3.5 Complete diagnosis of a system with CPU-Z
✅ Transparancy levels
- CPU-Z always shows a warning that it might have transparancy levels
- transparancy levels: i will show you everything except the things limited by the manufacturer
- how much it can show/or not
- If you have a high transparancy level, you cannot see many things from the manufacturer
The manufacturer can hide some things they do not want you to see
- 👀 HP has a high transparancy levels
- application HP Sure Sense lets you deactivate the transparancy level settings, and you can see
✅ CPU-Z
- CPU-Z: to check specific things for your computer
- there are 6 labels
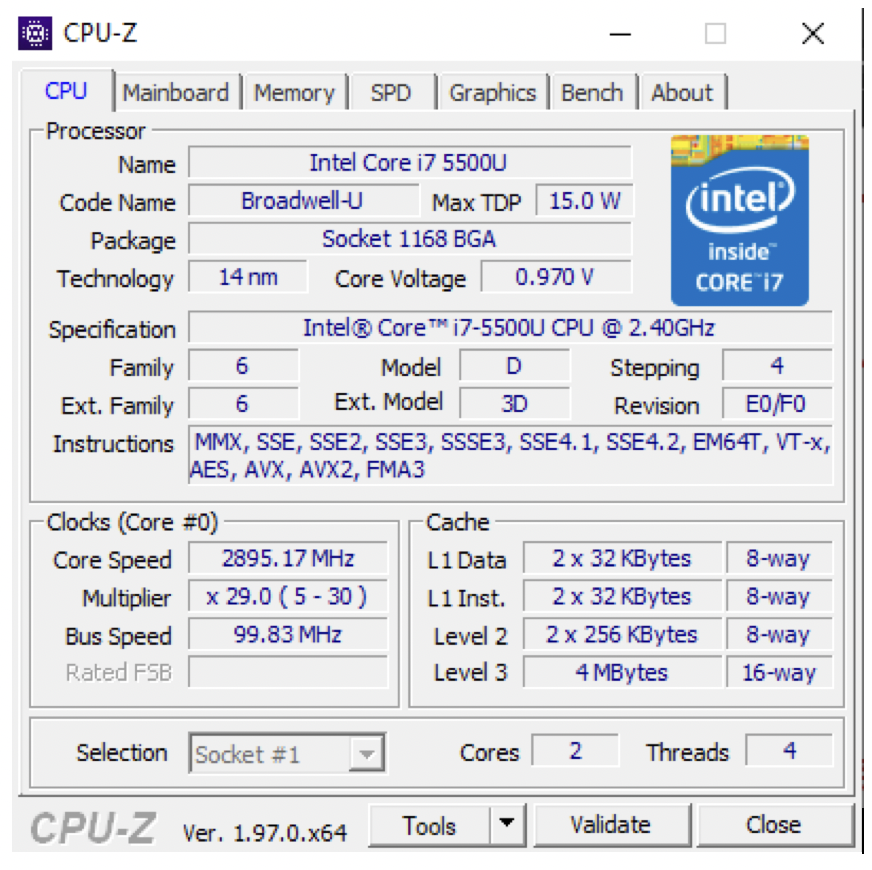
1️⃣ Label CPU
- ✔️
name: model/name of your microprocessor ✔️
code name: family to which the processor belongs- ✔️
package: if your socket is LGA or PGA or BGA(microprocessor has balls, not pins nor holes) or IFP(Integrated Form Platform, CPU is integrated on the motherboard, so you cannot take it out) if you do not see anything, grayish, means transparancy level
- ✔️
Technology: distance between transistors in nano meters - nano meter: (nm, 9 decimals,
14nm = 0.000000014nm, in total 9 digits) - if technology is small it means transistors are very close to each other ➡️ high temperature, faster communications, high speed
- so if technology is a small number, need better refrigeration, but faster
technology ⬇️ faster ⬆️
- ✔️
Max TDP: Thermal Design Power - number of watts that your computer can dissipate/resists
maximum capability of resisting the heat
- if Max TDP is 15.0w, it means your computer can get as warm as a bulb that has 15w
- if Max TDP is small, it means the computer does not dissipate/resists very well, your computer gets very hot
- if Max TDP is big, it means you are dissipating very well, your computer will not get hot
1
2
3
4
5
6
❓ If Max TDP was 20, instead of 15, how would your computer be?
👉🏻 better, it resists more, dissipates more
❓ If you want to bring your computer to the beach?
