1.3 Binary Coding and Decoding
- ⭐️ change decimal number into binary
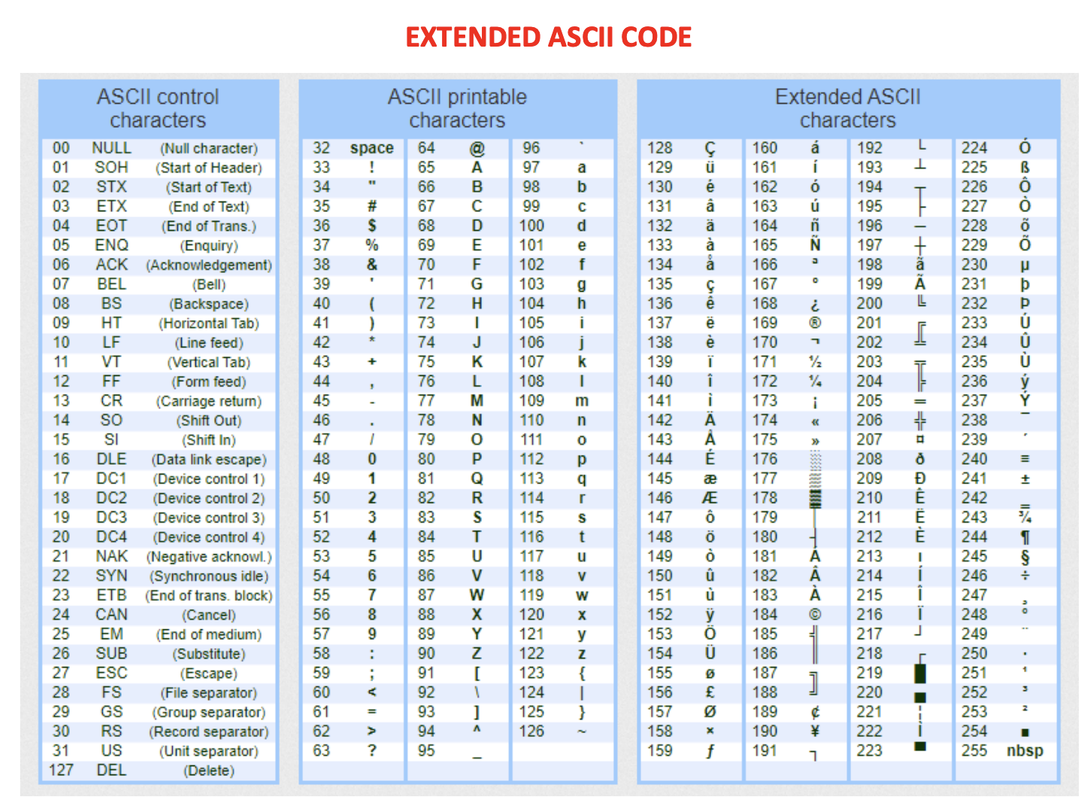
- ⭐️ look at ASCII table and change short text message into binary
- ⭐️ difference between raster and vector
- ⭐️ video question : need to write the formula and write the values
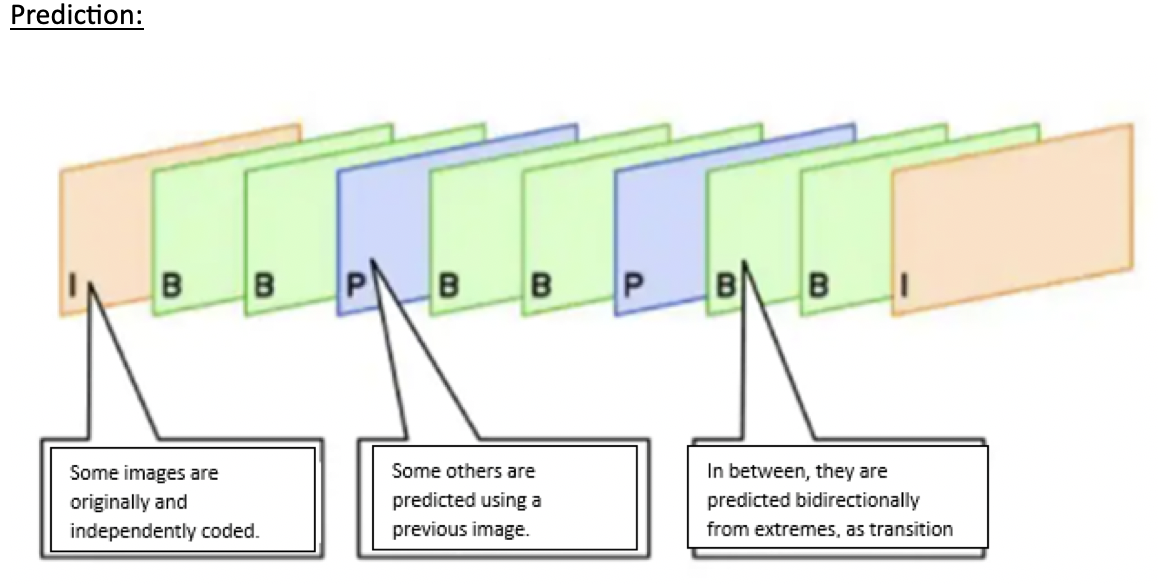
- ⭐️ what kind of pictures in video P/I(pictures that need to be recorded)/B(make up pics to make video more realistic)
- ⭐️ audio types .mp3
- ⭐️ video type .mp4
- ⭐️ forking: when system gets split into several branches
- ⭐️ UTF-8: it means multi lingual and it is VLC
- ⭐️ CJK: chinese, japanese, korean, UTF-8 covers CJK
✅ Positive Integer
- Integer: 8bits
- there are two ways to encode positive integers into binary
1️⃣ Use dividing by 2
- divide the
Integerby 2 several times - take the final quotient and the remainders
- from down to up, write the quotient and remainder down
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
33/2 = quotient: 16, remainder: 1
16/2 = quotient: 8, remainder: 0
8/2 = quotient: 4, remainder: 0
4/2 = quotient: 2, remainder: 0
2/2 = quotient: 1, remainder: 0
from down to up, 33 = 1(quotient) and 00001
👉🏻 33 = 100001
2️⃣ Use the weights rule of the power of 2
- use the
weights ruleof the powers of 2 - draw positions, and each position is double to the one at the right
- then add
1in positions needed and0in positions not needed
1
2
3
4
5
6
33 = __ __ __ __ __ __
32 16 8 4 2 1
👉🏻 1 0 0 0 0 1
❓ 0 = 00000000
❓ 255 = 11111111
✅ Negative Integer
🚩 Sign Flag
- 1️⃣ Change the positive
Integerinto binary - 2️⃣ Make the number into 8bits
- 3️⃣ Add a
