2.10 Optimization management
Which are the CPU cache that you use for instructions that are very frequently used?
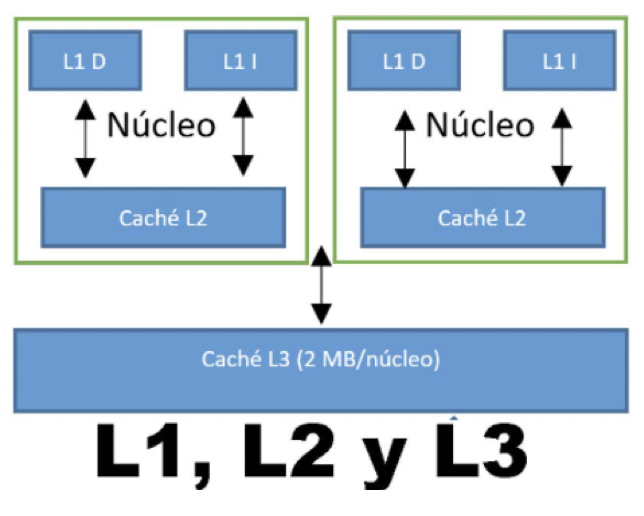
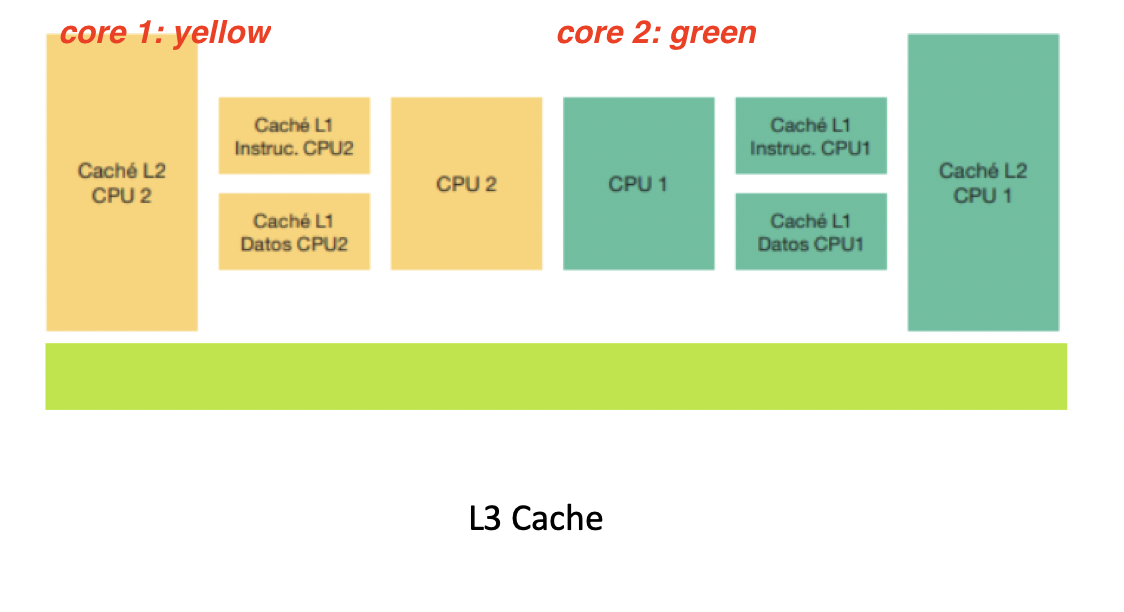
L1, L2 is replicated, L3 is not. If I have 4 cores, how many cache do I have? 4+4+4+1=13
How do you call when two processes share loaded on the RAM? sharing
virtual memory is a mixture of? RAM and secondary memory
calculate size of VM and SWAP
1/2 RAM <= SWAP area <= 2 RAM
3/2 RAM <= VM <= 3 RAM
sysdm cpl
how do you call the flag that turns to 1 when the process is creating problems?
