3.8 Partitions
✅ Partitions and Harddisk
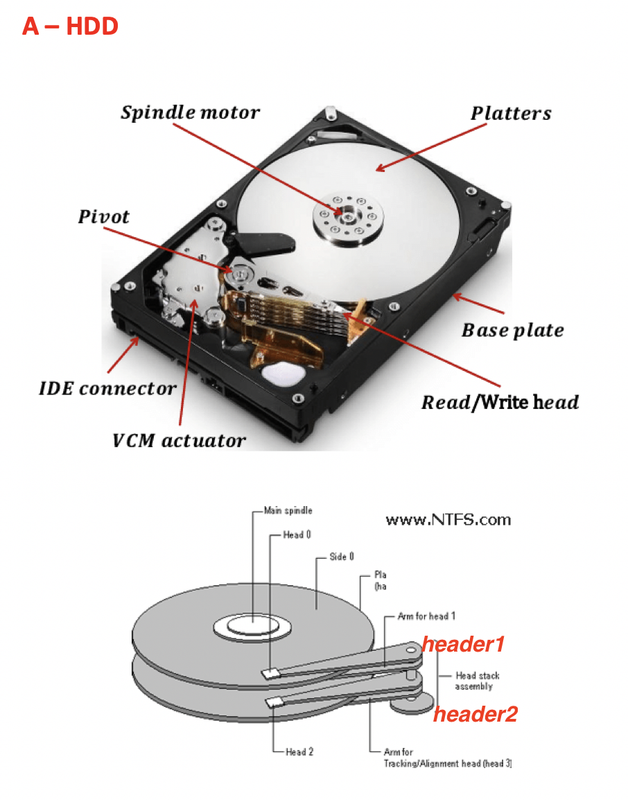
in secondary memory = hard disk
- the plates can use the two sides at the same time
- so one header per one side
in total, two headers
- plates rotate using spindle motor
- header does not move
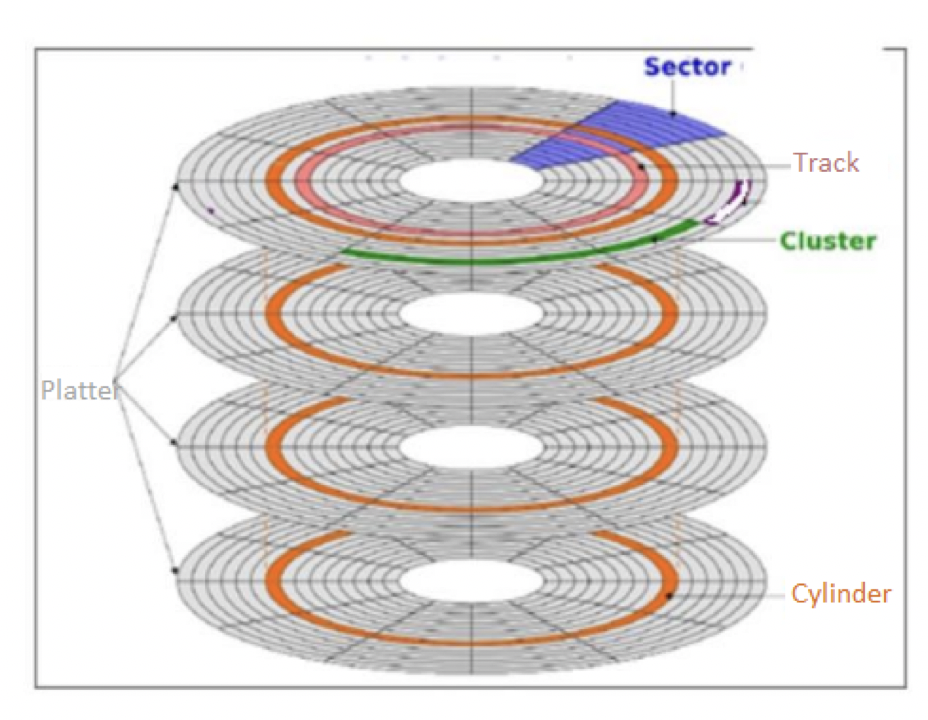
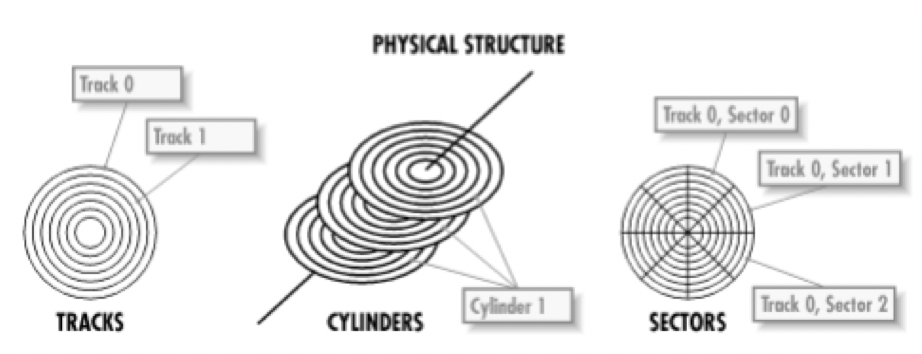
✔️ Track circle
- concentric circles called Track circle
- outmost circle is
0 - as you go inside, the number of the circle increses
1, 2, 3...
✔️ Sectors
- the circles are divided into sectors
- the triangles goes from 12 o’ clock : sector 0
- it turns like the clock direction
✔️ Unit
- intersection of track and sector
- all unites save the same bytes, although in the picture, size looks different
no matter distance to the center
- The external units and internal units save the same bytes
- The internal units have more information compressed
- this means the information stored in internal units are more safe
✔️ Unit 0
- intersection of sector 0 and circle 0
- ⭐️ unit 0 stores the booting system of my disk
- 😭 if we damage unit 0, the disk is useless, as we cannot run the booting system
also the key of transparent encryption in linux is stored in Unit 0
- But modern disks have a copy of unit 0 in the interior unit of the last disk
👍🏻 so more difficult to break, and more safer
- where: external circle and right next to 12’o clock
✔️ Rest of the units
- rest of the units are called just units, they are not numbered
✔️ Two technology of disks
- Magnetic technology disk
- old
- the headers are magnetic
- and the tracks had magnetic material
- ⭐️ if you use magnetic tech, in each of the unit, you can store 512Bytes, if the units are old
magnetic ➡️ 512Bytes per unit
- Optical technology disk
- new
- headers are lazer
- tracks are valleys