1at the very left, this is a special1 - ⭐️ Sign flag: special
1to indicate that thisIntegeris a negative Integer - This special
1is stored in a different place - sign flag means this
Integeris a negative 🚩 Flags are electric signals stored in specific places for special circumstances
- If the flag is off, you add it as part of the number
- If the flag in on, you turn it into a negative symbol
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❓ code -78 to binary
78 = 01001110
➕ add 1 on the left, why make 8 spaces? bc 8bits
👉🏻 101001110
❓ code -16 to binary
16 = 00010000
➕ add 1 on the left
👉🏻 100010000
✅ Decimal Integer
FLU(Floating Point Unit)
- Decimal numbers are stored in a special place called FLU(Floating Point Unit)
The convention used for this is
IEEE754for international technique,IE3754. The steps are as following- 1️⃣ Take the
Integerpart, transform into binary but discord all the0sat the left - no extra
0s - 2️⃣ Take the Decimal part
0.xxx, then multiply by 2 five times, but discarding the appearing1sinto0s. You take the0sand the1sAFTER the=from up to down - 👉🏻 now put it together with the coded integer + decimal part
- 3️⃣ The dot needs to be represented, and the decimal part is always
5bits. We are going to shift the decimal symbol(the dot) to the left until you leave it after theFIRST 1. AND you count how many steps/jumps you had to take. -Move the dot to the left until you reach the first number - ⭐️ In computing, we want things to always occupy the same number, this is a rule. NO variable length, always fixed length. So, we want the decimal to occupy
32 bits. - 4️⃣ To the number of steps/jumps, add 127 and then you code the result.