location of types of memory
✅ Optimize the computer
- File Management: FAT32
- RAM management: Segment, Paging
- Process management: FIFO, SJF
- IRQ/DRG: DMA, Polling, PIO
- 👉🏻 All this make the computer overloaded
- 👉🏻 We need to optimize the computer
✅ Priority of computer components
- CPU
- Main Memory RAM
- Secondary Memory (HDD, SSD)
- Peripherals
- 👉🏻 We should optimize the computer components following this order
1️⃣ Lets help the CPU
🤒 Problem that CPU suffers
- 1️⃣ speed problem, being slow ➡️ bottleneck problem
- 2️⃣ temperature problem 💊 better refrigeration problem, better ventilation
💊 Solve the bottleneck problem
- Use CPU cache
CPU cacheis inside CPU- The
CPU cacheis divided into 4 potions
💡 CPU cache is stable
- in general,
CPU cacheis not deleted CPU cacheis stable(not deleted after session finishes)- unless we manually clean them
4 types of CPU cache
- L1D: Level 1 Data cache
- For data that CPU uses very very often
- 👀
power of 2, as in computer everything is in binary, it is stored in cache for frequent access - 👀
1s and0s
- 👀
- ☝🏻 one L1D per core
- it needs to be close to the CPU, as it is used very often to the nueman machine
🐁 size: comparatively small, we just want them for super frequent things
- L1I: Level 1 Instructions cache
- for instructions that we use very very often
- 👀 standard mathametical instructions, like
sum,minus,mul,div,move(move data to another space),sqrt(square root)
- 👀 standard mathametical instructions, like
- ☝🏻 one L1I per core
🐁 size: comparatively small, we just want them for super frequent things
- L2: Level 2 Cache
- Both instructions and data mixed together that we use quite often
- 👀 mathametical operations that are not so frequent:
log,cos function...
- 👀 mathametical operations that are not so frequent:
- 🐇 size: bigger than level 1, need to save both instructions and data
- 🗺️ location: located further away from the neuman machine, compared to level 1
☝🏻 one L2 per core
- shared L3: Level 3 Cache
- Both instructions and data we use sometimes
- 👀
loops, like for, while
- 👀
- 🐳 size: bigger, very big
- 🗺️ location: far from neuman machine
- ✋🏻 Shared level 3: Not one per core, shared among all the cores
- Level 3 cache uses front side bus
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
❓ If I have 8 cores, how many CPU caches do I have?
- L1D: 8
- L1I: 8
- L2: 8
- L3 : one shared L3 per core
👉🏻 in total 25 CPU cache memory
💡 ISA
- Instructions Set Architecture
- set of instructions that the CPU needs to exectute
- the instructions that come by default when I buy my computer
- factory settings of my CPU
the instructions that the neuman machines do by default
CPU cachehelpsISA, as some ofISAinstructions are stored in theCPU cache
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❓ If I reset my computer to factory settings, pure nueman machine, am I deleting the CPU cache memory?
👉🏻 yes, we are deleting
❓CPU cache helps which of the following?
