3.6 OS Managers and HW visualizations
Extra things to check
- we can see things hidden by transparancy levels
📌 Memory Manager
- to check paging, segmenatation
1️⃣ How to check memory manager 1: task manager
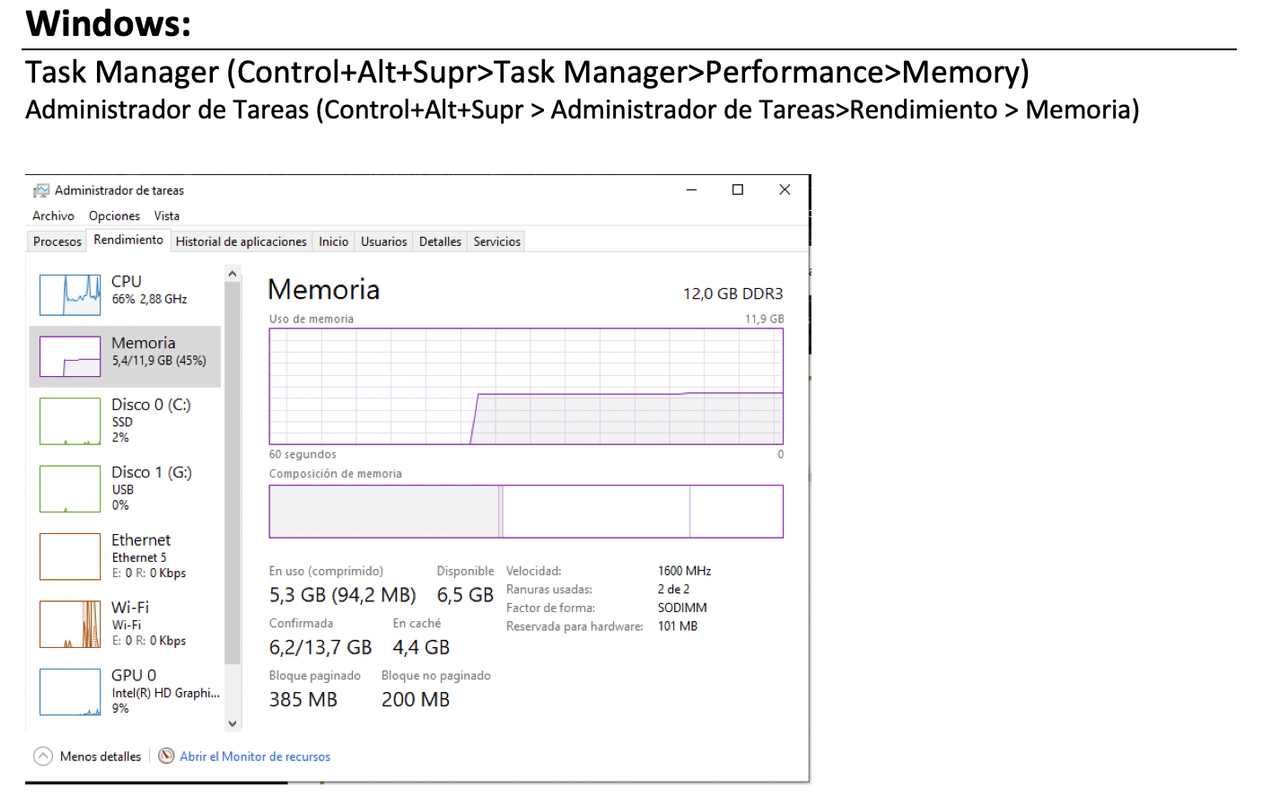
- Use task manager
1
Ctr+Alt+Supr>Administrador tareas > performance(rendimiento label) > memory
✔️ In task manager you will find the following things
- top right corner: capacity in RAM
paged block: how much of RAM is using pagingnon-paged block: how much RAM is using segmentationspeed: not frequency of access- means speed taking into account the delays
slots used/ranuras usadas: if you can add more cards or notreservada para hardware: size of the OS in RAMcache: size of the disk cache, free portion of the RAM used for frequent applications, helps the harddisk
2️⃣ Another way of checking memory manager: resmon
- use test resmon
windows+R+resmon- resmon: resources monitor
✔️ In resmon you will find the following things
- name of the process
PID- how many errors the process had
- how much the process occupies the RAM(different occupations of the process in the RAM)
✔️ In the important errors window
- errores grave
- in the right down corner
you will the see IPCs in the kernel, due to the processes in the RAM
- if there is a peak in the IPCs window
- and the peak disapeears,
it means the kernel solved the problem
- If you see a lot of IPCs, a lot of peaks
- 💊 save what you have been working on, and reboot your copmuter
- so you can clean your computer
📌 Process manager visualization
Dispatcher
- use task manager
☑️ process label
- we can see the list of all the processes
- we can see both
user processs+internal processes(deamons/services)
✔️ for each of the processes we can see the the following
- percent of CPU used
- percent of RAM used
- percent of secondary memory used
- percent of network used
- percent of CPU used
- percent of energy used
✔️ Kill and SIGKILL
- If we choose a process and click on
end task/finalizar tareawe can kill a process - this is killing a process with a command
KILL - however, this is different from killing a process with
KILL-SIGKILL - command
KILLwill end a process, but the processes will leave traces - so you can maybe later check
- whereas,
KILL-SIGKILLwill kill the process without leaving any traces
✔️ Forensic Analysis
- so when a system expert looks for traces
- for rebringing, restarting processes,
- he is doing Forensic Analysis
☑️ Details
- name of process
- PID
- state of process
- CPU/ RAM consumption
- name of the user
- if it is using Virtual Memory or not
1
2
3
choose the details screenshot
and for the process with the smallest PID
tell me the state and if it is using the VM or not