- 5️⃣ We place that at the END of the number, leaving extra space in between, the
IEEE754want the number to occupy32bits - 6️⃣ In order to have
32bits, if the number is negative, add a1at the left and BESIDES you light the sign flag. If the number is positive, add a0, so that it occupies the same number as a negative one.- add 1 to the left if negative
- or add 0 to the left if positie
- 7️⃣ We complete with
0sin order for it to sum up to32bits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
❓ code -17.33 to binary
1️⃣ Integer part into binary
17 = 00010001 ➡️ discord all the left 0s ➡️ 10001
2️⃣ Decimal part, multiply by 2, five times
0.33 * 2 = 0.66 ➡️ 0
0.66 * 2 = 1.32 ➡️ 1
0.32 * 2 = 0.64 ➡️ 0
0.64 * 2 = 1.28 ➡️ 1
0.28 * 2 = 0.56 ➡️ 0
👉🏻 01010
then add to 17
👉🏻 10001.01010
3️⃣ move the . to after the first number, count the jumps
👉🏻 1.000101010
count the jumps = 4
4️⃣ Add 127 to the number of jumps
4 + 127 = 131
👉🏻 change 131 to binary = 10000011
5️⃣ add the number 10000011 to the end with a space in between
👉🏻 1.000101010 ---space--- 10000011
6️⃣ If number is negative, add 1, if positive, add 0
👉🏻 11000101010 ---space--- 10000011 (19 digits)
7️⃣ Fill the space w 0s, so it occupys 32 bits
11000101010 0000000000000 10000011
----------- ------------- --------
1(neg) + 17 13 0s 4jumps + 127
👉🏻11000101010000000000000010000011
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
❓ code -28.46 to binary
1️⃣ integer: 28 = 11100
2️⃣ decimal: multiply by 2 five times
0.46 * 2 = 0.92
0.92 * 2 = 1.84
0.84 * 2 = 1.68
0.68 * 2 = 1.36
0.36 * 2 = 0.72
👉🏻 01110
👉🏻 11100.01110
3️⃣ move the .
👉🏻 1.110001110
steps: 4 times
4️⃣ add 127 to steps
4 + 127 = 131 = 10000011
5️⃣ add the number to the end with space
👉🏻 1.110001110 ---space--- 10000011
6️⃣ neg: add 1, pos: add 0
👉🏻 11110001110 ---space--- 10000011(19digits)
7️⃣ Fill the space w 0s
11110001110 0000000000000 10000011
(13 0s)
- all the numbers that use this protocals are called
floatssince they are stored in the FPU - If instead of
32bits, we made this in64bits(The standard is totally different procedure), we call themdouble floats Double floatshave more precision, always more than 2 decimals.- ⚠️ It is considered a bad programming technique to use double floats with things that could be in a regular float, since it is more accerlerated, more work for the PC.
✅ Text
☑️ Standard Text, Extended ASCII
- for
Standard Text, we useExtended ASCII Extended ASCIIis aFLC-8, each character is8bits- each character 🟰
Integer - so you can code the
Integerwith the weights rule - there are no spaces
- If you need a space, code the
number 32 - 👎🏻 However,
Extended ASCIIuses only256 characters(from 0 to 255)
1
2
3
4
❓ Transform I_miss_you with ASCII code.