1. IPC to the kernel
2. ISA
3. IRQ
4. DRQ
👉🏻 ISA
2️⃣ Lets help the RAM
🤒 Problem that RAM suffers
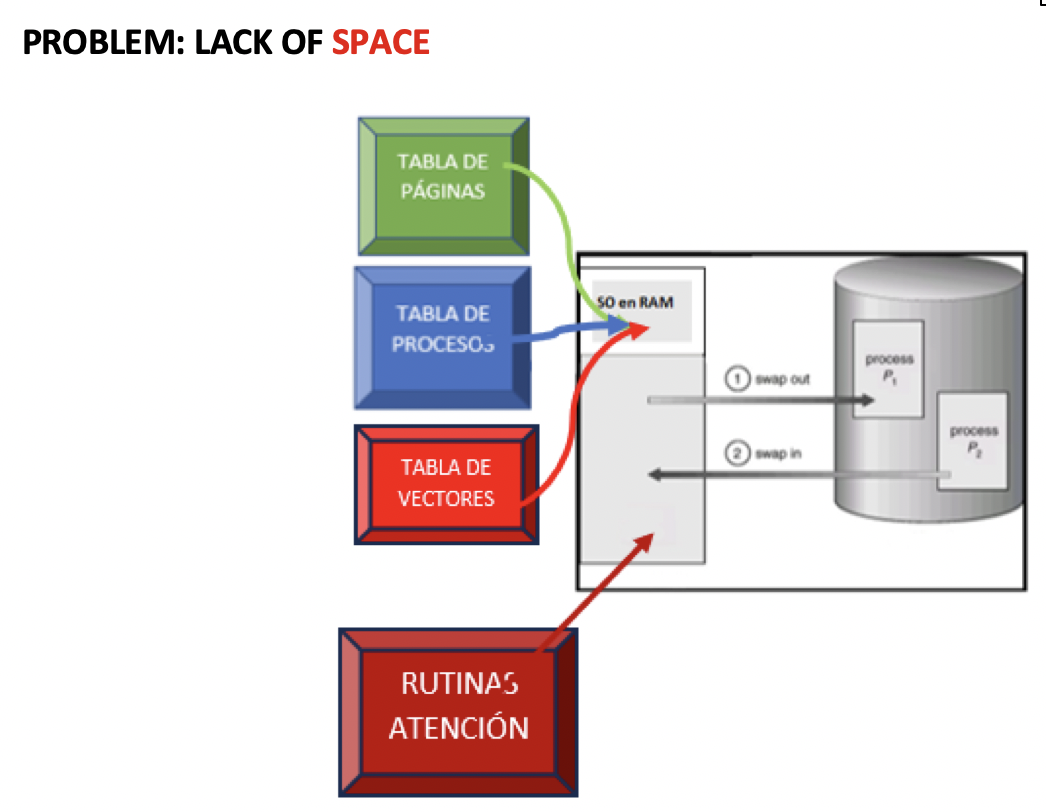
- 1️⃣ problem of space: even smaller bc of
process table, pages table, vectors table, service routinesand above all, processes!
💊 Sharing
- there are some common portions that several proecesses share
- 👀
menu bar in word, excel, ppt are more or less the same - If some processes have some elements in common,
- then put the same elements just one time on the RAM
and share it among the processes
- 👎🏻 the shared elements would be less secure
- as it can be accessed by several processes
- sharing can be deactivated
💊 Virtual Memory
✔️ Some processes are ok to be slow and is not used so frequently
- can be slow
- is not used all the time
- we do not need the process to be there all the time in the RAM
✔️ Page File and SWAP area
- we can leave the process in a specific part of the Harddisk(secondary memory)
- called in Page File
windows/mac/androidand SWAP area inlinux - 👉🏻 in
page file/SWAP areawe store the pages of the process that - we don’t use very often
- and we do not need so fast
- like having an extra storage
- 👍🏻 makes the RAM feel bigger than it seems
👍🏻 Feels like virtually, I have more RAM
- its called swap, bc when you need it,
- it seems the process is inside the RAM
But actually, the process is inside the hardddisk
- So in harddisk, it is generally for closed program
- but in SWAP part of harddisk, there are opened process
✔️ Format for Page File and SWAP area
- This area is in the secondary memory
- ⚠️ the format is different from starndard( NOT
FAT32,exFAT,NTFS,ext 2, 3, 4❌) - the format of
Page FileandSWAP areais called swap - as
Page FileandSWAP areais for helping the RAM,swap formatis similar to the RAM
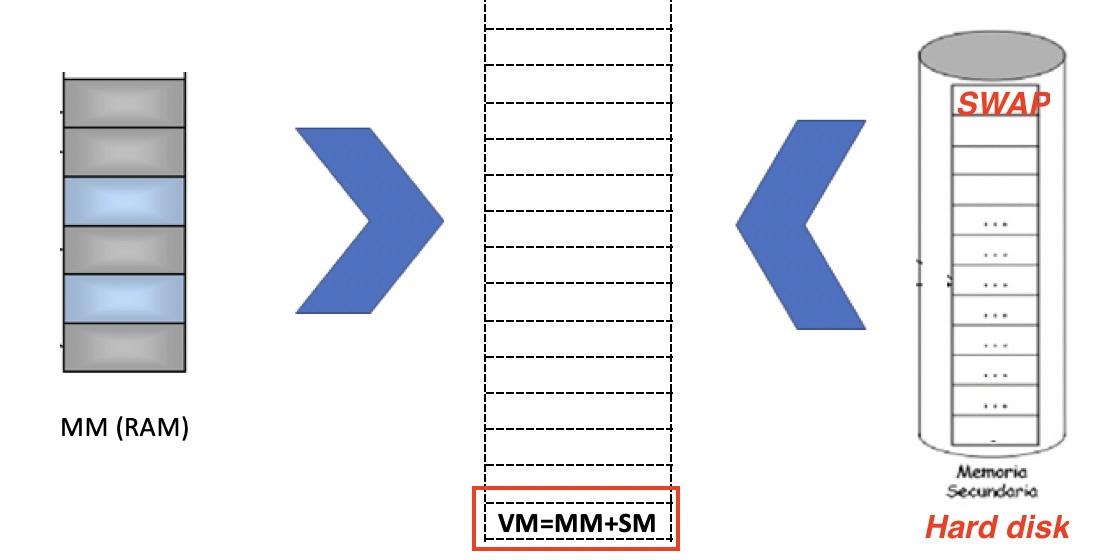
✔️ Virtual Memory
