1.13 Hardware specifications_2
📌 D. Boot System
Chip for booting the computer
- Boot System can
- Depending on Physical aspect
- Depending on Internal/logical aspect
☑️ Physical aspect of a booting system
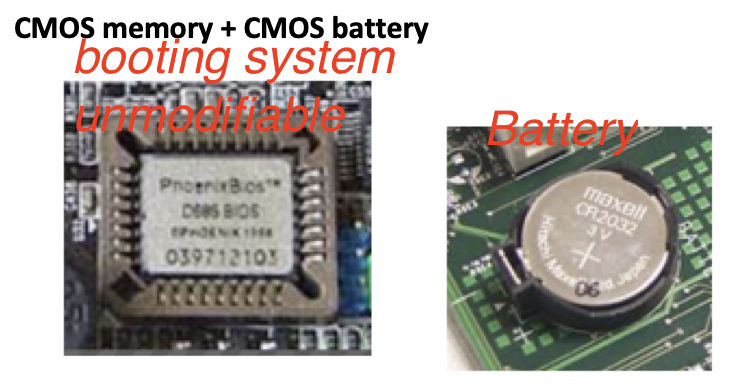
1️⃣ CMOS Booting System
Tiny chip + Battery
- has a
tiny chip + big battery - battery is bigger than the chip
- this battery feeds the portions of the CMOS, that cannot lose electricity
- 🔋 battery gives electricity to things that cannot go off, things that has to be charged 24hours
- for example, battery makes the
watch(current data, time) updated - also, battery feeds
the basic settingsof theCMOS, like language settings and others - ❓ If this battery is totally off/empty, can we boot the computer?
- Yes the computer will boot, bc the booting electricity itself will come by the power supply
- However, the setting of the language, time would be weird/wrong
- And the computer will have an error message
- for example, battery makes the
🔋 The rest of the electricity that the CMOS needs comes from the power supply
- in CMOS, the booting system is impossible to modify ❌
- unmodifiable/unchangeable booting system
your booting system is trapped in the factory settings
- has a firmware in the booting system to boot the computer
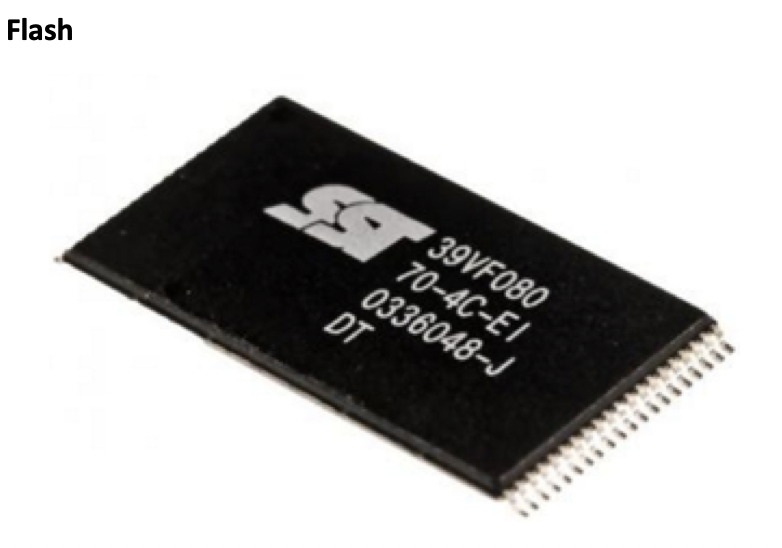
2️⃣ FLASH Booting System
Bigger chip with no battery
- Flash: Technology of USBs
- Flash uses USB technology,
- so it uses NAND gates like USBs
- can modify/adopt/change the booting system of your computer ⭕️
1
2
3
4
5
❓ Which is the name of the booting system that you can adopt to your needs, without battery?
- FLASH
❓ Which is the name of the booting system you cannot modify, with battery?