(lazer is kept, 0)and hills(lazer is reflected, 1) - ⭐️ 2048Bytes if new (🆚 4times more than magnetic disk)
- optical disks keep much more data than magnetic disk
optical ➡️ 2048Bytes per unit
- the size of bytes you can store per unit does not change on the size of the disk
- as disk is a circle shape, external units are bigger, but the amount of bytes we can save is the same
- the ones interior the disk the bits are more compressed, but save the same bytes
- 👉🏻 if you want to hide the information, save it in interior, compressed
- 👉🏻 for more safetey, use the internal tracks
- 👉🏻 so modern disks have a copy of unit 0 in the interior unit of the last disk
✔️ Cylinder
- if we take the same track in every plate, you have a cylinder
number of cylinder is the same as number of tracks
- if you get an error in track 20, linux will say
you have an error in cylinder 20 - it means the same thing!
✅ Cluster
- if you take several consecutive units, you have a cluster
- it means minimum size of a file
- even if the file is smaller than the size of the cluter, you need to fill it
- 👀 My picture is
3kbbut the cluster size is4kb. - If I save this picture in the harddisk, this picture file will still occupy
4kbin the harddisk. - not 3kb ❌
- and the extra
1kbadded to fill the cluster size is called redundance
✔️ Redundance
- used for parity, secutiry, protection
- used for protection of the file
- 👀 If the picture is
13kband cluster size is4kb, the picture file will occupy16kb. - File size will be cluster size, or be the multiple of cluster size
- the redundance will be
3kb - more redundance ⬆️ more secure the file ⬆️
1
2
3
4
❓ My video is 21kb, and my cluster is 4kb
- it will occupy 24kb, as it has to be a multiple of 4kb
- and 3kb will be redundance
❓ When you predesign a harddisk, what should I choose? small cluster or big?