- VIrtual Memory = my RAM ➕ SWAP in Harddisk
VM 🟰 MM ➕ SWAP area(SM)
✔️ Calculate the VM
- If RAM is small ⬇️ SWAP must be big ⬆️
- If
RAM < 4GB, SWAP must be two times the RAMSWAP = RAM * 2 - If
RAM = 4GB, SWAP must be same as the RAMSWAP = RAM - If
RAM > 4GB, SWAP must be half of the RAMSWAP = RAM / 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
❓ 3GB of RAM, my SWAP should be?
👉🏻 6GB
❓ Then how much is my VM?
👉🏻 9GB
------
❓ 4GB of RAM, my SWAP should be?
👉🏻 4GB
❓ Then how much is my VM?
👉🏻 8GB
------
❓ 16GB of RAM, my SWAP should be?
👉🏻 8GB
❓ Then how much is my VM?
👉🏻 24GB
⚠️ Error we can get if we do not follow the VM caculation rule
- If we follow these rules, we will never have a problem with the virtual memory
- However, if we do not follow these rules, we might get a problem
- ⭐️ When you have a VM error, the error starts by
0x000000 - cannot read instruction on
0x000000 if you see this error, you have a virtual memory problem
- this error occurs bc many OS take SWAP smaller than needed
- many OS prefer more pure HD than more SWAP
- 💊 deactivate the automatic VM supply(administración automatica memoria virtual)
- 💊 and supply VM manually
✔️ Perfect limits for VM
SWAPshould always be between half and double the size of theRAMhalf of RAM< size of swap <double of RAM- if my RAM is big, if my SWAP small, SWAP is
half of RAMmy VM would beRAM + RAM/2 = 1.5RAM - if my RAM is small, if my SWAP big, SWAP is
twice the RAMmy VM would beRAM + RAM*2 = 3 RAM - Thus, the VM size should always be
RAM * 1.5< size of VM <RAM * 3- 👉🏻 This size of VM would avoid the problem of VM
0xerror
1
2
3
4
❓ I have 8GB of RAM. Study the minimum and maximum limits of VM so I do not get the VM error.
👉🏻 8 * 1.5 < VM size < 8 * 3
👉🏻 thus, 12GB < VM size < 24GB
👉🏻 as long as I guarantee that my computer makes VM from 12 to 24GB, I will never get the 0x error.