- CMOS
☑️ Internal/Logical aspect of booting system
1️⃣ BIOS-legacy
basic booting
normally called BIOS-legacy
- little weaker booting system compared to UEFI
2️⃣ UEFI(Extended)
Extended booting
Also called BIOS-UEFI
Nowadays, theold BIOSis called legacy and theUEFIis called BIOS-UEFI
🤷🏻♀️ Thats why booting systems is many times called BIOS
- stronger booting system compared to UEFI
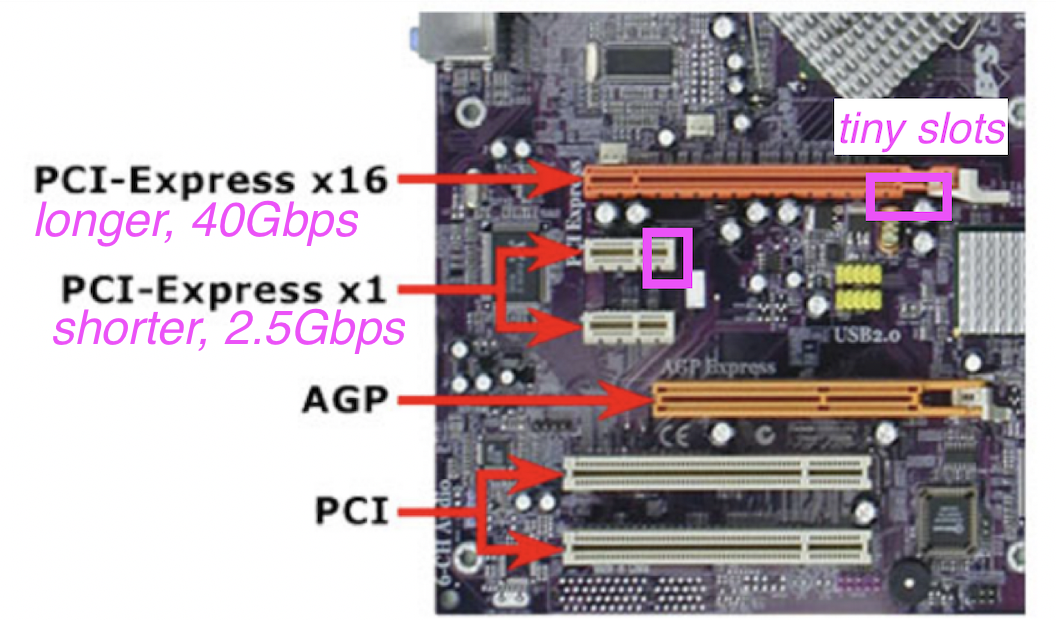
📌 E. Expansion Slots
For expanding the capability of my computer
☑️ Three types of Exansion Slots
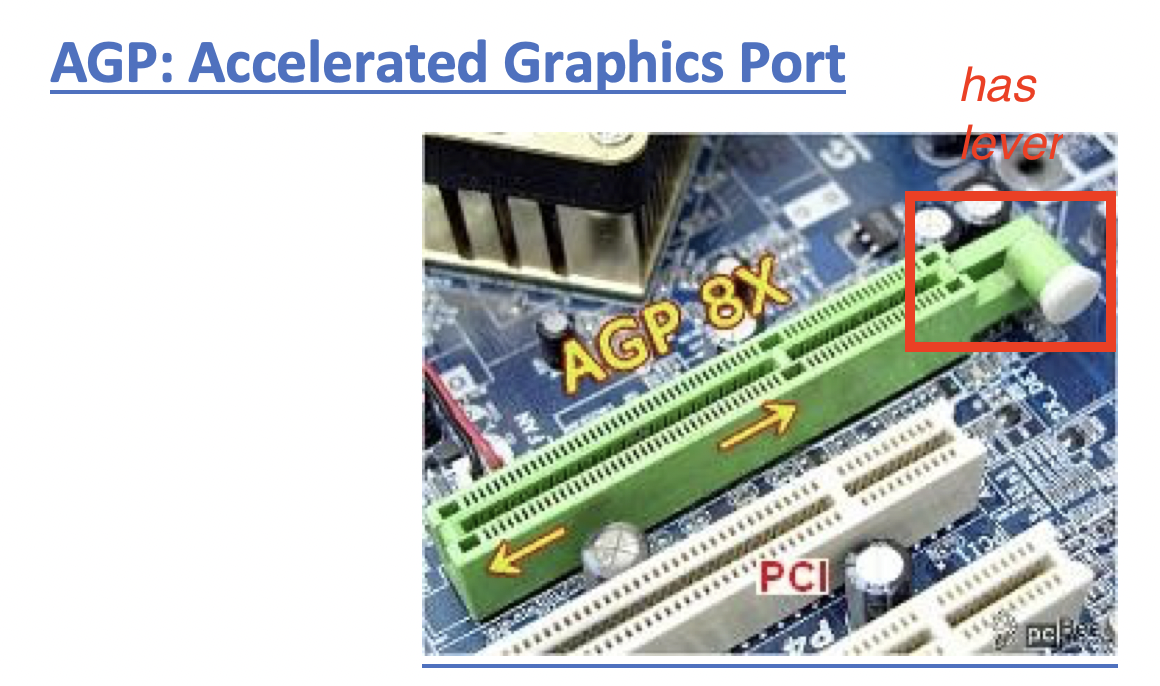
1️⃣ AGP
Accelerated Graphics Port
- very old, outdated
- was used for graphics
- it is not used anymore
- has a lever
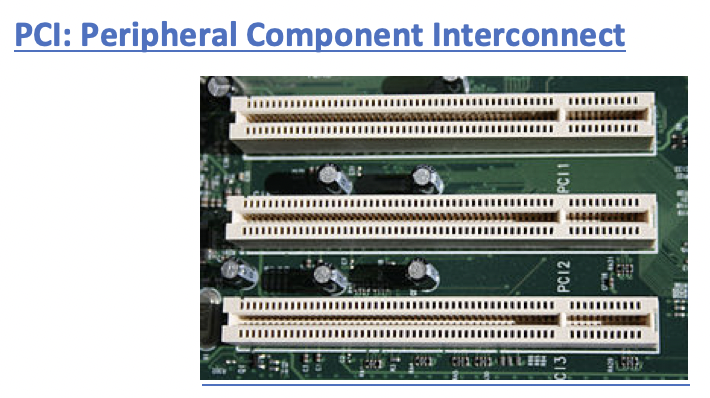
2️⃣ PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
- ⭐️ Peripheral
- For all types of expansions, not only graphics
- for example, if I want my computer to get an antena for TV, use
PCI expansion slot - for example, to do ecography on my computer, use
PCI expansion slot - to measure earthquakes, use
PCI expansion slot - to add bluetooth to my computer, use
bluetooth PCI expansion slot - If my computer does not have internet, use
Ethernet PCI expansion slot - use
RJ45 PCI expansion slotto connnect my computer to internet
- No lever in the end ↔️ AGP
- normally white color
no tiny slots ↔️ PCI-e
- 👎🏻 Half Duplex
1
2
3
4
5
❓ What does Half DUPLEX mean?