- small cluster size:
- files can be small, will not occupy a lot
- 👍🏻 you can store many files
- 👎🏻 but the files will be not very protected, not very safe
🛠️ for normal standard ppl who wants many files in one disk
- big cluster size:
- file sizes will be big
- 👎🏻 will not be able to save so many files
- 👍🏻 files will be very protected, lots of redundance
🛠️ for servers, for companies who need protection
- ❓ I do not know for what I will use this harddisk
- use standard
- use default for harddisk
- when I do not know the use of my disk
✔️ How to change cluster size
- you can choose the cluster size when you format the disk
- need to format the disk
- make sure to backup the disk
- right click(contextual)
- click on: format the disk
- choose dropdown
tamaño de unidades asignacion = cluster size - you can also choose harddisk format(NTFS, exFAT…)here
✔️ DEFRAG tool
- Due to clusters and redundancies, your HD will have several many holes
- what would happen all the extras are moved to the end of the disk
- and create a huge big extra at the end of the disk
- you can clean it and use it for extra files
that can free up more space
- DEFRAG tool: to collect all the holes and make a big space
- it improves the capacity of the disk
- you can use DEFRAG tool when your harddisk seems out of space
✔️ Patition
- set of many many clusters
even if you continue on the next plate
- If we go on with the cluster
we change sides, and to another plate, we create a partition
- Partitions are portion of a harddisk
- harddisk are connected with SATA
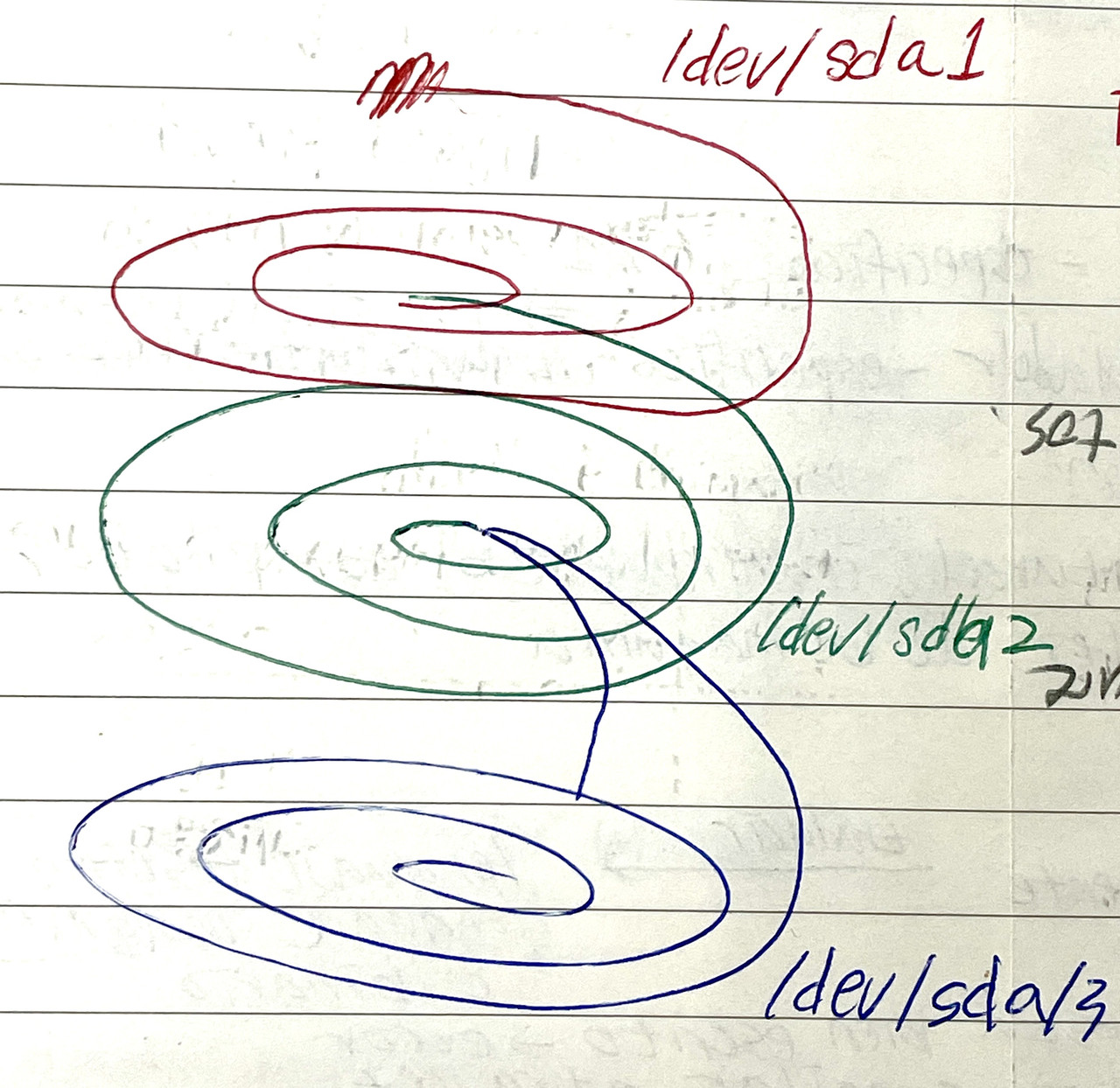
✔️ Partitions have a name
/dev/sd
alphabet/number
- disk: devices, called
/dev/sd/ - connected by SATA