1/2 RAM <= SWAP area <= 2 RAM
3/2 RAM <= VM <= 3 RAM
- these formulas guarantee that we will not have the
0x000000error - if I keep this formula, I will protect my computer from having the
0x000000error
✔️ Command to solve the VM error
1
sysdm cpl
- system setting commands start with
sys all the commands that start with
sysare for setting the system- all the commands that contain/end with
dmis for device management - all the commands that end with
cplare commands that are reachable through the control panel
✔️ How to run the commmand
- ⚠️ This process very very hidden,
- need to open three windows!
- bc of security purposes
- in order to run this command, press
windows keyandR
- then type the command
sysdm cpl - a new window appears
- go to advanced options
- Performance area
- Configuration button
- new window appears
- Advanced options
- Change button
- new window appears
- virtual memory
- Untick the automatic administration
- Choose custom size
- custom size needs to include the limits for the
virtual memory - So adopt the
virtual memory formula - If we use this formaula, we protect the system from VM errros
- initial size will be
1.5 * RAM, but in MB - maximum size will be
3* RAM, but in MB - we only manually choose the size when we get the
0x000000error
- We should do this when we really have a problem, at the moment we have a problem
- So do not manually change the size when you do not have an error
- If we do it even if we do not have an error, we are stealing capacity of the HD when we do not need it, so why do it?
- After writing the size manually, click on
accept ➡️ accept ➡️ accept three times, and close all three windows - Restart the computer
- Now you will not see the 0x000000` error!
✔️ How do you find the size of the RAM?
- Open task manager(administrador de tareas)
- shortcut:
Ctrl+Alt+Supr - or
Ctrl+Shift+Esc
- Task Manager
- Performance
- Memory
- You can find the size of the RAM in the top right corner
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
If my RAM is 8GB,
inicial size will be 8 * 1.5 = 12 GB
change to MB: 12 * 1024 = 12288 MB
maximum size will be 8 * 3 = 24GB
change to MB: 24 * 1024 = 24576 MB
3️⃣ Lets help the Secondary Memory
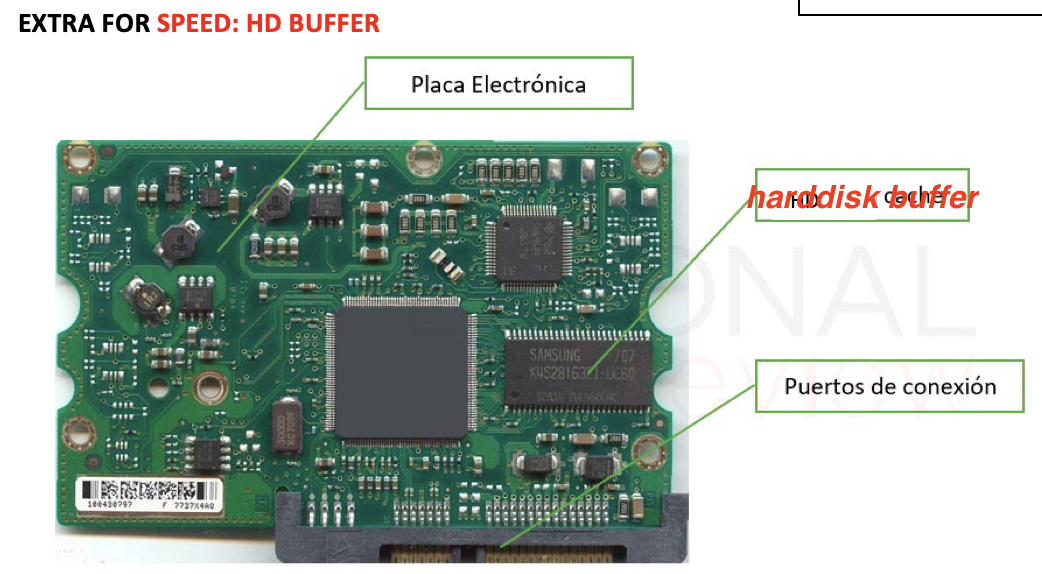
💊 Harddisk Buffer
- harddisk buffer is in the
Harddisk buffer: temporal storage for making profit of a data transaction
- the portion that you need now ➡️ goes to the RAM
- the portion that you do not need now, but you took following the proximity principle ➡️ goes to the buffer
💡 Proximity principle
- when you open a program, most probably you will need more than that
- 👉🏻 open more, also the ones next to the pointed program
- 👀 if you opened ejercicio 1, you will also open 2, 3,4…
- the extra can be stored in the
harddisk bufferto have it closer to you.
