4.5 Connect VM to the network
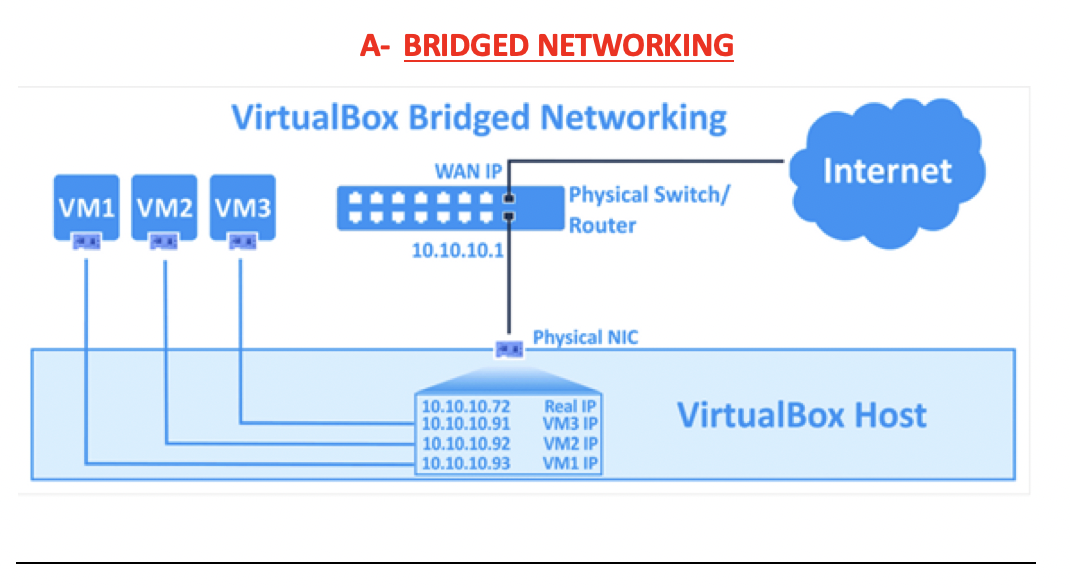
✅ Bridge Networking
Each VM has its own IP address
and the VM’s IP address is different from the host
👍🏻 each machine has its own traffic
RJ45 + ethernet wire(if wired)orwireless connectionbelong to the RM- the bandwidth is shared by the RM and the VM
1
2
⭐️ bandwidth: how many bits travel per second of that connection
mega bits per second
- 4 IPs, 4 traffic
- but only one wire,
- so all traffic share the bandwidth
distributed by
percentage %- ❓ What if one machine goes very slow?
- 💊 you can resize the bandwidth distribution
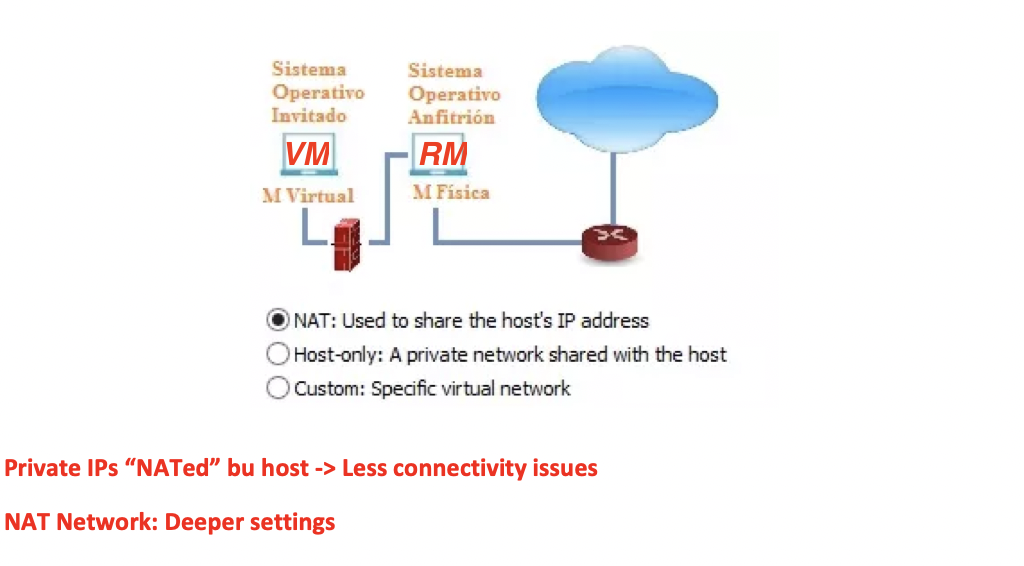
✅ NAT mode
Network Access Translation