73 32 109 105 115 115 32 121 111 117 46
01001001001000000110110101101001………00101100
☑️ Extension of ASCII, UTF-8
UTF-8is an extension of theextended ASCII- also known as Unicode
- bc it is to be used with every language int he world
- UTF
8does not mean8bitsper symbol - it means
multiple of 8bitsper symbol - Some symbols are
8bits(1byte)likeASCII - Some symbols are
16bits(2bytes)likeGreek, Cyrilic, Hebew, Arab... - Some symbols are
24bits(3bytes)like CJK,Korean Some symbols are
32bits(4bytes)likePersian, Fenician, old languages and ALSO math- Each language, if possible uses its own version of
ASCII - but due to Internet, a code was invented to allow intercommunication and translation between different languages
✅ Image
☑️ Two types of pictures
1️⃣ Raster
- divided into pixels, get pixelized when increase size
JPG,gig,png- HR: Horizontal Resolution: how many pixels in horizontal
- VR: Vertical Resolution: how many pixels in vertical
- Resolution = HR * VR
✔️ Color Depth in Raster
- Color Depth: how many bits you need for your image
1or8or24- black and white ➡️ need 2 combos, need
1 bit(2^1)➡️ color depth: 1 - gray-scaled ➡️ need 256 combos, need
8 bits(2^8)➡️ color depth: 8 full-colored ➡️ every color is
R(0~255) + G(0~255) + B(0~255)➡️ each R, G, B need 8 bits ➡️ need24 bits➡️ color depth: 24- pure red would be
255.0.0 - pure green would be
0.255.0 - black would be
0.0.0 - white would be
255.255.255 - as soon as there is one colored pixel, even if all pixels are black and white, color depth will be 24
- if full color, each pixel will have 24bits, graphic card will write the bits
- pure red would be
- color codes are stored in graphic cards, in the driver
- Red =
111111110000000000000000 - I can use up to
2^24colors, more or less 16000000(16 million)(2^4)*(2^10)*(2^10)= more or less 16 _ 1000 _ 1000
If a graphic card had 64bytes, it can have
2^64colors(2^4)*(2^10)*(2^10)*(2^10)*(2^10)*(2^10)*(2^10)
✔️ Picture size in Raster
- Picture size =
HR * VR * D(color depth)
1
2
3
Q: How many bits would a black and white picture have of 100 * 50?
- Picture size = HR * VR * D(color depth)
- 100 * 50 * 1 = 5000
1
2
3
Q: How many bits would a gray picture have of 100 50?
- Picture size = HR * VR * D(color depth)
- 100 * 50 * 8 = 40000
1
2
3
Q. If all the sound that my computer can make are 8, how many bits do my computer have?
- 3
- because 2^3 = 8
1
2
Q: How many bits would a full color picture have of 100 * 50?
- 100 * 50 * 24 = 120000
2️⃣ Vector
- more professional, more efficient when picture is not so detailed
svg- do not use pixel, use
area by area/zone by zone - call the color just once, then call the length/size/measurements of the area that has that color
red(255.0.0)* 10 meters + white(255.255.255) * 2 meters- the picture tends to be more compressed
- 👍🏻 more efficient
- 👍🏻 when the area is uniform, no big transition of color, use vector
- ⭐️ big areas of same color(like football field, all green)
- ↔️ image with many color changes, use Raster(like a christimas tree with lights)
- if I make the picture bigger, zoom in, then just have to change the length/size/measurements
do not get pixelized
- 👎🏻 however, as measuring device is more expensive,
- vector is only used for professional purposes
📌 Main Computing Principle
- 0: 0.5v
1: 5v
- If you have
n bitsto store 0s and 1s, you can have total of2^ncombinations - 1 bit: 2 combinations
0, 1 - 2 bits: 4 combinations
00, 01, 10, 11
✅ Audio
- Audio is vibration, need air to transmit
- microphone has a small surface to capture vibration
- microphone transforms the vibration to binary code
- extension for audio is
.wav - when compressed/summarized
.mp3 - if
la, la, la, la,.mp3summarizes sound and savela * 4 - ⭐️
.mp3does not lose sound, but just summarized .mp3is very compressed when there are uniform, repetitive sounds in the track- if many different sounds,
.mp3will not be so efficient
☑️ Sampling Frequency(Hertz)
- how many times per second the computer pays attention to the microphone/vibration
- sampling frequency ⬆️ better sound quality, capture more details of the sound wave ⬆️
- sampling frequency ⬇️ cannot capture all the details of the sound ⬇️
- if frequency is
1Hz, then listening1 time/sec - if frequency is
1KHz, then listening1000times/sec - if frequency is
1MHz, then listening1000000 million times/sec - if frequency is
1GHz, then listening1000000000 thousand million times/sec - ⭐️ If you capture a sound with a high sampling frequency, will get more details of the sound
☑️ Amplitudes(bits)
- number of all the different sounds you want to capture
- in an orchestra, you want to capture more instruments, need higher amplitude
higher amplitude ⬇️ more variety of sounds ⬇️
- Q: If orchestra used 16 different sounds, how many bits would we need?