We can send or recieve information
one at a time
- like a walkie talkie
- If I am recieving, I cannot send
- These days, PCIs are disappering little by little
- we use PCI-e
3️⃣ PCI-e
- you can distinguish them physically bc it has tiny slots
- ↔️ PCI does not have slots
- lever is optional
🛠️ Use for job that requires fast speed
- 👍🏻 fast 🟰 e, Express
- 👍🏻 Bidirectional 🟰 FULL DUPLEX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❓ What does fast mean?
2.5Gbps per second
- 2.5 thousand million bits per second/per direction
- 2.5 thousand million bits per second/per send and recieve
- I can send 2.5 thousand million bits per second
- and recieve 2.5 thousand million bits per second at the same time
- This is bandwidth
1
2
3
4
❓ What does FULL DUPLEX mean?
We can send and recieve information at the same time
The card can send and recieve information at the same time
- Phone, two ppl can speak in a phone call at the same time
- ⭐️ EXAM: types of
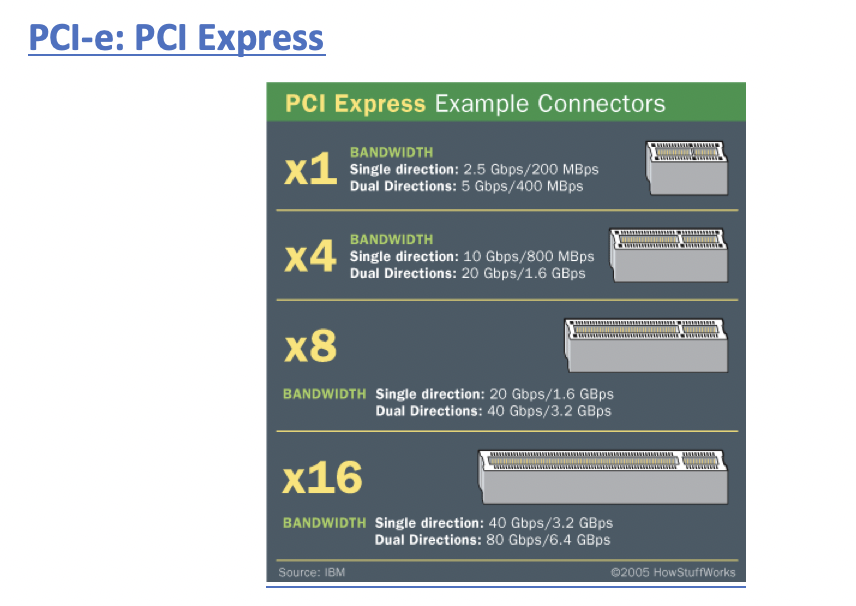
PCI-e PC1-e X1: 2.5Gbps/per directionPC1-e X4: 10Gbps/per direction(2.5 * 4)PC1-e X8: 20Gbps/per direction(2.5 * 8)PC1-e X16: 40Gbps/per direction(2.5 * 16)- ⭐️ memorize bandwidth