💊 Web cache, Broswer cache
- when we download elements from the web and we visit web pages
- most probably, we will use the element/web page later
- store the elements in the broswer cache
- web cache is a folder in the harddisk
- when we empty the cache, we are emptying the web cache
✔️ Two things you save in the web cache?
- web cache saves the 1️⃣ history of web pages
- and components you have 2️⃣ downloaded from the web pages
✔️ Where is broswer cache?
- Harddisk
✔️ How many web cache?
- one folder per user
- one folder per browswer
- also the same for cookies, one folder per browser, one folder per user
- 🆚 cookies: my preferences/ web cache: my history, downloads
1
2
❓ If I have two users, and three web browsers, how many web cache do I have?
👉🏻 6 web caches
1
2
3
4
5
❓ When you delete the history in your browser, what are you deleting?
👉🏻 you are just deleting the list of visited web pages,
but not downloads, components history
👉🏻 so you are not fully deleting, you can still see downloads history
4️⃣ Lets help the Peripherals
🤒 Problem that RAM suffers
- 🐢 normally peripherals are slower than the other computer compoenents
- so we need to help peripheral speed
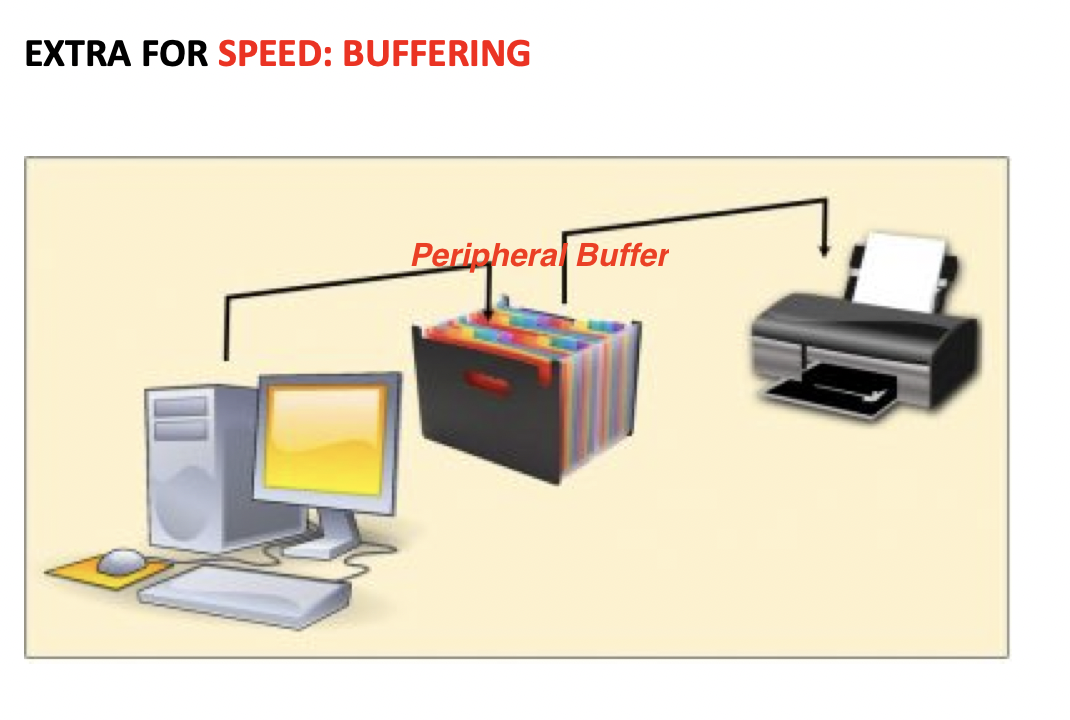
💊 Peripherals buffer
