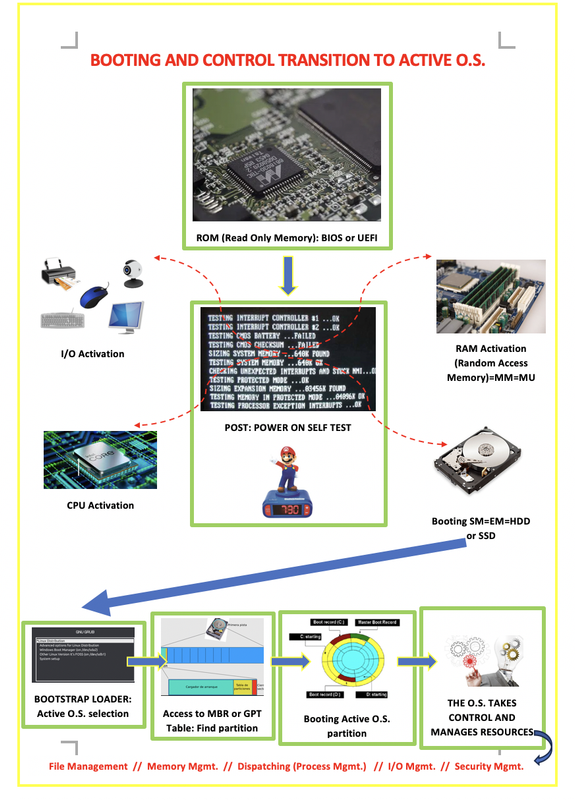
3.13 Booting and Transition to Active OS
- ⭐️ Name of process: POST
⭐️ Peripherals wake up before the HD
- 3-2: picture of
msinfo32questions about the architecture - 3-3: can you have 64bit OS on x86? NO
- 3-4: minimum and recommended, if you have multitasking OS, does it make sense with one core, one thread? NO.
- 3-5: not in exam!!!!
- 3-6: CPU-Z memorize the portions
- 3-7: which is the name of the application that you want to create a bootable USB for microsoft? which is the name of the application that you want to do unattended install for windows?
- 3-8: diff portions of a disk, sector, cluter, type of partitions, format of partitions, concept of volume, SSD is not on exam
- look at disk manager and questions about partitions
- can you reach partition D? Depends on your BIOS, bc with legacy, you can reach only the first four partitions
- 3-9: diff about MBR, GPT
- 3-10: diff of Legacy and UEFI
- concept about boot sequence, HD comes first, then network then external
- 3-11: compatibility, if you have windows numbers or vista…
- 3-12: tunneling, dual booting
- 3-13: order of POST: first CPU, then RAM, then HD…
1️⃣ BIOS
- recieves electricity with
ATX-P1 ATX-P1is the cable that provides electricity to the motherboard- BIOS has a firmware printed
2️⃣ POST
- Power On Self Test
- process launched by the BIOS
process for saying
"computer! wake up!"- when the firmware on the BIOS is executed, starts the POST process
- the POST is not saved on the RAM ❌
process that starts when the BIOS starts
- ➡️ POST wakes up the computer
✔️ The order that POST wakes up the computer
- (1) CPU: first wake up the brain
- (2) RAM: second wake up the body
- if the RAM is incorrect, there will be
three long beeps
- if the RAM is incorrect, there will be
- (3) Peripherals: to show error messages
(4) Harddisk
- Inside the harddisk, again there are orders
(5) Bootstrap loader, GRUB, the menus: these are not related to the partitions ❌
- (6) Index:
- if you are in MBR, MBR table
- if you are in GPT, MBR protective(the 4 first Primary, this is very important for legacy)
- But if you are using UEFI, you will not use MBR protective
- if you have an error in the index, this is also not related to the partitions ❌
- (7) Big index:
- the GPT partitions table for GPT
- if there is an error in index, you will have another
index error 2
- (8) the active partition and (9) the booting partition of the selected partition boots
- only the selected partition boots
- not all the partitions boot
- also, including the booting partition of the selected partition
- if there is an error in booting windows, do not reformat
:c,/ - but reformat the
/bootorEFI - if there is an error is in the kernel
:cor/ - then reformat the kernel
- (10) When everything is ok….
- 💡 Note 1:
- GRUB errors are not related to partitions
- GRUB errors mean
rebuild the menu - so, when you see a GRUB error, do not format your HD!
- 💡 Note 2:
- Index errors are also not related to partitions
- so, do not format, do not change structure of the partitions
- 💡 Note 3:
- if there is an error in booting windows, do not reformat
:cor/ - but reformat the
/bootorEFI - 💡 Note 4:
- if there is an error is in the kernel
:cor/ - then reformat the kernel
3️⃣ When everything is OK, OS starts to boot….
- (1) Dispatcher
- manages FIFO, RR…
- (2) Memory manager
- segmentation, paging…
- (3) Interruptions manager
- interruptions in the RAM
- (4) Tools for manaing the HD
- the DEFRAG tool
✅ Use GPartEd
- use GPartEd to create partitions
1️⃣ Download GPartEd
- stable versions are for normal users, compatible for all architectures
👎🏻 however, might not be complete, very general
- as a systems expert, use the specific version for the architecture you have
- you can check the architecture of your computer with
msinfo32 - and you download the version according to it
- if you have
x64, download theamd64.iso amd64means that the version is optimized foramdmicro processors, but compatible withintel- but
i686might be optimized forintel, but not compatible withamd
2️⃣ Create a bootable USB
- now you have
gparted.isoin your downloads folder - you have two choices
- 1️⃣ if you have a real computer: create a bootable USB
2️⃣ if you have a VM: add the
.isoto the VM- 1️⃣ create a bootable USB: if you have a real computer
- to make a bootable USB, you cannot use the normal tools like
Rufus, UUI, Lili, Mediacreation, Ventoy you should use specific tool
Real GPartEd USB creator- 2️⃣ add the
.isoto the VM
✅ Rufus, UUI, Mediacreation, Ventoy
- Rufus is widely used
- UUI2 works very stable
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.