dev: devicesd: SATA Drive, harddisks are connected to the motherboard using SATA wire- letter: order of the disk(first/second/third…)
A: internalB, C, D: external
- so,
/dev/sda: first internal secondary memory in my computer /dev/sdb/: second disk in my computer, could be internal or external/dev/sbc: third disk in my computer- then a number indicating partition of the disk
/dev/sdb/1: first partition of the second disk/dev/sba/3: third partition of the first diskThe booting unit does not count as a partition
- if there is an error in
/dev/sdd3: it means in my computer I have at least three disks, and the third portion is failing. - This does not mean my computer will fail, it just means my fourth fisk, an external disk is failing, but my internal disk is safe
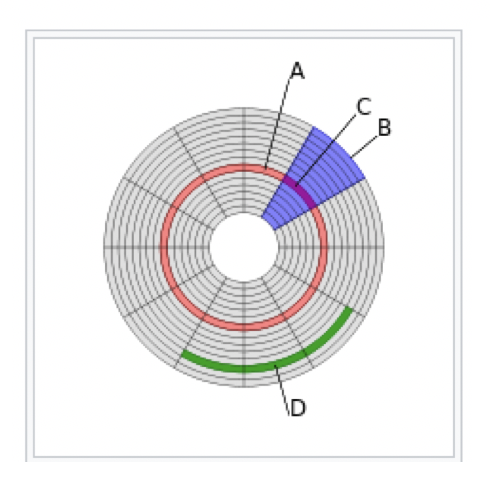
⭐️ Exam Question
- A: cylinder, track
- B: sector
- C: unit, intersector and and track, unit 0 is the most important!
- D: cluster
- partition: several clusters(not on picture, but partition is several clusters)
✅ Capacity of a disk
- Capacity of a disk is total number of sides in a disk
unit is H(
header)- If I have 4 plates, I have 8 sides
- I have 8 heads
so
number of sides = number of heads- Capacity of a disk
- multiply number of heads
- multiply number of sectors(triangles 🔺)
- multiply number of tracks(circles 🔴)
capacity of each unit
- 👉🏻 Capacity of a disk
H * S * T * U
✅ Partition table
- If I want to go to the very last partition,
- can I jump? YES ⭕️
or do I have to roll down all the partition? NO ❌
- In disk, there is an index of partitions
- It is called the Partition table
- this table is located inside the harddisk
- It is also inside the Unit 0 of the harddisk
✔️ What is inside the partition table?
