2.9 Input/Output and general interruptions management
tipo test questions
⭐️ service routine, vector table, program counter
💡 Peripherals interrupt when they have problems
and more situations that interrupt…
👀 Example of interruptions
- mouse that runs out of battery
- mouse/keyboard that lost connection with bluetooth
- keyboard that one key is broken
- printer is out of paper
- Ventilator is broken, temperature is rising
- try to divide by 0
blue screen bc of an internal problem
- 🛑 If an interruption occurs,
- stop everything
and pay attention, solve the interruption immediately
⚠️ Algorithms are interrupted when there is an interruption
- 💊 There are two techniques to solve the interruptions
PIOorDMA - 💊 There is one technique to prevent interruption,
Polling
✅ PIO
Processed Input Output
- There is an interruption in the middle of executing a process
- If you are in the middle of a process
- and there is an interrption
- 1️⃣ need to stop the process
- 2️⃣ solve the interruption
- 3️⃣ and go back to the same spot of the process
✔️ Service routine
- 💊 each interruption has a different solution to solve
💊 each interruption needs a different mini program to be solved
- Service routine: mini program to solve the interruption
- there is one service routine for possible interruption
no paper in printer->show error message "no paper"computer temperature so hot!->turn the fan on
✔️ Area of Service Routines
- Service routines are on the RAM
- Service routine should be loaded on the
RAM - several Service routines are saved at the end of the RAM
- called Area of Service Routines
this means that from the RAM, we are using a small portion for the service routines
- 👎🏻 We are reducing the RAM very much, for storing the service routines
- so if you buy a
16GB RAM, actually you can only use14GB - as you use some for
OSRAMandservice routines
✔️ You need to prepare the RAM for the service routines
- As the service routines are in the RAM, when we turn the computer off, we delete them from the RAM
- when we switch the computer on, we have to upload the service routines again to the RAM
when we switch the computer on, and the RAM is not properly connected, the service routines cannot be loaded, causing an error. The computer will not boot. It will make long beeps.
- 🚨 Service routines are important, as computer should be ready for interruptions from
second 0
✔️ Jump to the service you need
- All the service routines are together, one after the other
- however, it makes no sence to run all of them one by one
- Jump to the service routine you need, and exectute only the routine you need
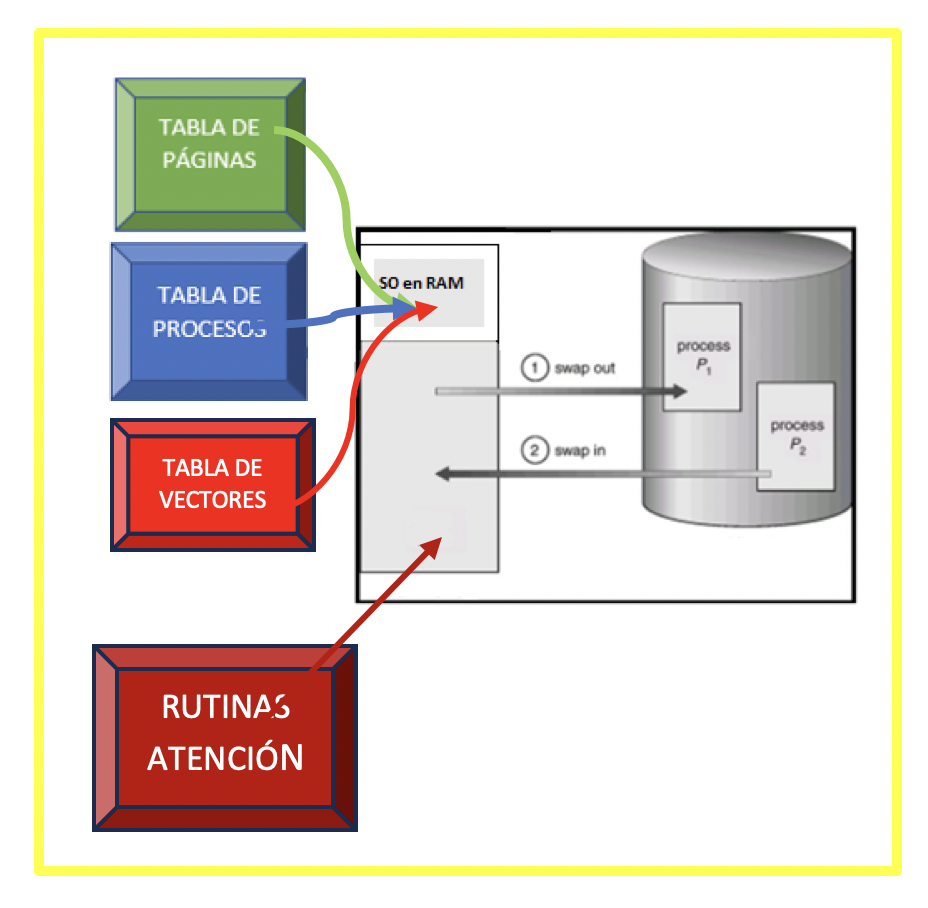
✔️ Vectors table
- In order to jump to that service routine,
- you need a vector table that acts as an index
- indicating the beginning the service routine for each of the interruptions
- tells you where to go if one interruption occurs
- you can go there, and run the service routine
- 👀
mouse interruptions->FA23h - 👀
keyboard interruptions->FB123h - 👀
temperature interruptions->FF213h - This table is loaded in the
OSRAM, along with theprocess tableandpages table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PRocess table
Vector table
pages table
are all the in the OSRAM,
so the RAM is getting smaller!