- ⭐️ smaller the number ⬇️ physically shorter the slot ⬇️
📌 F. Storage Devices - Secondary Memory
- 🟰 External Memory 🟰 Harddisk
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❓ Why is Secondary Memory External? It is inside the computer!
If the component is inside the mother board ➡️ internal
If the component is outside the mother board ➡️ external
- So, even if HD is inside the computer
- it is outside the motherboard,
- so HD is external
- In laptops, there could be some internal secondary memories
- bc they insert a HD on the motherboard
- then, it would be an internal HD
- However, if it is connected by a wire, outside PCB, then it is external secondary memory
☑️ Types of Secondary memory
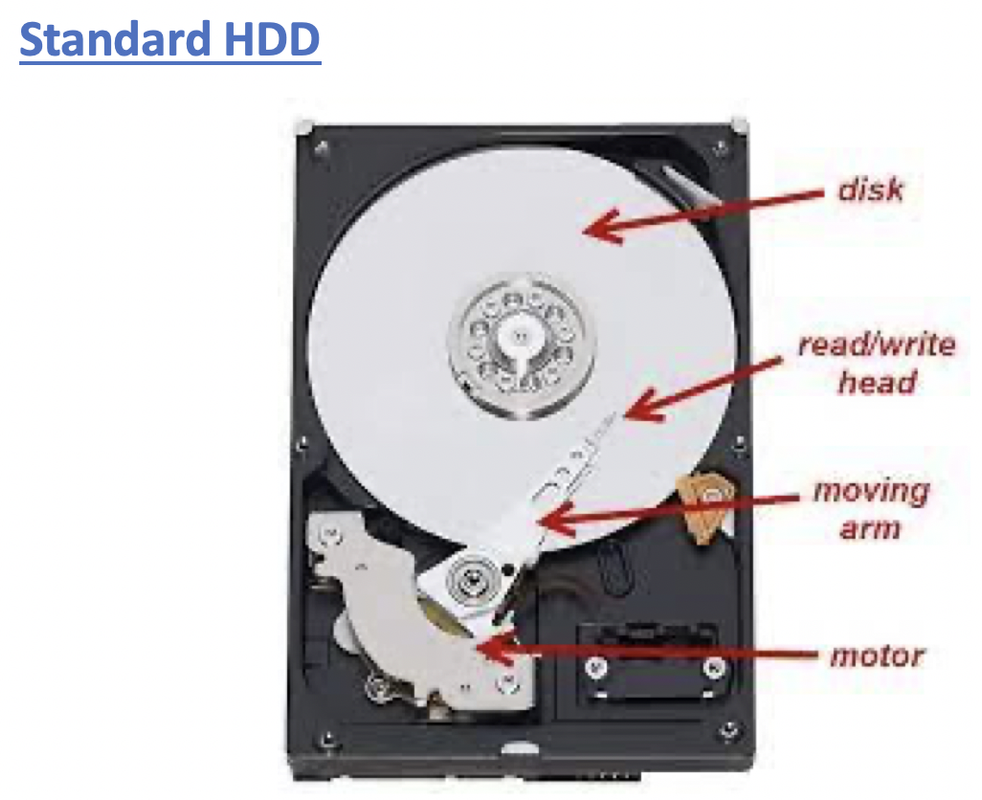
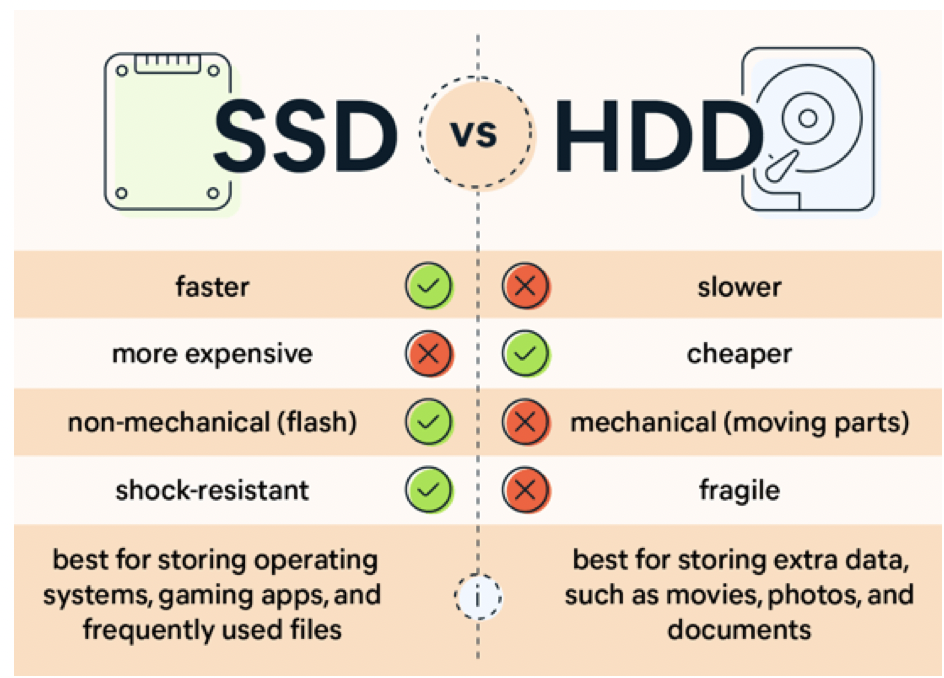
1️⃣ HDD
Hard Disk Drive
- 1️⃣ has plates
- have a roation system
when it turns, makes noise/sound
- 2️⃣ Slow 🐢
plates have to rotate, move header to get data
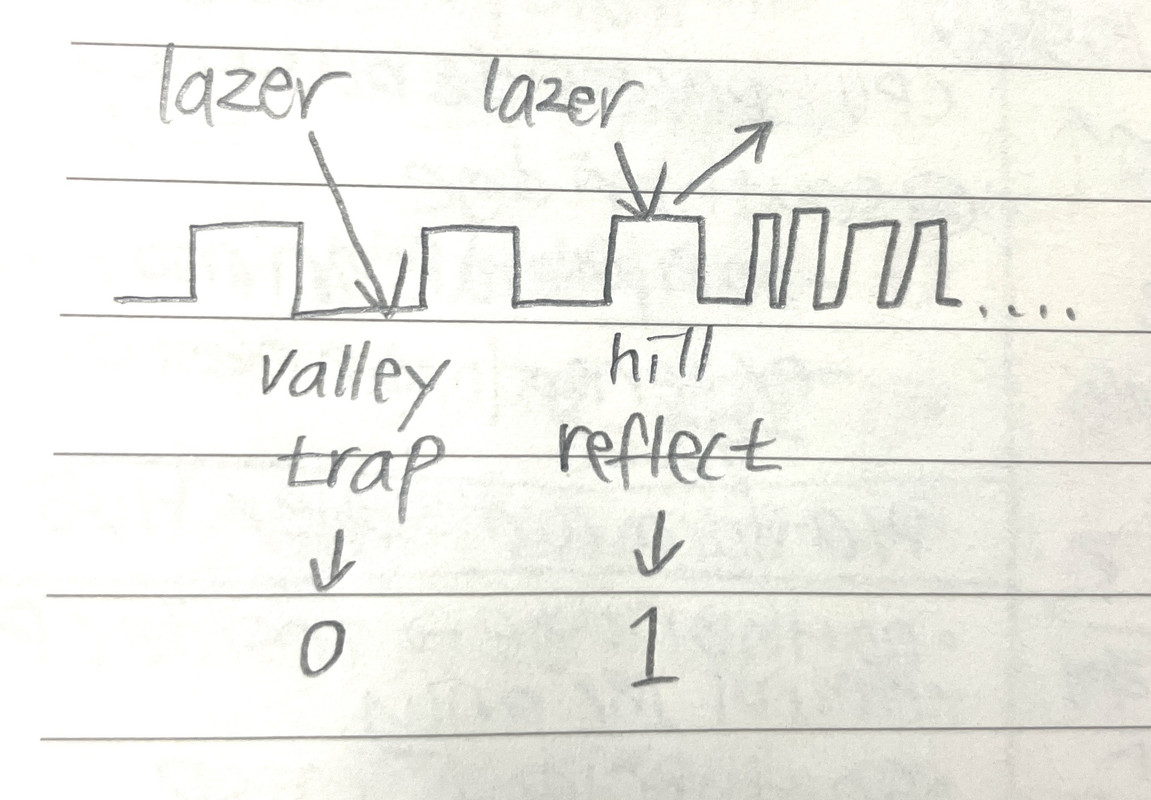
- the 0, 1s in HDDs are physical
- surface of HDD would have hills and valleys
- valley trap the lazer
- hills reflect the lazer
- trap: 0
- reflection: yes light, 1
1
2
3
4
❓ What would happen if you scratch a HDD?