☑️ services label
- we only see deamons
we do not see user services
- deamon(process) name
- PID
- description
- state of the deamon
- group of the deamon
✅ to check processes command
Windows+R> cmd > tasklist- tasklist shows
- both
internal/deamons+ user services - process name
- PID
- memory use
1
2
use tasklist
What is the smallest PID, and what is its RAM usage?
📌 Interruptions and input, output management/Peripheral,Device management
DMA, PIO, drivers…
- use Device manager(administrador de dispositivos)
✔️ how to access device manager
search/buscar > Administrador de dispositivos- when you open
Administrador de dispositivos, you always get a error message - bc os hides info from peripherals
✔️ what we can see in device manager
- for every peripheral, show what driver that the peripheral is using
✔️ How to check if device is having problem
- if there is no exclamation sign it is perfectly working
- however, if there is an excalamation sign, the driver is corrupted
💊 you should update the driver
- you can also see the properties of the driver
- brand, model, date of driver, driver of the peripheral…
✔️ How to update
- to update, right click on the peripheral
- If you see an exclamation mark, but there is no update option, it means you cannot update it.
- that is most probably because, that component exisited,
- but it does not exist anymore!
✅ Open device manager by terminal 1
- How to open the device manager
Win+R > devmgmt.msc
1
2
3
all the command that starts with dev: related to devices
mgmt: shortcut for management, all commands for administration, management
.msc: microsoft corporation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❓ Sohee's computer cannot connect to WIFI.
Please check if she has any driver problems.
How can she check if she has any driver problem, and how can she fix it?
- open device manager
- find smth that has to do with wireless,
- and if it has a !, update
✅ Open device manager by terminal 2
- Also
Win+R > cmd > driverquery(list of active windows drivers) - some commands need an intermediary step,
cmd, to keep the window open
✔️ What can we see in the driverquery
- 1️⃣ Type of driver
- There are two types of driver
- if the type of driver is
kernel, it is from the core, from windows, by default - if the type is
file system, optional it means an updateable, modificable driver(not official, so you can change)
- 2️⃣ linking/link date(fecha de vinculo)
- date in which the component was fixed/installed in the system
- manufacture date of the component
- even if the installation is later
- 👀 If the link date is 2015, it does not mean this driver was installed in 2015
- it means it was build in 2015.