also service routines have to be saved in the bottom of the RAM
making the RAM smaller
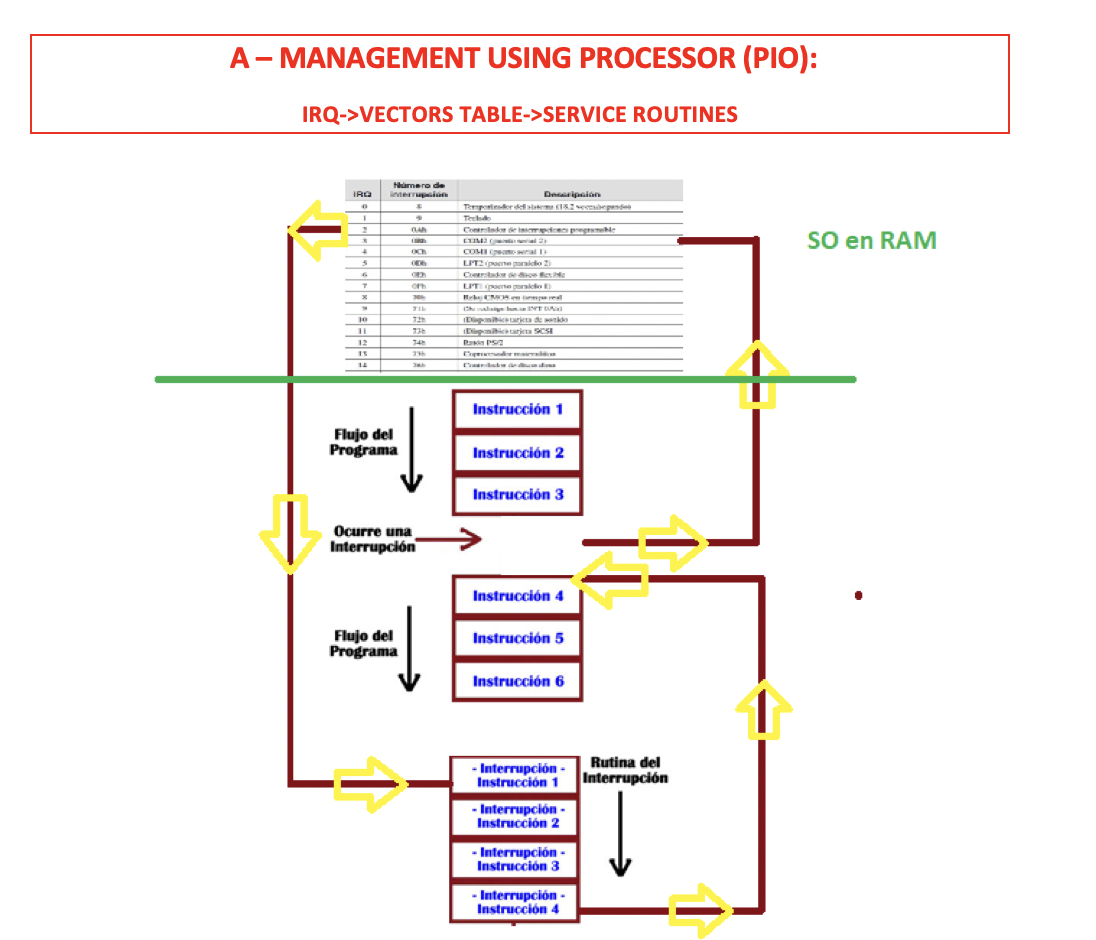
✔️ Tecnique 8
- Due to the location of the vectors table
- when there is an interruption
- go to the
OSRAM - check the
vectors table - find the location of the
service routine - go down to the location of the
service routine - then go back to where you were running
- This is called the tecnique of the number 8
- bc the shape that yellow arrows make looks like a 8
✔️ Program Counter
- program counter is the element that sends you up and down the RAM
- PC is inside the CPU, the micro processor
- that is why this technique is called process input/output
- this technique overloads/uses/warm up the processor
- Processor is involved in this technique
✔️ IRQ: Interruptions Request
Interruptions Request: official name of interruption in PIO- Each interruption is called IRQ
- Each IRQ has a
codeto indicate what problem you are having - 👀
printer is out of paper➡️code OOP - 👀
printer is out of ink➡️code OOI - 👀
trying to divide by 0➡️code DIV0 - 👀
high temperature➡️code IRQ HT IRQis only forPIO- 🚌 all
IRQtravel through the front side bus, they need the CPU and RAM
1
2
❓ I have a IRQ-HT who has the solution?