- The hills and valley would be destroyed
- making your 0 and 1s damaged
- so you would lose all the data
- 3️⃣ 👎🏻 Very vulnerable, non resitant to shocks
should NOT be thrown, scratched
- 4️⃣ 👎🏻 Very vulnerable to vibration
- if there are vibration, lazer will not be reflected
- as plates would move
- you cannot get proper data
cannot use HDD in a vibrating situation
- 5️⃣ Hard disk do not lose information in a long time
- as 0 and 1s are physical
- data is longlasting, as long as HDD is not damaged
can last 30s~~~ of years
- 🛠️ So companies prefer use harddisks
- not to lose data for a long time
2️⃣ SSD
Solid State Disk
- use
CellsandNAND gates - have technology simillar to USBs
- in cells, save small 0 and 1s
- 1️⃣ everything is electricity
- no rotation ❌
- no sound ❌
no movement ❌
- 2️⃣ Fast 🐇
- everything is done by electricity
0: 0.5v1: 5v- 3️⃣ 👍🏻 Nothing is moving, so vibrations do not affect the SSD
4️⃣ 👍🏻 Shock Resistant: More resistant to shock
- 5️⃣ In SSD for 0 and 1, use electricity
- need to lower, higher for 0.5v and 5v
- 👎🏻 at some point, the cells lose elasticity탄성(like 고무줄)
- they can lose information with time
- bc the cells get less elastic
- so between
0.5vand5v, there can be electricity value like3and the data could be confused with another number
1
2
❓ How long would a SSD last?
- start to have problems more or less in 10years
- 🛠️ Personal users prefer SSD bc it is faster
☑️ Storage connector for HDDs
- IDE and SATA only apply to HDDs
- so IDE, SATA apply to plates
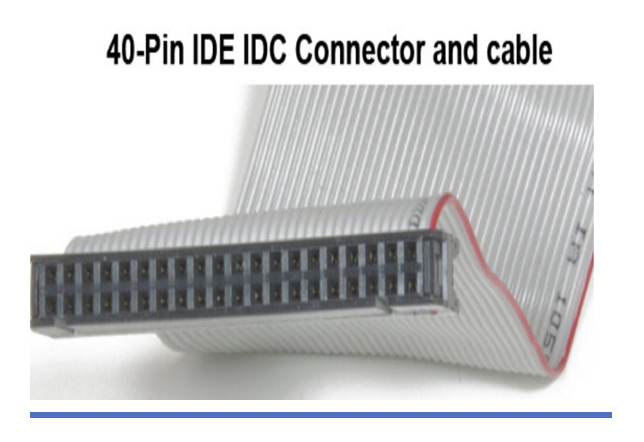
1️⃣ IDE
Integrated Drive Electronics
Also called Parallel ATA(Advanched Technology Attatchment)
PATA
1
2
3
4
PATA
- In computer parallel means bits travel in groupd
- ↔️ serial means bits travel one by one
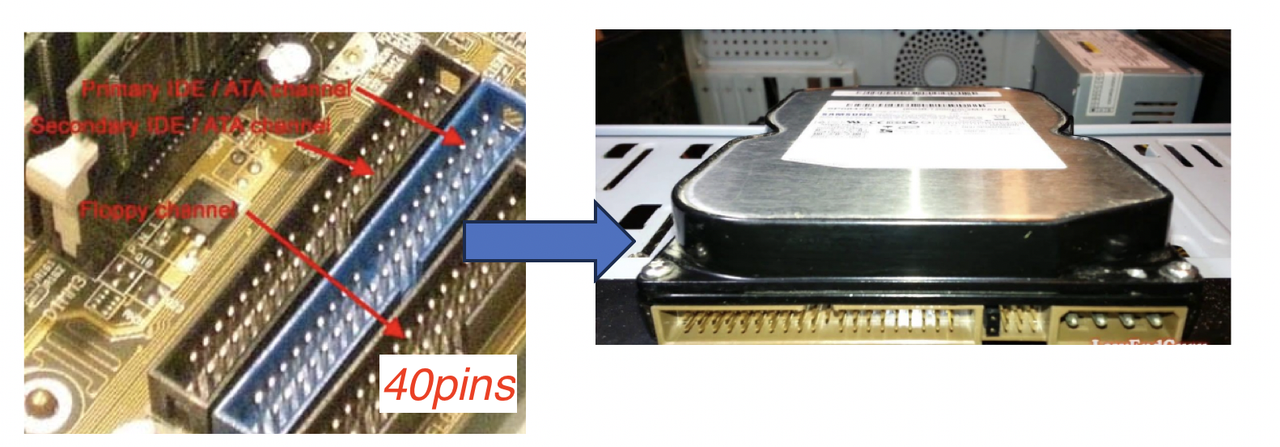
- So in IDE, bits travel in parallel using the 40pin connectors
- 1️⃣ connect to Power: IDE has