- name of the partition
/dev/sda1,/dev/sda2 - beginning of the partition
plate 0, side 0, sector 1, track 10 - end of the partition
plate 0, side 1, sector 10, track 10
✅ What happens if I break/damange my unit 0?
- you lose the index ⭕️
you do not lose the information stored in the HD ❌
- Can I still recover the data?
- If there is a way of restoring the index, you can restore your disk 👍🏻
- If you cannot restore the index, the HD will just be a huge 0s and 1s,
- we do not know where things start and end
✅ Type of partition
- there are four
- and three more optional, more specific types
1️⃣ Primary Partition
- store the OS
- OS that I want to boot/ use
- If there is an OS that you want to use, you need to store it in the primary partition
- 🆚 If there is an OS that you want to test, save it in the logical patition
2️⃣ Active Partition
- chosen OS
- partition that you choose to use
- the partition that contains the chosen OS
- when Jose gives class, he uses windows active partition
when Guadalupe gives class, she uses linux active partition
- bc one header can read at once
- so only one active partition
3️⃣ Logic Partition
- used for (1) storing data
- and (2) OS for demo(for testing) mode
4️⃣ Extended Partition
- set/group/conjunto of logical partitions
- several logical partitions gathered together
used for organizing logical partitions purpose
- also called umbrella
like an umbrella that embraces the logic partitions
- in a disk, there can be only one extended partition, with several many logical partitions
✔️ Distribution of partition is always symbolized with a formula
number of primary + if use extended + num of logical
2P + E(3L)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
In my computer I want...
Windows 10, bootable(useable), kernel of the OS
Ubuntu 24, bootable(kernel)
Mac OS, just for testing
Data of the windows OS separated from the OS system, in a different partition
Data of Ubuntu OS separate from OS
Which type of partition should I give to Windows 10?
- primary partition, I want to use it
Which type of partition should I give to Ubuntu?
- primary partition, bc I want to use it
Which type of partition should I give to Mac OS?
- logic partition, just for testing
Which type of partition should I give to data windows?
- logical partition
Which type of partition should I give to Ubuntu data?
- logical partition
- and create an extended partition for three logic paritions
👉🏻 2P + E(3L)
- ✔️ Furthermore, there are three special types of partitions
5️⃣ Reserved Partition
- partition used for factory settings
when you want to make the computer to factory settings, use this partition
- not obligatory ❌
- optional ⭕️
6️⃣ Recovery Partition
- storing recovery points
- like taking snapshots
- Recovery point: situation of the computer that you want to remeber
all recovery points are stored in recovery partition
- not obligatory ❌
- optional ⭕️
7️⃣ Booting Partition
- NOT Unit 0 ❌
- partition for storing the menu that helps you to choose
which partition who want to activate
- Bootstrap loader: the technical name of the menu
so the booting parition saves the bootstrap loader
- not obligatory ❌
- optional ⭕️
💡 Unallocated space
- Final partition that you leave at the end, you leave it for future use
- If there is a partition that I do not use the use for
- recommended to have it
✅ Format of the partition
which use you are going to give to the partition
- format is the same as file system
1️⃣ NTFS
- when using partition for windows
2️⃣ ext2, 3, 4
- when using partition for Linux
3️⃣ FAT 32
- for files less than or equal to 4GB
4️⃣ exFAT
- files bigger than 4GB
5️⃣ HFS, Hierarchical FS
- Mac, IOS
6️⃣ F2FS
- Flash Friendly
- Android
👉🏻 When we design a disk, we need to decide type and format of partition
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
In my computer I want...
Windows 10, bootable(useable), kernel of the OS
Ubuntu 24, bootable(kernel)
Mac OS, just for testing
Data of the windows OS separated from the OS system, in a different partition
Data of Ubuntu OS separate from OS
1.