👉🏻 the RAM, and the CPU PC has to work to get it
✔️ Result of PIO
- 👎🏻 warms up the CPU
- 👎🏻 collapses the RAM
✅ DMA
Direct Management Access
- The peripherals have a
its own specific RAM memoryand uses that memory to solve its own interruptions - So the solution is not saved in the RAM ❌
- it is saved on the small memory of the peripherals itself ⭕️
- 👍🏻 RAM is happy, I do not have to save all the service routines of all the peripherals!
- 👍🏻 CPU is happy, as it does not have to use PC to go up and down the RAM
✔️ DRQ: Direct Request
- official name of interruption in DMA
DRQis the interruption name forDMADirect Requestis for the Direct Management Access- 🚌 all
DRQtravel throught the back-side-bus, they are inside each peripherals
1
2
3
4
5
❓ I have a DRQ-OOP which peripheral has a problem?
👉🏻 printer
❓ Who has the solution?
👉🏻 the printer itself
1
2
❓ What is the interruptoin solution that needs CPU?
- PIO
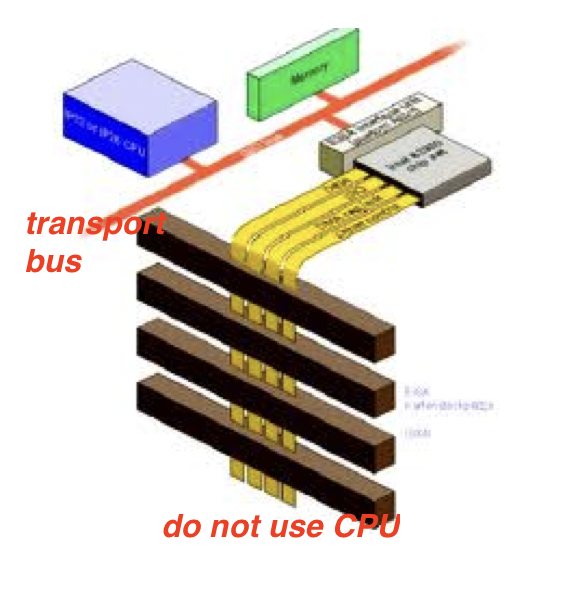
✔️ UDMA
- If the
DMAis solved at a very high speed, it has a change of name toUDMA, Ultra DMA - Means it can solve the interruptions very fast
- 🚌
UDMAuses the transport bus - transport bus is for high speed peripherals
1
2
❓ What is the interruption solution that uses transport bus?
