there is no north bridge nor south bridge
✔️ North bridge
inside CPU, control MC only
- the north bridge inserted/internal in the CPU/processor
- so we do not see
- but as it is inside the CPU, north bridge only controls the Memory Controller
✔️ Platform controller HUB(PCH)
South bridge works more, needs ventilation, change name to PCH
- and the south bridge gets all the job of the traditional north bridge
- and does all the work
- it becomes very very powerful
- 🥵 and now south needs the ventilation
- now called Platform controller HUB(PCH)