Which type of partition should I give to Windows 10?
- primary partition, I want to use it
Which format should I give to windows 10?
- NTFS
2.
Which type of partition should I give to Ubuntu?
- primary partition, bc I want to use it
Which format should I give to Ubuntu, which is a type of Linux?
- ext2, 3, 4...
3.
Which type of partition should I give to Mac OS?
- logic partition, just for testing
Which format should I give to Mac OS?
- HFS
4.
Which type of partition should I give to data windows?
- logical partition
Which format should I give to data windows?
- NTFS
5.
Which type of partition should I give to Ubuntu data?
- logical partition
- and create an extended partition for three logic paritions
Which format should I give to Ubuntu data?
- ext2, 3, 4...
👉🏻 2P + E(3L)
👉🏻 When we design a disk, we need to decide type and format of partition
❓ Is it a good idea to have data and OS in different partitions?
- If OS and data were in a same partition
- and I want to update to Windows 11,
- then you lose the data!
- 👎🏻 If we put kernel and data in the same partition, it is all mixed
if you change the OS, you lose the data
- So, we keep them separate
- as we can change the system without losing the data
✔️ Version hopping, Distro hopping
- Version hopping: putting OS and data separate in Windows
- Distro hopping: putting OS and data separate in Linux
- change the OS without losing the data
✅ Tunnel/Channel of communication
- If I store data in a logical partition in one certain format, like
NTFS - that file will not be reachable by the other OS system that has
linux UNLESS you create a common channel/tunnel for the both OS systems
- 1️⃣ If I want to create a communication channel
lin-winfor documents of 3GB - logical partition, as it is for data
- all logical partitions are inside the umbrella
- logical partition out of the umbrella will be dangerous!
umbrella will have to extend to also include this communication channel
format will be FAT32, as common for linux and windows, and less than 4GB
- 2️⃣ Create another communication channel
lin-winfor Virtual Machines, that has 30GB - type of partition should be logical, as it is data
- virtual machines, even if they contain OS, they are considered data
- inside the umbrella
need to extend the umbrella a bit more
- format will be exFAT, as it is for both linux, windows
- and more than 4GB
- 👉🏻 together with the previous exmaple, it would be 2P + E(5L)
❓ Can I create a partition without a format?, Unallocated parition
- I can create it, but it will not be useable
- You can have it for future use
- for extra space for future partitions
- as we do not know the use yet, we leave it without format
- Unallocated parition: partition without format
✔️ Volume
- volume: set of partitions with the same format
- several partitions with the same format
- example: in the example above, there are several NTFS
- they all together
1, 4create avolume NTFS several ext
2, 5createvolume ext- ❓ If I format a volume, is it the same as formatting a partition?
- No, if we format partition 3, we are just losing the data
- If we format the volume NTFS, we are also losing the OS and the data
- also destroy data and kernel
⚠️ If you format the volumne, you will format all the partitions of the same format
- ❓ If windows OS is formatted, but the logical partition with data is still there,
- you can access the data if you pass it through the communication tunnel
- and read it
✔️ Tunneling
- when we create tunnels for communication among different OS
✅ Let ISO in Nextmode?