- UDMA
✅ Polling(Sondeo)
- the most famous solution these days
- before an interruption occuring, there are many symptoms
- 👀
oof the temperature is rising, rising, rising...➡️we can predict temperature interrutpions
✔️ Prediction of interruptions
- 👉🏻 Let’s try to predict interruptions before the interruptions happen
- do not wait until things are out of control
- the way of avoiding real interruptions 👉🏻 asking components of the computer every certain time
- ask each component
Are you ok, printer? Are you ok, thermometer?every 10 minutes - 🏆
Pollingcannot solve an interruption, it is for prevention
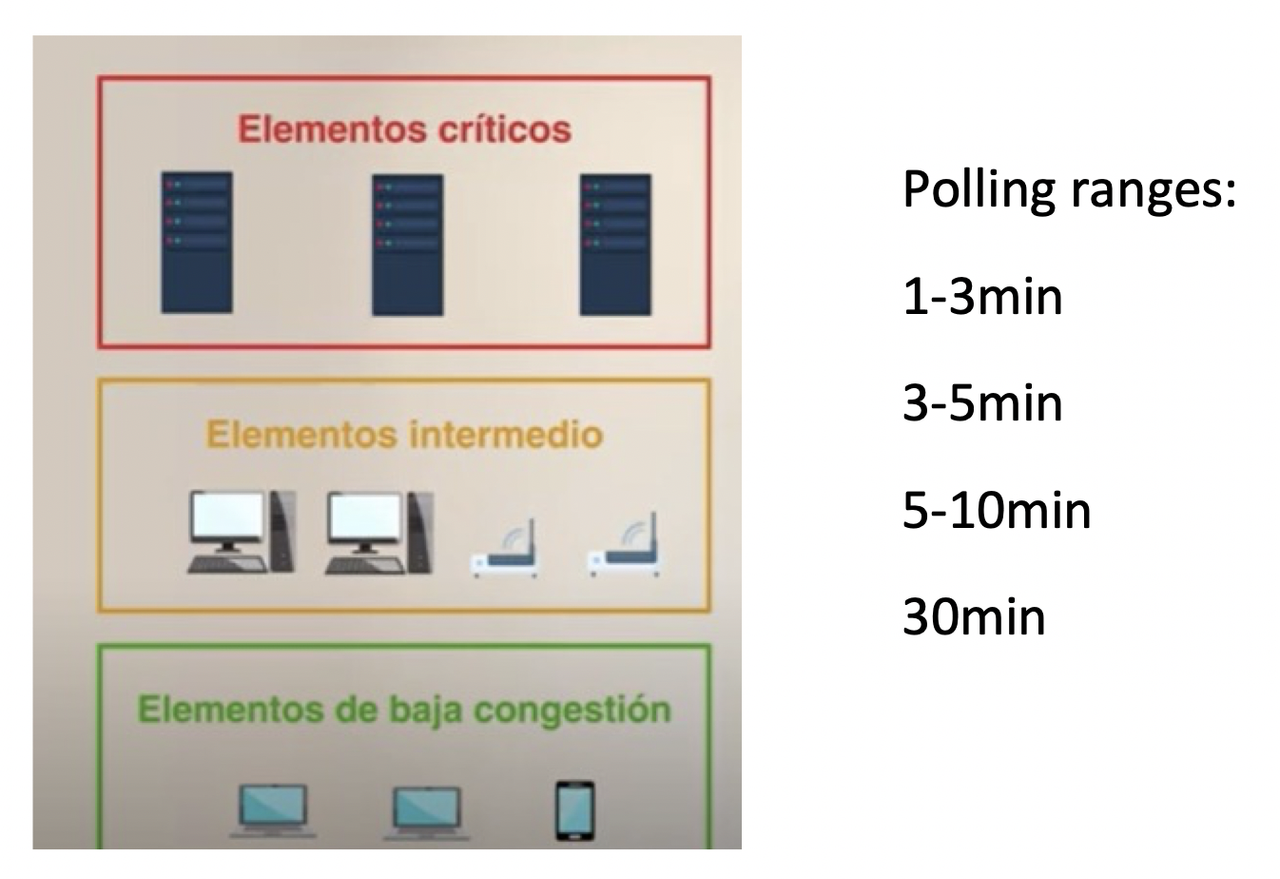
⏱️ Polling Range
- The number of seconds between the questions is called polling range
- number of seconds between
Are you okquestions - 💡 Each componenet has its own
polling range polling rangefor printer andpolling rangefor thermometer is different- some components need more
polling range
⏱️ Different compoents have different polling range
- ✔️ Critical Component
- components that need small polling range:
- need to checked more often
👀 CPU, temperature sensors, RAM,
keyboard…- ✔️ Intermediate components
- need Medium polling range
👀 Expansion slots, north bridge, south bridge,
mouse…- ✔️ Low congestion components
- polling range very high
- you do not have to check/ask so often
- do not have to worry so much
👀
printer…- ⭐️ Exam questions
1
2
3
4
5
How do you call components you need to check more often?
- critical compoenent
How do you call polling range very high component?
- low congestion component
✔️ Network Management System
- THe
NMSwould be asking all the components, every certainpolling time, “Are you ok?” - The asking component cannot be in the same computer
- it is external, connected through network