ATX-P3for energy supply ATX-P3has4 thick pinsfor feeding the Harddisk- 2️⃣ connect to Data: and
40 pin connectorfor data(gray color) - So IDE has 2 connectors, for
ATX-P3(4 pins), for energy, connected to power supply - and
40 pin connectorfor data(gray color) - and IDE
40 pin connectorfor data is connected to the mother board
IDE is not actively in use anymore, disappearing trend
- 👎🏻 IDE
40 pin connectorfor data(gray color) is too big, too thick - 👎🏻 Interference
💡 Rule of computer components: the bigger an element is, the more interference it can suffer
- 🛠️ It is still in use, in companies, servers
- as it is difficult to shut down a company server(Harddisk of a company)
- 🛠️ Also used for DVD readers
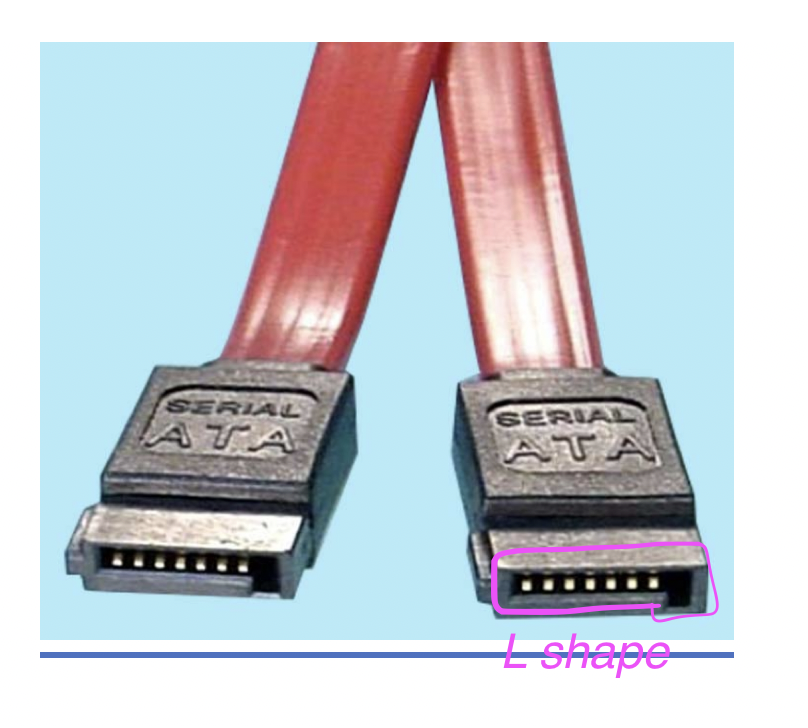
2️⃣ SATA
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
- 2️⃣ connect to Data: Data travel through very narrow cable/wire
- has an
Lshape - SATA always end in
L - 👍🏻 Less interference
- 1️⃣ connect to Power/Electricity: set of several tiny/small pins, super thin
- not
ATX-P3, not 4 pins - as in SATA for supplying electricity, it uses more pins
- more pins splits/distributes the electricity better
👍🏻 so good in temperature/heat
- 👍🏻 Faster than IDE, PATA 🐇
- even it is serial
bc even being serial, the speed of transmission is fast
- USB is also serial, but it is also fast
- bc the speed of transmission is fast
- Serial is always faster than parallel
1
2
3
4
5
6
❓ Which connector is faster?
- SATA
❓ Which connector has less interference?
- SATA
❓ Which connector is better in terms of heat?
- SATA
☑️ Storage connector SSDs
- use
USB Cfor connector
✅ Solid State Disk types
Internal structure of the SSDs
1️⃣ 2.5 SATA SSD
- SSD on the motherboard
- internal memory
1
2
3
4
5
6
⚠️ SATA in internal strucutre of SSDs does NOT mean connector for HDD
SATA means speed/bandwidth in 2.5 SATA SSD
🤷🏻♀️ SDDs do NOT use SATA connector.