- Which is the typical situation for systems if we let
isoinNext Mode? - If the technician does not control the disk, just let
isodo what it wants
✅ How to check my partition in my computer
✔️ In windows
- to check how is my partition in my computer
- you can see this with command
Win+R>diskmgmt.msc it creates three partitions
(1) one NTFS partition: named letter C
- inside we have
booting+kernel+SWAP(helper for RAM, in linux its calledPaging file) - booting not separate ❌
- It is named
Cbecause in the first windows,A, Bwas taken for disket unit - although now we do not have external diskets, it uses
C
- inside we have
(2) reserve partition
- saves factory settings for windows
- (3) recovery partition
- saves recovery points
👉🏻 Windows take all the disk for itself, partioning in 3
- point 1: one for saving myself, going back to factory setting and recovering myself
- point 2: no verison hopping ❌
- but it will let update from Windows 10 to 11, as it makes backup on the internet
- windows 11 makes you be connected to internet while you update to windows 11, and take your data to the cloud, and brings your data back
- so ppl can change their OS without losing the data
- point 3: no tunneling ❌
- point 4: booting is not in its own parition, it is mixed with other data
- If windows its not perfect, it will not boot at all(blue screen)
- as in windows, system and booting is mixed, if there is a problem in the system, you cannot even boot
- 🆚 this is a difference between linux and windows
✔️ In Linux
- Linux is very adaptative
- But if you let linux do whatever it wants to(
Next mode), it will take the whole HD as well you can see this with command
sudo fdisk-lfdisk: show format of the disk-l: long information, read me all the detailssudo: super user do, you have to be an administrator permission
linux will create two partitions
(1) partition for booting
- separate partition for booting
- 👍🏻 as linux has boot separate from the system, it can always boot
- it can also boot with errors in the system
- so you can boot, and fix the errors in the system
- 👍🏻 Linux always!!! boot
- (2) all the rest
👉🏻 Linux also takes all for itself
- point 1: no tunneling ❌
- point 2: no partition for data, no distro hopping ❌
- If we do not have hopping, we are trapped in the systems, as we do not want to lose the data
✅ Predesign the disk
- If the technician designs the copmmuter
- do not let iso do whatever it wants, the technician becomes the boss and controls the disk
✔️ Perfect partition with both Windows and Linux
should have 7 partitions
- (1) Windows C partition: for windows kernel + windows booting + windows SWAP
(2) Windows D partition: for windows data, NFTS ➡️ version hopping
- other five partitions: for linux partitions
- they are visible, you can see it exists, but not understandable by windows
- (3) Linux root: one partition of the kernel, the OS of Linux, as Linux is a tree
- (4) Linux /boot: for booting Linux, it is kept separate so we can boot even with errors in the system. Linux always boots!
- (5) Linux /home: partition for data, home for data ➡️ distro hopping
- (6) Linux SWAP: if SWAP is mixed in the system, if there is a problem in the system, SWAP will also have problems. Thus, Linux separates SWAP.
- (7) Linux /boot/efi: for extras needed in booting if BIOS is UEFI booting
- without /boot/efi, you cannot use extras
- this partition is created automatically when the booting has UEFI
👍🏻 with this 7 parititions: flexible, adapative, can change system without losing data
- version hopping ⭕️: separating data from booting
- tunneling ❌ : tunneling is only made when the disk is big
for tunneling, you need more or less
1TB- Only 5% of computers in companies have this structure
- Companies are very outdated
✔️ (Review) Two types of BIOS
- legacy: very simple basic booting, rest of work is yours, easier
- UEFI: controls the systems interactively, more complicated, more extras
- booting with UEFI need extras
📌 In SSD
- SSD do not have plates
SSD have pages
- like a book with pages
- SSD has two sides per page
- has a grid with transistors that it places it
0 and 1 store data in transistor
- cluster in SSD: portion of a page, minimum size of a file
- partition: set of clusters in several pages
Unit 0: tiny portion of the first page
- Rule of SSD: you cannot start a partition at the end of a page
even if there is space left in the end of the previous page, you have to start in the next page
- 👎🏻 SSD has two problems:
- 👎🏻 losing space, so solid states are very fragmented
👎🏻 loss of information bc of loss of elasticity, some day information will be lost
- as SSD is fragmented, there are many portions between partitions
- that portion between partition does not belong to any partition
- those fragments are not protected, as neither Window or Linux will protect it
- The zombie cookies love the unprotected proportions
👎🏻 create unsafe space in SSD
- 💊 we should give to the partition a very specific size
- in order to avoid fragments
- If cluster size is
4KB, the perfect cluster size would be a multiple of the cluster size and a multiple of the page - calculate the common and non common factors to the maximum power
- if cluster size is
4KB, page size is30KB, partition size should be60KB