📌 Disk Management
- Disks
- Paritions
- disk system(NTFS, FAT32…)
- accessible or not…
✅ Use disk manager
use administrador de discos
- using search to open diskmanager is not a good idea
- as search depends on the windows version, it is not fixed
so command is better, it will always work
Windows + R > diskmgmt.msc- however, it will not work as you need administrator permission
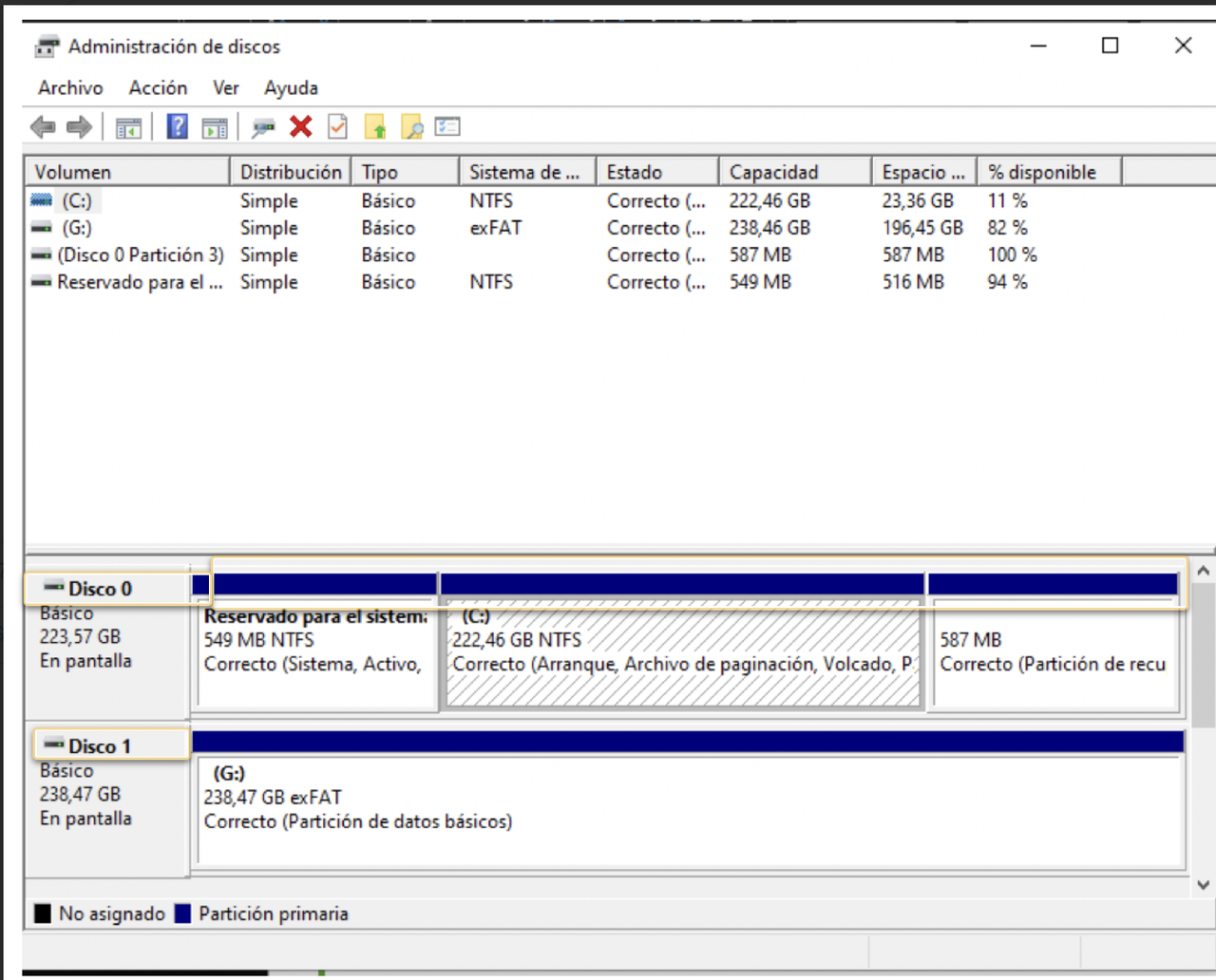
✔️ What can you see in disk manager
- disk 0: internal disk you have in your computer
- disk 1, 2, 3…: external disks, your USBs
disk 1, 2, 3…could be internal, but normally external
- fragments: three blue bloxes
- so in disk0, it is fragmented into three parts
in disk 1, it has a long blue box, so it is not partitioned
- size and type of partitions
first box: 549MB, NTFS, so it has windows partitions!
- On the top, last two columns
- you can see the free space
- how much free space you have on your disk, and the percentage
1
2
3
4
5
❓ Can you tell me if you can use VM of 30GB on my USB?
- YES, your USB uses exFAT
- also, the available space is 196GB
✔️ Before installing anythings check two things
- your disk format(exFAT)
- available free space(196GB)
1
2
3
4
5
❓ Can I break partition C and intall two windows?
Each windows is 50GB
- yes, format is NTFS
- and the capacity is 222GB
💡 In mobile…
- In mobile technologies in
x86, as RISC(Reduced) - In mobile technologies in
x86-64, as ARM(Advanced)