- specific folder
- in which the peripherals stores the pending documents
- and takes them at its own speed
👀 like the printer queue
- If the peripheral uses the
peripheral buffer - we say it is using
Buffering
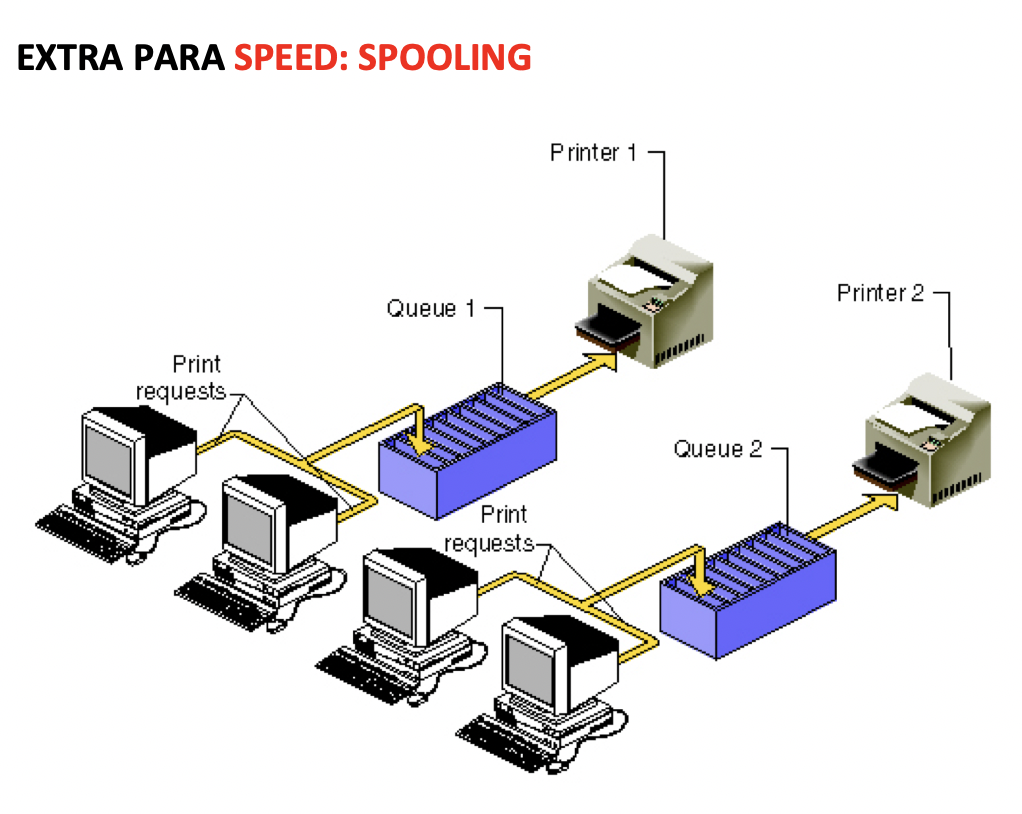
💊 Spooling
- If the buffer is shared by several computers on the network
- one printer is shared by several computers
- we call it spooling
- same as buffer, but with several computers connected to one peripheral
✅ How can I protect my system?
- Due to optimization techniques, all the computer components are interconnected
- so one problem in one component can affect the whole computer
- 👀 If I have a problem in SWAP, will affect HD and also the RAM
✔️ Stamp a process
- when a process creates a problem in one component
- the process is stamped
- Stamp a process: set a flag
NX: Non Executeto 1 NXmeansplease, do not execute the proecss!- so when the process reaches another component,
if
NX = 1, the entrance will be blocked! forbidden- Then the process that is stamped
NXwill be swapped out - and if it is a malware
- (the anti virus will tell you)
- 3 layer protection(me, my parent, my children)
- antivirus will expel the process and its 3 generations from the RAM
✔️ Where is the NX flag?