👉🏻 bring the one with bigger TDP
- ✔️
Core Voltage: maximum level of volts considered 0, resistance to peaks - 0 is
0.5vand 1 is5.0v - up to which level(bolts) it is stilla a 0
- so in the picture, until 0.970v, the computer would consider it a 0
- 👍🏻 if Core Voltage is high, the computer is more resistant to peaks in the electric systems
if Core Voltage is low, the computer can lose information in the case of a peak of electricity
✔️
Specification: the speed of the clock or generation of the micro processor(CPU)
- the higher the generation, the most modern manufacturing process
- if the number at the end, if it appears, with
GHz, it tells you the clock speed 2Gmeans 2 thousand million instructions in a second- ✔️
Instructions: ISA, Instrucion Set Architecture
- instructions that come by default with the CPU
- if you see 64 anywhere, your architecture is
x64 - if you do not see any 64, your architecture is
x86 an alternative for checking motherboard architecture, alternative for
msinfo32,systeminfo- If you have an
Intel + VT-xyour computer can use virtualization from manufacturing - you can use virtual machine just by factory settings
- however, if you do not
VT-x, virtualization needs to be activated in the BIOS - 👍🏻 activating in the BIOS is more secure,
than being activated by the factory setting
If your processor is
AMD, the instruction for virtualization will beAMDV- ✔️
Core speed: similar to the clock speed - if you do not see the clock speed in the specification, you can see it in core speed
- it keeps changing, bc its the real speed of the clock at this moment
the pace that the computer is following at that moment
- ✔️
Bus speed: speed of the front side bus higher the faster
- ✔️
Cache: how many cache you have and the capacity - multiplier means the number of cores
2 x 32KBmeans there are two cores- L3 is shared among cores, so there is only one
if you want to see how many cores you have, you can see here
- ✔️
cores: how many real physical cores I have in my CPU - if you have
4p + 4ethis meansp: real cores,e: efficiency cores your computer is so fast, that although you have 4 cores, it is acts like an 8 core
- ✔️
Threads: how many logical cores, how many thread in total I have
1
2
3
❓ Cores = 2, in total I have threads = 8, how many threads per core do I have?
👉🏻 4 thread per core
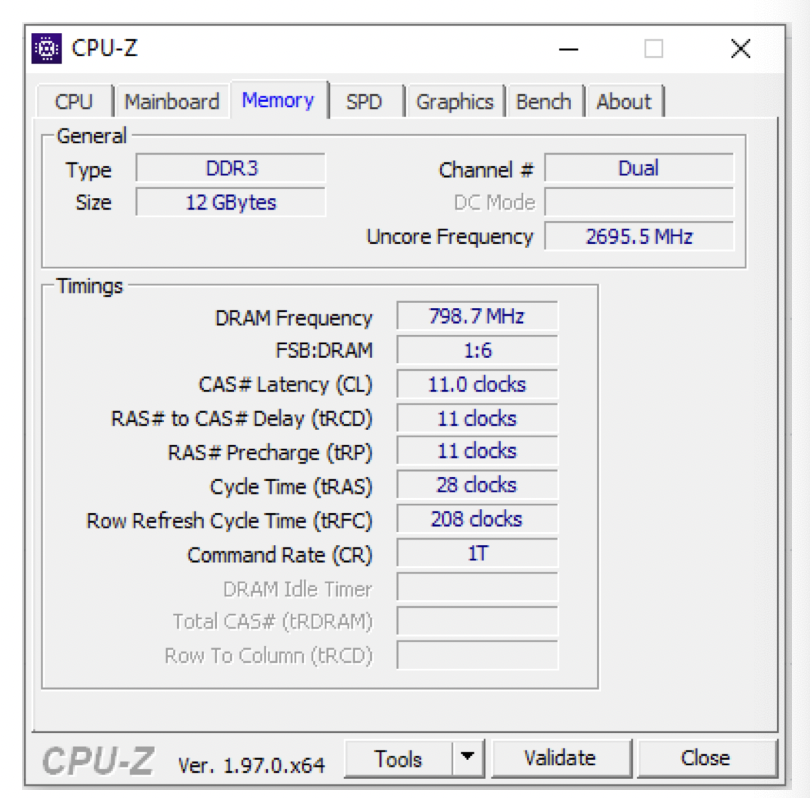
2️⃣ Label Memory
- information about the RAM
- ✔️
Type: Type of SD RAM(Synchronized Dynamic) - SD RAM has the same speed as the clock
- DDR1 means
2 to the power of one, 2times of read and write at the same time - DDR2 means
2 to the power of two, 4times of read and write at the same time DDR3 means
3 to the power of three, 8times of read and write at the same time✔️
Capacity: size of the RAM- ✔️
Channel: dual/triple/quadraple channel - dual: two sets of two slots of RAM, up to 4 RAM
- triple: three sets of two slots, up to 6 RAM
quadraple: four sets of two slots, up to 8 RAM
2*32bmeans you have 2 slots, and 4GB of RAM each, so you can have up to 8GBthis means you have only single channel, only two slots, no set
- ✔️
DRAM Frequency: how many times per second you can access your RAM if 798.7MHz, means you can access the RAM 798 million times per second
- Important to have a combo of type and DRAM frequency
1
2
In the photo per second,
you can access the RAM 798 million times and can do 8 read/write
- ✔️
Latency: waiting time since you accessed the RAM, until you get the information - waiting time from access to getting the info
- latency ⬇️ less delay
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❓ Frequency = 800MHz
Type = DDR4
Latency = 11.o clocks
I can access my RAM 800 milllion times in a second
in every access, I can get 16 informations
But I have to wait 11 clocks until the results come out