❗️ SATA connector is for HDD
💡 But as the 2.5 SATA SSD connector has the same speed as SATA connector for HDD, they call it SATA wires
- very compatible w any computer
- 2.5 means size of the disk
SATA means speed, bandwidth
1.5Gbpsormultiple of 1.5- so there is also SATA with
3Gbps = 1.5 * 2^1of speed/bandwidth - or
6Gbps = 1.5 * 2^2
2.5 SATA SSD: I want to buy a SSD that has speed1.5Gbpsand has size 2.5👵🏻 old type of SSDs
- ↔️ has a special connector to connect to motherboard
- you cannot just connect SSD, need special connector, special help
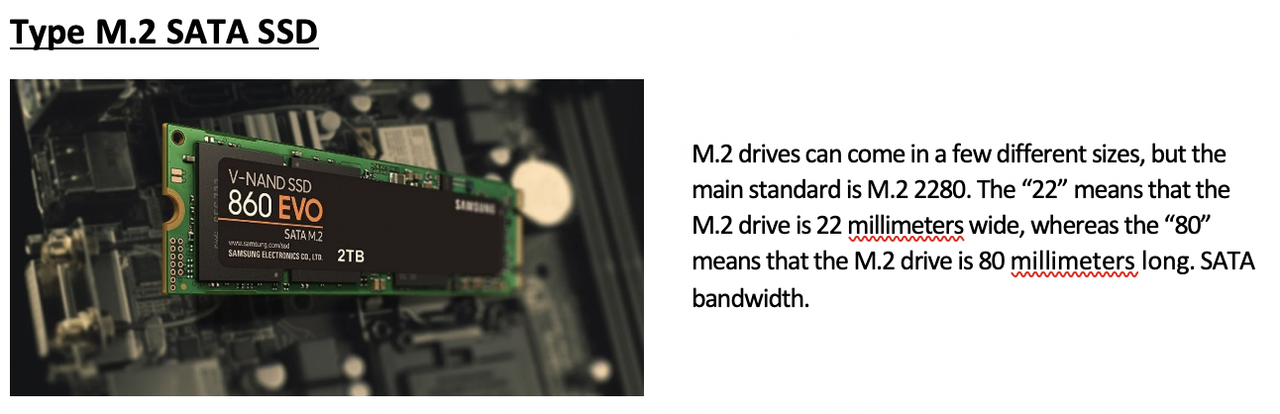
2️⃣ M2 SATA SSD
- speed: again SATA speed, like
2.5 SATA SSD - size is diffeent than
2.5 SATA SSD - in
M2,2means22mm, so narrower and longer - 👍🏻 When smaller, less interference
👍🏻 bc it is smaller, can fit more easily in computers, in
all-in-ones,laptops…- ↔️ has a special connector to connect to motherboard
- you cannot just connect SSD, need special connector, special help
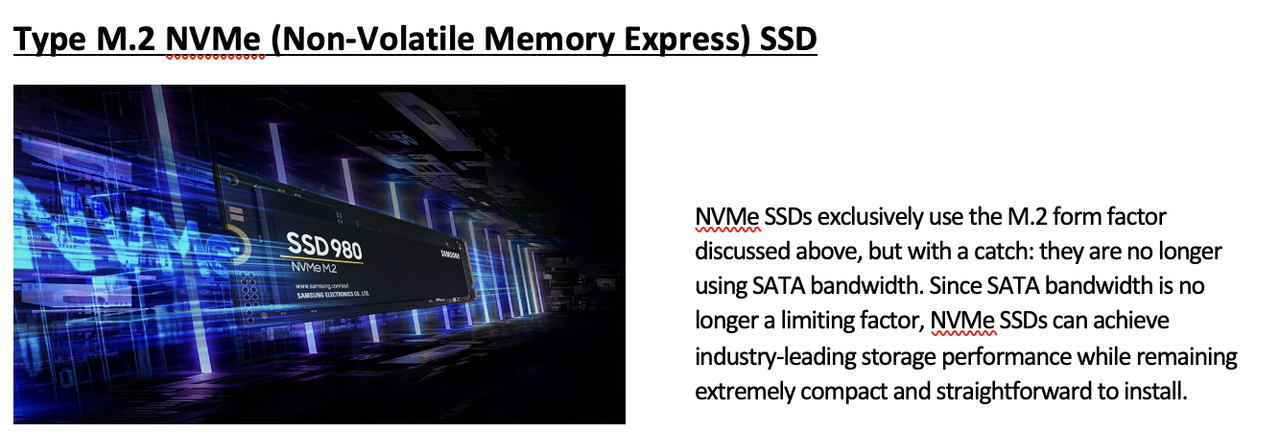
3️⃣ M2 NVM2
Non-volatile Memory Express SSD
- express: fast
- not SATA speed anymore, faster than SATA speed
- size is also small
- 👍🏻 so small size and fast speed
- 👍🏻 low interference
👍🏻 most modern, and most efficient SSD
- ↔️ has a special connector to connect to motherboard
- you cannot just connect SSD, need special connector, special help
4️⃣ PCI-Express SSD
- one solid disk that you can insert in a
PCI expansion slot - do not need connector
- can just insert in
PCI expansion slot - You can just insert the SSD in the
PCI expansion slot - 👍🏻 do not need special connector, special help
- 👉🏻
PCI-Express SSDwas invented for SSD to old motherboards that were not prepared for SSDs, that has no room for SSDs
1
2
❓ If a customer wants to insert a SSD in a old motherboard that has NO room for SSDs, what can you do?
- use a PCI-Express SSD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
❓ In a vibrating environment what do you use?
- SSD
❓ For info you want to keep forever, what to you use?