- Only 1 IP for all RM and VM
- for the VM to access internet, has to go through RM
- the traffic is signed by the host
- so the RM will check the VM access to the internet
the RM will control the connectivity
- 👍🏻 security
- 👍🏻 No connectivity problems, and RM will control all
👎🏻 If I want to do hacking with VM, I cannot as RM will know my IP
- ⭐️ NATed: there is only one IP, and it is used by all virtual machines
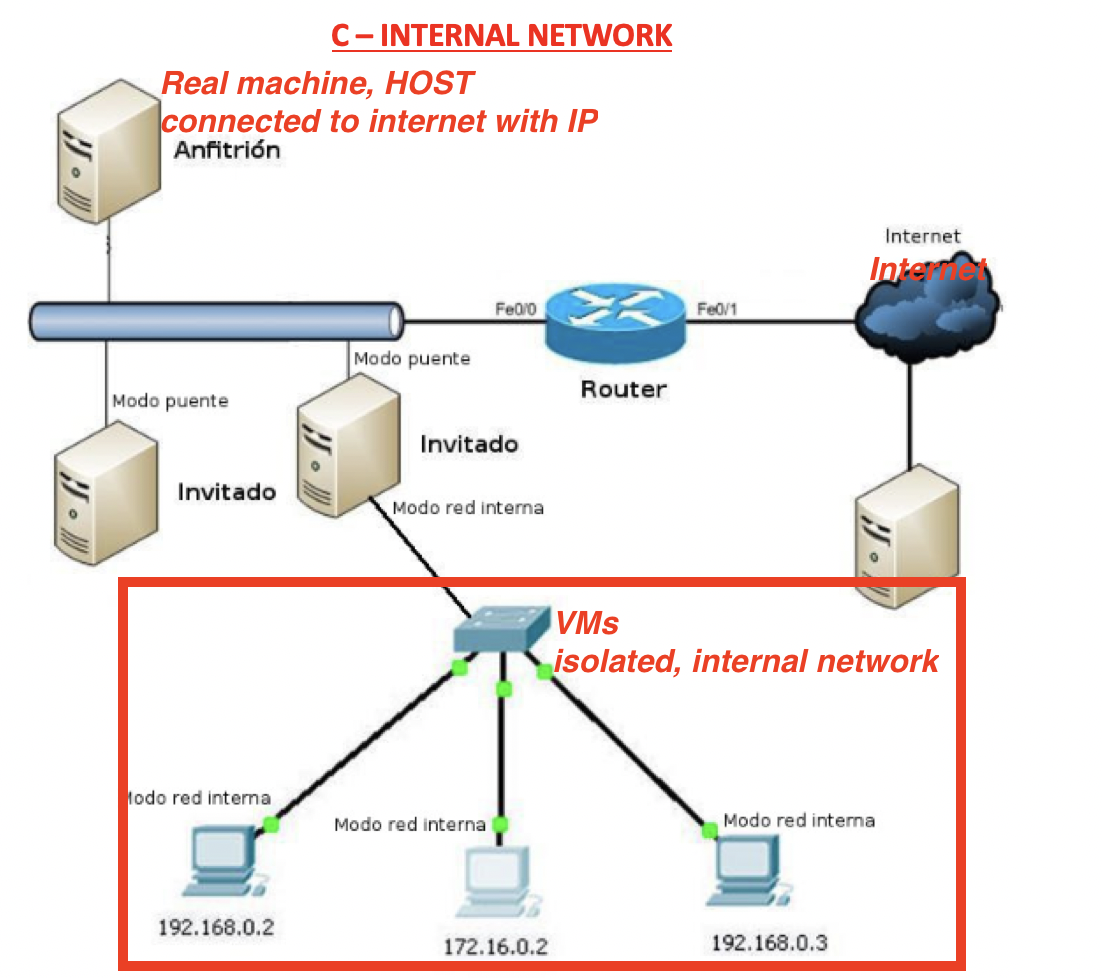
✅ Internal Network
- RM: connected to Internet, with its own IP
- can connect to Internet
Anfitrion: RM
- VM: some VMs create an internal, isolated network
- Invitado: one virtual machine, acting as a boss for the internal VMs