- need 4 bits
Amplitude = 4
- Q: If orchestra used 80 different sounds, how many bits would we need?
- need 7 bits (2^7 = 128)
- Amplitude = 7
☑️ Time(seconds)
- how long the music lasts, measured in seconds
- more time ⬆️ can save longer song ⬆️
☑️ Stereo
- full stereo: use two sequences of bits(2bits) per ear, duplicate the sound
- left and right ear listen to the whole song
need to multiply formula by 2
- mono stereo: one sequence of bit, divide sound in two
- left ear: background music, right ear: singer voice
✔️ Audio Size
- size:
Hertz * A * t
1
2
3
4
Q: How many bits do you need for an orchestra for a 4 minute song, with 300 amplitude, sampled at 2GHz?
- size: Hertz * A * t
- 2*10^9 * 9 * (4*60)
= 2000000000 * 9 * 240` bits
✅ Video
- sequence of pictures + sound
.avi,.mov- compressed into
.mp4 - however,
.mp4suffered from forking - forking: people started using another form of video
.wmv, not compatible with.mp4
☑️ FPS, Frames per second
- how many images video shows per second
- fps ⬆️ better quality of video ⬆️
☑️ Prediction in video
- in video use prediction
- as some pictures are important,
- but other pictures are evident, so not as important
- use picture I, P, B
✔️ Types of picture in video
- Picture type I: Important
- independent pictures, important pictures
mandatory to record them independently
- Picture type P: Predicted
- predicted pictures
can predict them, as it is very similar to the previous picture
- Picture type B: Bidirectional
- Bidirectional
- extra movement to make video transition more natural
- pictures used to improve transitions
- make video look softer
✔️ Video size
picture size * fps * t + Audio * 2(stereo)HR * VR * D * fps * t+Hertz * A * t * 2- ⭐️ audio is added
1
2
Q: How many bits a 5 minute video have that has resolution of 1920\*1090 full color at 1000fps with stereo sound of 100 amplitudes sampled at a frequency of 25MHz?
- {(1920*1920 * 24) * 1000 * (5*60)} + {( 25 * 10^6) * 7 * (5*60) * 2 bits}
- ⭐️ only color depth and amplitude has to be converted into bits
✅ File
- all the bits are stored in a unit called
file file: set of bits with informationmetadata: extra information about the file- ⭐️ metadata is stored in the Operating system
Timestamp:
created_date,last_modified_dateowner of the filesize of the fileextension of the filepermissions over the file, read/write/execute permissions, what you can do with the fileaccess control, who can access the file
- Linux keeps metadata very far from data itself, 👍🏻 safe from haking
- However, Windows keep metadata close to the data itself, not very safe
✅
✅
✅
CC BY Izzie [CC] Integers, Text part of the notes were completed thanks to Izzie, by referencing her notes. Thank you Izzie!