-HD
❓ Low interference?
- SATA
❓ Why do we still have PATA?
- bc of servers, companies
❓ High speed?
- SATA
❓ If I do not have much space in my computer, but I want to add a SSD, what do I use?
- PCI-Express SSD
❓ If I need to choose between M2 and NVM2?
- recommend NVM2 bc it is faster
❓ Which has less interference? 2.5 SSD or M2 SSD?
- M2 bc it is smaller
📌 G. External Connectors
connectors for external elements
☑️ Types of External Connectors
1️⃣ Mini-DIN
- round connectors to connect mouse/keyboard
2️⃣ PS/2
- round connectors to connect mouse/keyboard
- mouse: green
- keyboard: purple
3️⃣ VGA
- for monitor
4️⃣ USBs
- high speed
✔️ Aspect of USBs
- USB type A: rectangular shape
- USB type B: smaller than A, square
- USB type Micro B: if it is like a line
USB type C: for chargers, tiny and less pins
- among A, B, C, smallest is C, biggest is A
1
2
❓ Which is the USB with biggest case format?
- A
✔️ USB speed
- USB 1: slow
- USB 2: faster than 1
- USB 3: faster than 2
1 < 2 < 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
❓ Which is the USB with fastest transmission speed?
- 3
❓ Which is the USB slowest?
- 1
❓ Which is the smallest USB?
- C
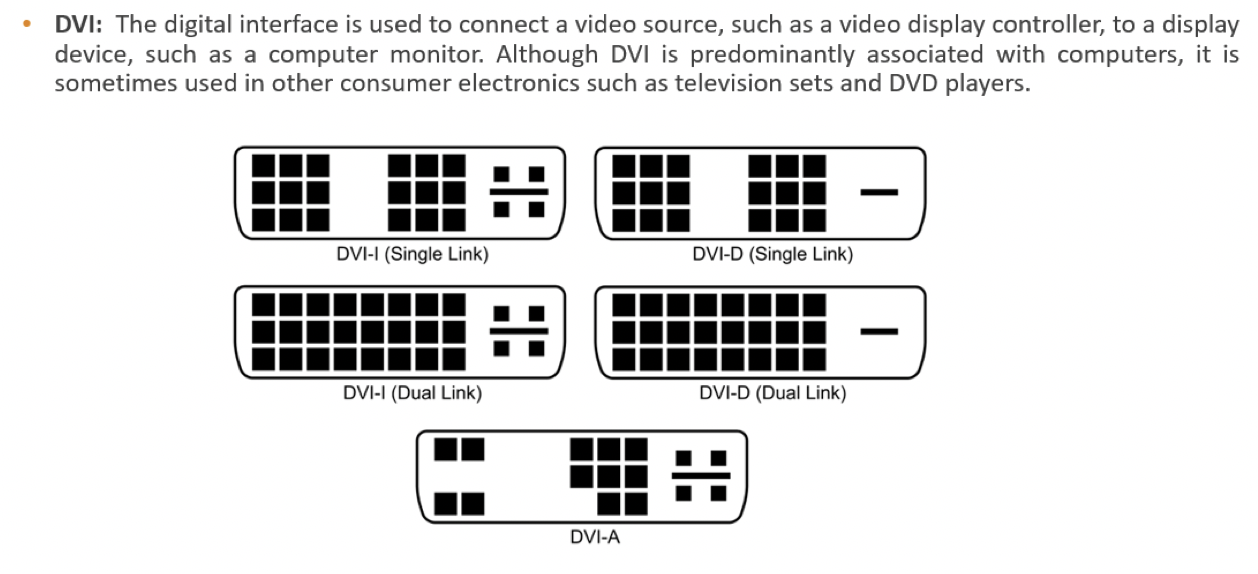
5️⃣ DVI
- for video
6️⃣ HDMI
- high definition
1
2
❓ Which is the connector for high definition?
- HDMI
7️⃣ RCA
- for audio and video
- professionals who need little vintage
8️⃣ Jack
- connector normally for audio
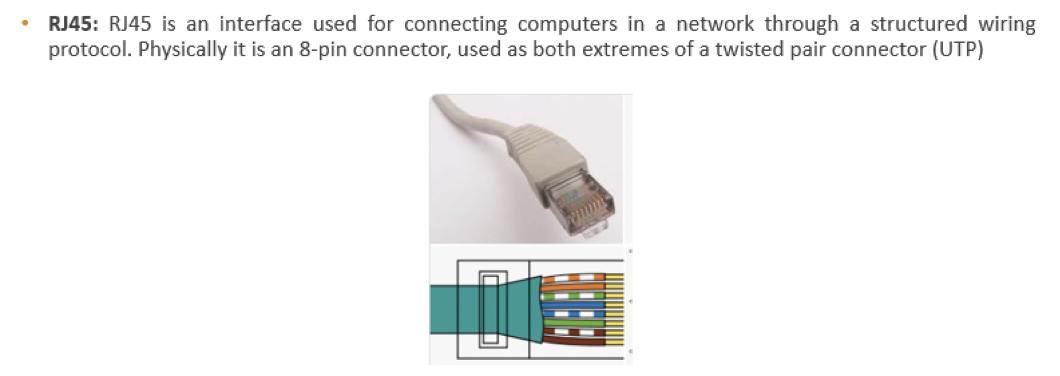
9️⃣ RJ45
- connector for internet