all VMs are connected to the boss VM, invitado
- It is similar to creating a VPN(Virtual Private Network) with VMs
- 🛠️ Used for company intranet
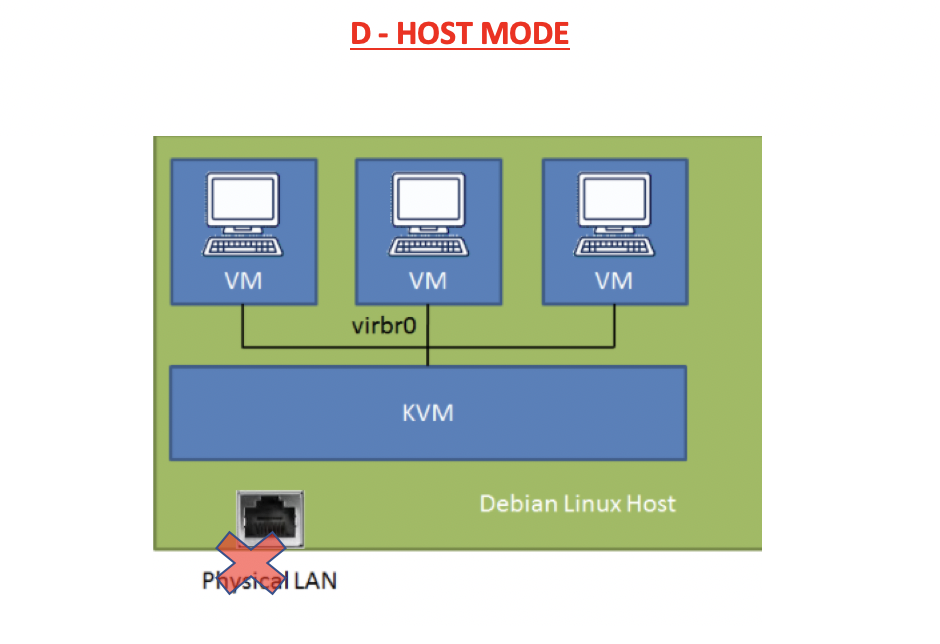
✅ Host Mode
- VM is connected to the RM
- but connection to internet is lost
- nobody has connection to the internet
- only connection between VM and RM
- 🛠️ Designing a secret project
- so that spies cannot look at me!
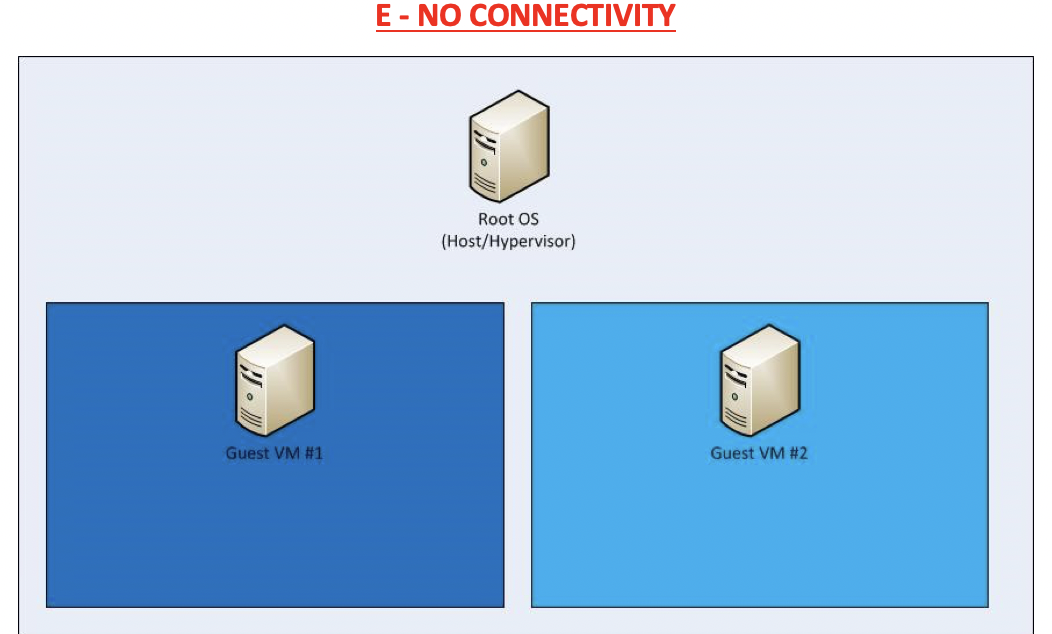
✅ No connectivity
- nobody has connection to the internet
- no connectivity between VM and RM
- 🛠️ Used for VMs that spy on your computer, without being noticed by the RM
- 🛠️ Virtual malware
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.