- the flag is stored inside the process table, in the OSRAM
- 👉🏻 way a protecting the system
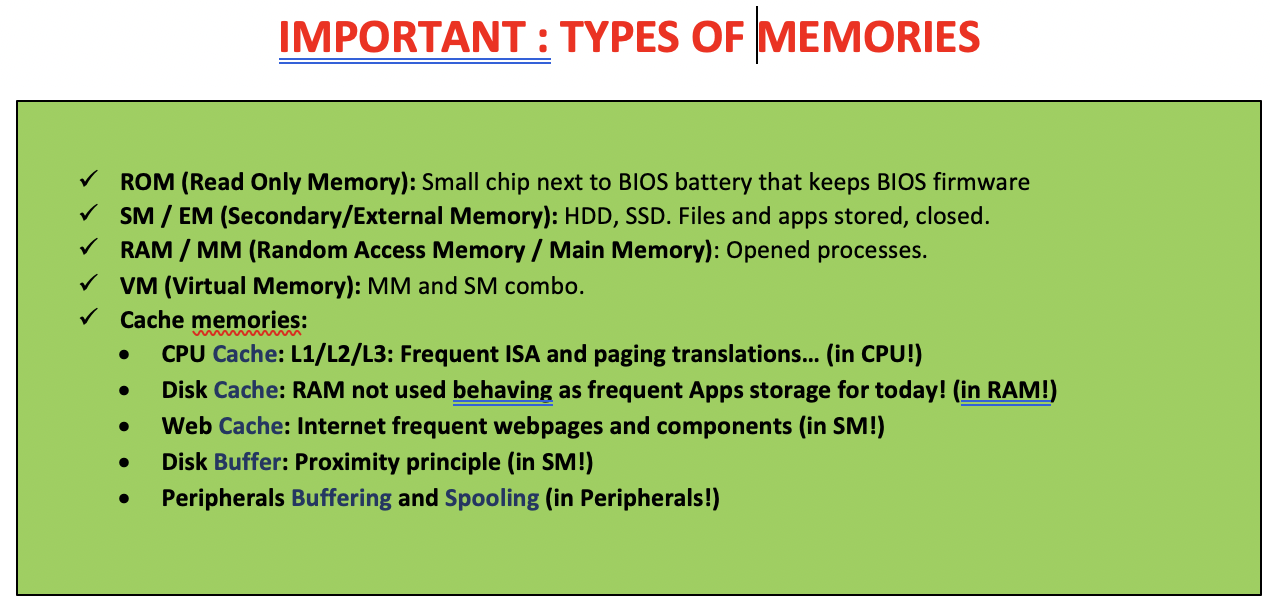
✅ Type of memories
✔️ ROM: memory you can only read, you cannot modify
- these days, the only element that is
ROMisBIOS - find the battery, and the
BIOS/ROMwill be next to the battery
✔️ SM/EM: HDD, SSD
- files when they are closed, stored
✔️ RAM, MM
- opened processes
- Random: bc processes will be placed randomly, incontinguously, not ordered
✔️ VM:
- combination of memory both in HD(SWAP) and RAM
- Can you point to the VM physically? 👉🏻 NO, VM is a concept
✔️ CPU Cache:
- inside the CPU
✔️ Web Cache:
- in the harddisk, it is a folder
✔️ Disk Buffer:
- in the harddisk
✔️ Buffering and Spooling:
- in the peripherals
✔️ Disk Cache:
- A portion of the RAM helping the HD
for frequently opened/closed applcations
- Sometimes, you have free space in the RAM
🐇RAM is always faster than the 🐢HD
- If we have an application that we
open(RAM)andclose(HD)several times, - if there is free space in the RAM,
- it makes sence to just keep it in the RAM
- even when you close it
- beacuase
1. as RAM is fastand2. we have free space on the RAM - 👉🏻 So the RAM is helping the HD
- We call that disk cache
🆚 Disk cache and Virtual Memory
- Disk cache: RAM helping HD
- Virtual Memory: HD helping RAM